课前作业:
- Service 的 start 和 bind 状态的区别?
- 同一个 Service,先 startService,然后再 bindService,如何把它停止掉?
- 注意过 Service 的 onStartCommand 方法的返回值吗?不同返回值有什么区别?
- Service 的生命周期方法 onCreate、onStart、onBind 等运行在哪个线程?
正式开始
一、Service 的启动方式:startService() 和 bindService()
MyService.java:
public class MyService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate: ");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, "onStart: ");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, "onStartCommand: ");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i(TAG, "onDestroy: ");
super.onDestroy();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
public MyService getService() {
return MyService.this;
}
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "onBind: ");
return null;
}
}
记得在 AndroidManifest.xml 中 application 标签下配置
<service android:name=".MyService"/>
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Intent mIntent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class);
}
//======测试 startService() 的代码,开始======
//点击按钮,执行 startService()
public void start_Service(View view) {
startService(mIntent);
}
//点击按钮,执行 stopService()
public void stop_Service(View view) {
stopService(mIntent);
}
//======测试 startService() 的代码,结束======
//======测试 bindService() 的代码,开始======
//声明 Service
private MyService myService;
//是否已绑定 Service
private boolean isBind;
ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
isBind = true;
//得到了 myService,就可以调用 Service 中的方法
myService = ((MyService.MyBinder) service).getService();
Log.i(TAG, "onServiceConnected: ");
}
/**
* 一般不会被调用,异常情况下才被调用
* 当服务丢失时调用,这通常当托管服务的进程崩溃或被杀死时发生
*/
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
myService = null;
Log.i(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected: ");
}
};
//点击按钮,执行 bindService()
public void bind_Service(View view) {
bindService(mIntent, conn, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
//点击按钮,执行 unbindService()
public void unbind_Service(View view) {
if (isBind) {
unbindService(conn);
isBind = false;
}
}
//======测试 bindService() 的代码,结束======
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (isBind) {
unbindService(conn);
isBind = false;
}
}
}
Activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/bind_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/unbind_service"
android:onClick="bind_Service"
android:text="bind service"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbind_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/start_service"
android:onClick="unbind_Service"
android:text="unbind service"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/start_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/stop_service"
android:onClick="start_Service"
android:text="start service"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/stop_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:onClick="stop_Service"
android:text="stop service"
android:textAllCaps="false" />
</RelativeLayout>
1. startService() 情况下的生命周期
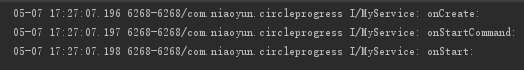
首次调用 startService():执行 onCreate()、onStartCommand()、onStart()
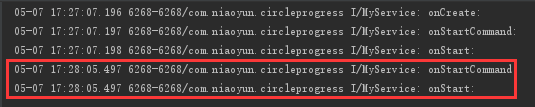
之后调用 startService() 或按返回键退出再进入后再调用 startService():执行 onStartCommand()、onStart(),不再执行 onCreate()
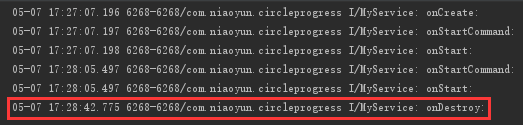
多次调用 stopService():只打印一次 onDestroy()
2. bindService() 情况下的生命周期
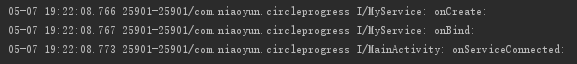
多次 bindService():只执行一次 onCreate()、onBind()、onServiceConnected()
多次 unBind():会抛异常,可声明一个 boolean,在 bindService() 置为 true,在 unBind() 中置为 false,防止多次 unBind() 后抛异常
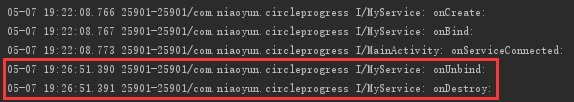
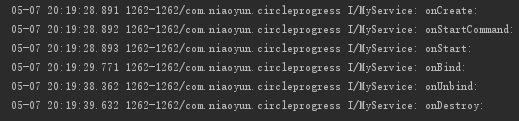
二、同一个 Service,先 startService,然后再 bindService
先 startService(),再 bindService(),经测试,要停止那个 Service 需要执行完 stopService() 和 unbindService(),执行顺序不分先后
只要 stopService() 和 unbindService() 这两个方法执行完,就可以停止那个 Service,只是打印的效果不一样
a. 先 stopService() 后 unbindService() 时,先执行 stopService(),但是不打印 onDestory,当执行 unbindService() 后依次打印 onUnbind: 、onDestory
b. 先 unbindService() 后 stopService() 时,执行 unbindService() 打印 onUnbind,执行 stopService() 打印 onDestroy
MyService 对应的打印结果:
三、Service 的 onStartCommand 方法的返回值
1.START_STICKY:
系统会保留启动状态但不会保存 Intent 对象,之后系统会用一个 null 的 Intent 对象来调用 onStartCommand() 方法,在这个情况下,除非有一些被发送的 Intent 对象在等待启动服务,Intent 可能为空,需要做非空判断
2.START_NOT_STICKY:
除非重新执行 startService() 接收到新的 Intent,否则系统不会保留启动状态并重新创建该 Service
3.START_REDELIVER_INTENT:
系统在 onStartCommand() 方法返回后,系统会自动重启该服务(调用 stopSelf() 方法的除外),并且用发送给这个服务的最后的 Intent 对象调用了 onStartCommand() 方法,在该服务调用 stopSelf() 方法之前,能够一直保留 Intent 对象数据
4.START_STICKY_COMPATIBILITY:
START_STICKY 的兼容版本,但不保证服务被终止后一定能重启
四、Service 的生命周期方法运行在哪个线程
Service 的生命周期方法运行在主线程,不能在 Service 中做耗时操作
作业答案:
1.Service 的 start 和 bind 状态的区别?
a. 首次调用 startService():执行 onCreate()、onStartCommand(),之后再次调用 startService():只执行 onStartCommand()
b. 多次 bindService():只执行一次 onCreate()、onBind()、onServiceConnected()
2.同一个 Service,先 startService,然后再 bindService,如何把它停止掉?
先 startService(),再 bindService(),经测试,要停止那个 Service 需要执行完 stopService() 和 unbindService(),执行顺序不分先后
3.注意过 Service 的 onStartCommand 方法的返回值吗?不同返回值有什么区别?
参考上方 三、Service 的 onStartCommand 方法的返回值
4.Service 的生命周期方法 onCreate、onStart、onBind 等运行在哪个线程?
主线程























 325
325

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








