转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/fnng/p/6863616.html
一,安装PyMySQL
Python是编程语言,MySQL是数据库,它们是两种不同的技术;要想使Python操作MySQL数据库需要使用驱动。这里选用PyMySQL驱动。下载地址:
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/PyMySQL
https://github.com/PyMySQL/PyMySQL
当然,最简单的安装方式还是使用pip命令。
> pip install PyMySQL(这是在未安装基python2-pip情况下,若已经安装python-pip,则需安装python3-pip,终端输入sudo apt-get install python3-pip安装,pip3 install pymysql)
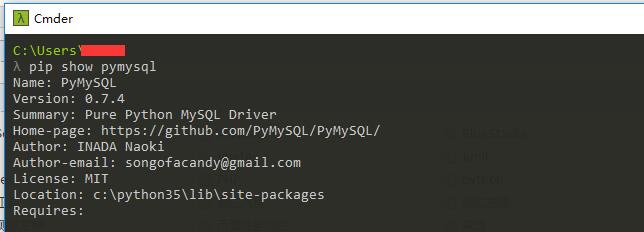
把install 换成show命令,查看PyMySQL安装是否成功。
二,创建MySQL表
执行下面的SQL语句,创建一张users 表。
CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `email` VARCHAR(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL, `password` VARCHAR(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin AUTO_INCREMENT=1 ;
三,Python操作MySQL
接下来才是重点,Python操作MySQL数据库。
4.1插入数据:
import pymysql.cursors
# 连接MySQL数据库
connection = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='198876', db='guest',
charset='utf8mb4', cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 通过cursor创建游标
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 创建sql 语句,并执行
sql = "INSERT INTO `users` (`email`, `password`) VALUES ('huzhiheng@itest.info', '123456')"
cursor.execute(sql)
# 提交SQL
connection.commit()
不管你使用的是什么工具或库,连接数据库这一步必不可少。host为数据库的主机IP地址,port为MySQL的默认端口号,user为数据的用户名,password为数据库的登录密码,db为数据库的名称。
cursor()方法创建数据库游标。
execute()方法执行SQL语句。
commit()将数据库的操作真正的提交到数据。
4.2. 查询数据1
import pymysql.cursors
# 连接MySQL数据库
connection = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='198876', db='guest', charset='utf8mb4', cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 通过cursor创建游标
cursor = connection.cursor()
# 执行数据查询
sql = "SELECT `id`, `password` FROM `users` WHERE `email`='huzhiheng@itest.info'"
cursor.execute(sql)
#查询数据库单条数据
result = cursor.fetchone()
print(result)
print("-----------华丽分割线------------")
# 执行数据查询
sql = "SELECT `id`, `password` FROM `users`"
cursor.execute(sql)
#查询数据库多条数据
result = cursor.fetchall()
for data in result:
print(data)
# 关闭数据连接
connection.close()
查询操作2
import MySQLdb db =MySQLdb.connect(host='localhost', port = 3306, user='root', passwd='123456', db ='xiewu', charset = "utf8") cursor = db.cursor() sql = "select * from student where id=3" result = cursor.execute(sql) aa = cursor.fetchall() for bb in aa : print bb cursor.close() db.commit() db.close()
查询结果
/usr/bin/python2.7 /home/xiewu/数据库操作/.idea/Mysql
(3L, u'\u5f20\u4e09', '\x01', '\x00', datetime.datetime(1992, 5, 15, 0, 0))
Process finished with exit code 0
接下来的操作就是数据库的查询了。
fetchone() 用于查询单条数据。
fetchall() 用于查询多条数据。
close() 最后不要忘记了关闭数据连接。
运行结果:








 本文介绍如何使用Python的PyMySQL库连接并操作MySQL数据库,包括安装PyMySQL、创建MySQL表及执行插入和查询操作。
本文介绍如何使用Python的PyMySQL库连接并操作MySQL数据库,包括安装PyMySQL、创建MySQL表及执行插入和查询操作。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








