转载https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/eson_15/article/details/51121833
上一章学习了Collection的架构,并阅读了部分源码,这一章开始,我们将对Collection的具体实现进行详细学习。首先学习List。而ArrayList又是List中最为常用的,因此本章先学习ArrayList。先对ArrayList有个整体的认识,然后学习它的源码,深入剖析ArrayList。
1. ArrayList简介
首先看看ArrayList与Collection的关系:
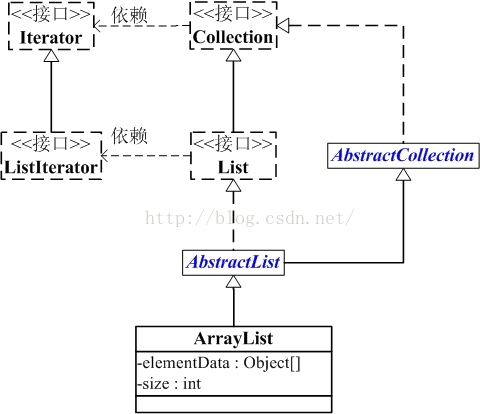
ArrayList的继承关系如下:
-
java.lang.Object -
↳ java.util.AbstractCollection<E> -
↳ java.util.AbstractList<E> -
↳ java.util.ArrayList<E> -
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> -
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
ArrayList继承了AbstractList,实现了List。它是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组。提供了相关的添加、删除、修改和遍历等功能。
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,即提供了随机访问功能。RandomAccess是java中用来被List实现,为List提供快速访问功能的。在ArrayList中,我们即可以通过元素的序号来快速获取元素对象,这就是快速随机访问。下文会比较List的“快速随机访问”和使用“Iterator迭代器访问”的效率。
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能被克隆。
ArrayList实现了java.io.Serializable接口,这意味着ArrayList支持序列化,能通过序列化去传输。
和Vector不同,ArrayList中的操作是非线程安全的。所以建议在单线程中使用ArrayList,在多线程中选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList。
我们先总览下ArrayList的构造函数和API
-
/****************** ArrayList中的构造函数 ***************/ -
// 默认构造函数 -
ArrayList() -
// capacity是ArrayList的默认容量大小。当由于增加数据导致容量不足时,容量会添加上一次容量大小的一半。 -
ArrayList(int capacity) -
// 创建一个包含collection的ArrayList -
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> collection) -
/****************** ArrayList中的API ********************/ -
// Collection中定义的API -
boolean add(E object) -
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) -
void clear() -
boolean contains(Object object) -
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) -
boolean equals(Object object) -
int hashCode() -
boolean isEmpty() -
Iterator<E> iterator() -
boolean remove(Object object) -
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) -
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) -
int size() -
<T> T[] toArray(T[] array) -
Object[] toArray() -
// AbstractCollection中定义的API -
void add(int location, E object) -
boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) -
E get(int location) -
int indexOf(Object object) -
int lastIndexOf(Object object) -
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) -
ListIterator<E> listIterator() -
E remove(int location) -
E set(int location, E object) -
List<E> subList(int start, int end) -
// ArrayList新增的API -
Object clone() -
void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) -
void trimToSize() -
void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
ArrayList包含了两个重要的对象:elementData和size。
elementData是Object[]类型的数组,它保存了添加到ArrayList中的元素。实际上,elementData是一个动态数组,我们能通过ArrayList(int initialCapacity)来执行它的初始容量为initialCapacity。如果通过不含参数的构造函数来创建ArrayList,则elementData是一个空数组(后面会调整其大小)。elementData数组的大小会根据ArrayList容量的增长而动态的增长,具体见下面的源码。
size则是动态数组实际的大小。
2. ArrayList源码分析(基于JDK1.7)
下面通过分析ArrayList的源码更加深入的了解ArrayList原理。由于ArrayList是通过数组实现的,所以源码比较容易理解:
-
package java.util; -
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> -
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable -
{ -
//序列版本号 -
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; -
//默认初始化容量 -
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; -
//空数组,用来实例化不带容量大小的构造函数 -
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; -
//保存ArrayList中数据的数组 -
private transient Object[] elementData; -
//ArrayList中实际数据的数量 -
private int size; -
/******************************** Constructor ***********************************/ -
//ArrayList带容量大小的构造函数 -
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { -
super(); -
if (initialCapacity < 0) -
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ -
initialCapacity); -
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; //新建一个数组初始化elementData -
} -
//不带参数的构造函数 -
public ArrayList() { -
super(); -
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;//使用空数组初始化elementData -
} -
//用Collection来初始化ArrayList -
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { -
elementData = c.toArray(); //将Collection中的内容转换成数组初始化elementData -
size = elementData.length; -
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) -
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) -
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); -
} -
/********************************* Array size ************************************/ -
//重新“修剪”数组容量大小 -
public void trimToSize() { -
modCount++; -
//当ArrayList中的元素个数小于elementData数组大小时,重新修整elementData到size大小 -
if (size < elementData.length) { -
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); -
} -
} -
//给数组扩容,该方法是提供给外界调用的,是public的,真正扩容是在下面的private方法里 -
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { -
int minExpand = (elementData != EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) -
// any size if real element table -
? 0 -
