nms为直接将iou>阈值的框全部移除,而softnms 对iou>阈值的框 降低它的权重,遍历完所有预测框之后,再通过一个阈值选择留下还是移除这个框。
import numpy as np
import cv2
def py_cpu_softnms(dets, sc, Nt=0.3, sigma=0.5, thresh=0.001, method=2):
"""
py_cpu_softnms
:param dets: boexs 坐标矩阵 format [y1, x1, y2, x2]
:param sc: 每个 boxes 对应的分数
:param Nt: iou 交叠门限
:param sigma: 使用 gaussian 函数的方差
:param thresh: 最后的分数门限
:param method: 使用的方法
:return: 留下的 boxes 的 index
"""
# indexes concatenate boxes with the last column
N = dets.shape[0]
indexes = np.array([np.arange(N)])
dets = np.concatenate((dets, indexes.T), axis=1)
# the order of boxes coordinate is [y1,x1,y2,x2]
y1 = dets[:, 0]
x1 = dets[:, 1]
y2 = dets[:, 2]
x2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = sc
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
for i in range(N):
# intermediate parameters for later parameters exchange
tBD = dets[i, :].copy()
tscore = scores[i].copy()
tarea = areas[i].copy()
pos = i + 1
#
if i != N-1:
maxscore = np.max(scores[pos:], axis=0)
maxpos = np.argmax(scores[pos:], axis=0)
else:
maxscore = scores[-1]
maxpos = 0
if tscore < maxscore:
#每次把最高score的 往上拿
dets[i, :] = dets[maxpos + i + 1, :] #行置换,score,area也一样
dets[maxpos + i + 1, :] = tBD
tBD = dets[i, :]
scores[i] = scores[maxpos + i + 1]
scores[maxpos + i + 1] = tscore
tscore = scores[i]
areas[i] = areas[maxpos + i + 1]
areas[maxpos + i + 1] = tarea
tarea = areas[i]
# IoU calculate
xx1 = np.maximum(dets[i, 1], dets[pos:, 1])
yy1 = np.maximum(dets[i, 0], dets[pos:, 0])
xx2 = np.minimum(dets[i, 3], dets[pos:, 3])
yy2 = np.minimum(dets[i, 2], dets[pos:, 2])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[pos:] - inter)
# Three methods: 1.linear 2.gaussian 3.original NMS
if method == 1: # linear
weight = np.ones(ovr.shape)
weight[ovr > Nt] = weight[ovr > Nt] - ovr[ovr > Nt]
elif method == 2: # gaussian
weight = np.exp(-(ovr * ovr) / sigma)
