我们知道在Java所有方法中参数值的传递都是传值而不是传引用,如果我们只是简单的使用三变量法交换两个Integer类型的值,肯定是不行的。但是由于Integer是不可变类,我们通过Integer的引用不能改变其状态,因此要交换两个Integer变量第一种思路就是使用放射:
private static void swapInteger(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
try {
Field field = Integer.class.getDeclaredField("value");
field.setAccessible(true);
int num = i1;
field.setInt(i1, i2);
field.setInt(i2, num);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}这也是网上大多数人给出的一种解法,没有问题,解决了这个问题。
这里给出另外一种解决思路:使用Unsafe类来解决这个问题,关于Unsafe类的介绍可以参考Java魔法类:Unsafe应用解析,下面给出具体代码:
private static long VAL_OFFSET;
private static Unsafe unsafe;
static {
try {
unsafe = UnsafeUntil.getUnsafe();
VAL_OFFSET = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Integer.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
private static void swapInteger1(Integer i1, Integer i2){
int num = i1;
unsafe.putInt(i1, VAL_OFFSET, i2);
unsafe.putInt(i2, VAL_OFFSET, num);
}好了,我们将两种方法放在一块测试一下:
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class SwapInteger {
private static long VAL_OFFSET;
private static Unsafe unsafe;
static {
try {
unsafe = UnsafeUntil.getUnsafe();
VAL_OFFSET = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Integer.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer i1 = 10; Integer i2 = 100;
System.out.println("before swap");
System.out.println("i1 = " + i1 + " i2 = " + i2);
swapInteger1(i1, i2);
System.out.println("after swap1");
System.out.println("i1 = " + i1 + " i2 = " + i2);
System.out.println("after swap2");
swapInteger2(i1, i2);
System.out.println("i1 = " + i1 + " i2 = " + i2);
}
private static void swapInteger1(Integer i1, Integer i2){
int num = i1;
unsafe.putInt(i1, VAL_OFFSET, i2);
unsafe.putInt(i2, VAL_OFFSET, num);
}
private static void swapInteger2(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
try {
Field field = Integer.class.getDeclaredField("value");
field.setAccessible(true);
int num = i1;
field.setInt(i1, i2);
field.setInt(i2, num);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
UnsafeUntil是我自己写的一个工具类用于获取Unsafe实例:
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class UnsafeUntil {
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
field.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe)field.get(null);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
最后输出如下:
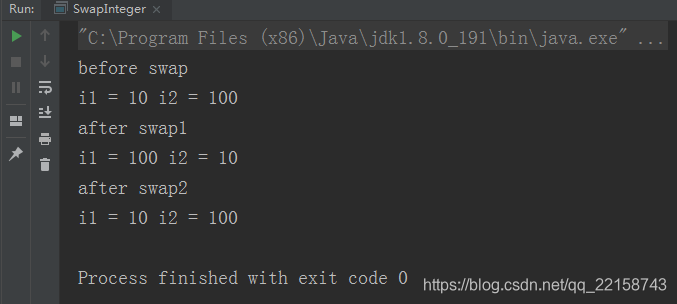
可以看到我们给出的两种交换方案都正确的工作了。





 本文探讨了在Java中如何交换两个Integer类型的值,由于Java参数传递的特性,常规方法无法直接交换。文章提供了两种解决方案:一是使用额外的临时变量,二是利用Unsafe类。通过测试验证了两种方法的有效性。
本文探讨了在Java中如何交换两个Integer类型的值,由于Java参数传递的特性,常规方法无法直接交换。文章提供了两种解决方案:一是使用额外的临时变量,二是利用Unsafe类。通过测试验证了两种方法的有效性。
















 8582
8582

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