else: # original NMS
weight = np.ones(ovr.shape)
weight[ovr > Nt] = 0
scores[pos:] = weight * scores[pos:]
# print(dets)
# print(scores)
plot_img(dets, scores)
# select the boxes and keep the corresponding indexes
inds = dets[:, 4][scores > thresh]
keep = inds.astype(int)
print(keep)
return keep
# boxes and scores
boxes = np.array([[200, 200, 400, 400], [220, 220, 420, 420], [200, 240, 400, 440], [240, 200, 440, 400], [1, 1, 2, 2]], dtype=np.float32)
boxscores = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5], dtype=np.float32)
def plot_img(boxes,score):
img = np.ones((600, 600))
for i, bbboxes in enumerate(boxes):
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(bbboxes[0]), int(bbboxes[1])),(int(bbboxes[2]), int(bbboxes[3])),(0,0,255), 1)
cv2.putText(img, str(score[i]), (int(bbboxes[0]), int(bbboxes[1])),fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX, fontScale=0.7, color=(0,0,244))
win = cv2.namedWindow('image', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow('image', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
plot_img(boxes, boxscores)
index = py_cpu_softnms(boxes, boxscores, method=1)
print(index)
我们来可视化一下,第一个是最初的权重(置信度) ,首先选择0.9这个框,计算所有与它iou>阈值的框,3个都大于,然后对他们降低权重,如下面,这里使用的线性方法
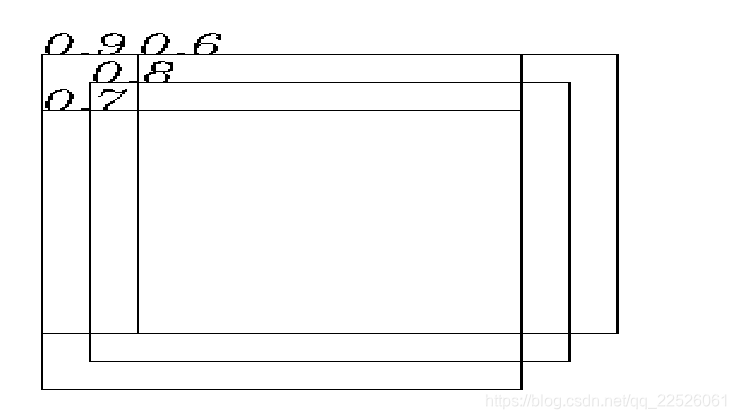
3个权重都被降低一次后
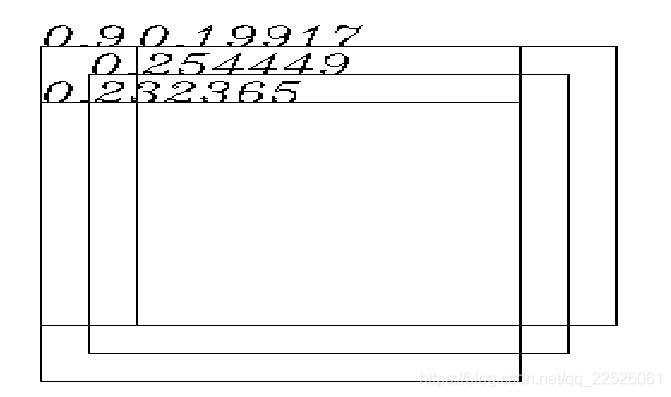
这次选择的是0.254449这个框,第一个0.9的不管,两外两个都与它重叠超过阈值,降低权重,如下图
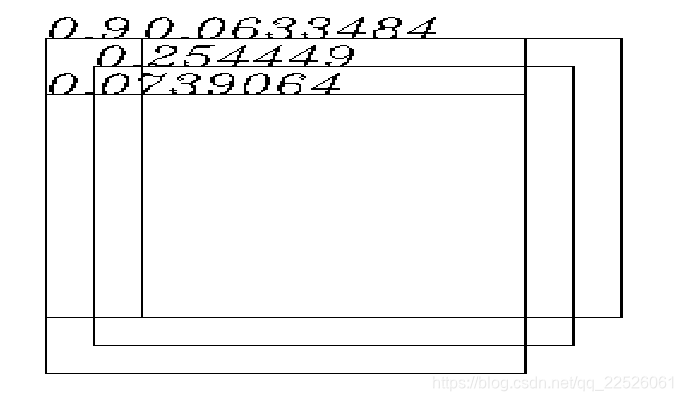
然后选择0.07这个框,最后一个也是大于阈值,降低权重后
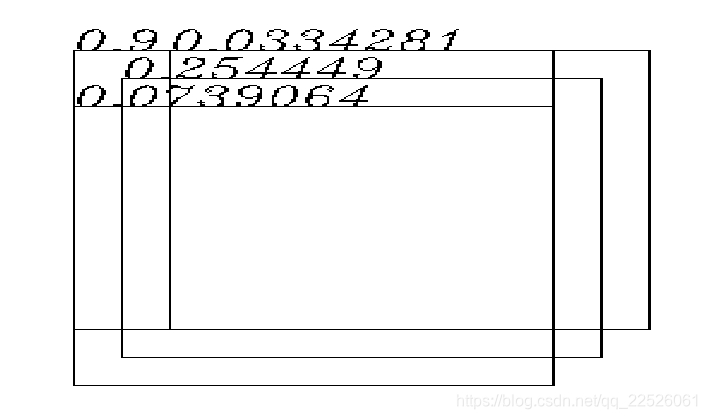
最后再来一个阈值来选择 是否留下,这里阈值是0.001 , 所以全部留下





 本文介绍了一种改进的目标检测算法——Soft-NMS,并提供了一个详细的Python实现。相较于传统的NMS算法直接移除重叠框,Soft-NMS通过降低重叠框的权重来保留更多潜在的有效检测结果。
本文介绍了一种改进的目标检测算法——Soft-NMS,并提供了一个详细的Python实现。相较于传统的NMS算法直接移除重叠框,Soft-NMS通过降低重叠框的权重来保留更多潜在的有效检测结果。




















 1299
1299

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