// larger than default for empty table. It's already supposed to be -
// at default size. -
: DEFAULT_CAPACITY; -
if (minCapacity > minExpand) { -
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); -
} -
} -
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { -
//如果是个空数组 -
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { -
//取minCapacity和10的较大者 -
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); -
} -
//如果数组已经有数据了 -
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); -
} -
//确保数组容量大于ArrayList中元素个数 -
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { -
modCount++; //将“修改统计数”+1 -
//如果实际数据容量大于数组容量,就给数组扩容 -
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) -
grow(minCapacity); -
} -
//分配的最大数组空间 -
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; -
//增大数组空间 -
private void grow(int minCapacity) { -
// overflow-conscious code -
int oldCapacity = elementData.length; -
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //在原来容量的基础上加上 oldCapacity/2 -
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) -
newCapacity = minCapacity; //最少保证容量和minCapacity一样 -
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) -
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); //最多不能超过最大容量 -
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: -
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); -
} -
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { -
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow -
throw new OutOfMemoryError(); -
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? -
Integer.MAX_VALUE : -
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; -
} -
//返回ArrayList的实际大小 -
public int size() { -
return size; -
} -
//判断ArrayList是否为空 -
public boolean isEmpty() { -
return size == 0; -
} -
/****************************** Search Operations *************************/ -
//判断ArrayList是否包含Object o -
public boolean contains(Object o) { -
return indexOf(o) >= 0; -
} -
//正向查找,返回元素的索引值 -
public int indexOf(Object o) { -
if (o == null) { -
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) -
if (elementData[i]==null) -
return i; -
} else { -
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) -
if (o.equals(elementData[i])) -
return i; -
} -
return -1; -
} -
//反向查找,返回元素的索引值 -
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { -
if (o == null) { -
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) -
if (elementData[i]==null) -
return i; -
} else { -
for (int i = size-1; i >= 0; i--) -
if (o.equals(elementData[i])) -
return i; -
} -
return -1; -
} -
/******************************* Clone *********************************/ -
//克隆函数 -
public Object clone() { -
try { -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
ArrayList<E> v = (ArrayList<E>) super.clone(); -
//将当前ArrayList的全部元素拷贝到v中 -
v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); -
v.modCount = 0; -
return v; -
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { -
// this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable -
throw new InternalError(); -
} -
} -
/********************************* toArray *****************************/ -
/** -
* 返回一个Object数组,包含ArrayList中所有的元素 -
* toArray()方法扮演着array-based和collection-based API之间的桥梁 -
*/ -
public Object[] toArray() { -
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); -
} -
//返回ArrayList的模板数组 -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { -
//如果数组a的大小 < ArrayList的元素个数, -
//则新建一个T[]数组,大小为ArrayList元素个数,并将“ArrayList”全部拷贝到新数组中。 -
if (a.length < size) -
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); -
//如果数组a的大小 >= ArrayList的元素个数, -
//则将ArrayList全部拷贝到新数组a中。 -
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size); -
if (a.length > size) -
a[size] = null; -
return a; -
} -
/******************** Positional Access Operations ********************/ -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
E elementData(int index) { -
return (E) elementData[index]; -
} -
//获取index位置的元素值 -
public E get(int index) { -
rangeCheck(index); //首先判断index的范围是否合法 -
return elementData(index); -
} -
//将index位置的值设为element,并返回原来的值 -
public E set(int index, E element) { -
rangeCheck(index); -
E oldValue = elementData(index); -
elementData[index] = element; -
return oldValue; -
} -
//将e添加到ArrayList中 -
public boolean add(E e) { -
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! -
elementData[size++] = e; -
return true; -
} -
//将element添加到ArrayList的指定位置 -
public void add(int index, E element) { -
rangeCheckForAdd(index); -
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! -
//将index以及index之后的数据复制到index+1的位置往后,即从index开始向后挪了一位 -
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, -
size - index); -
elementData[index] = element; //然后在index处插入element -
size++; -
} -
//删除ArrayList指定位置的元素 -
public E remove(int index) { -
rangeCheck(index); -
modCount++; -
E oldValue = elementData(index); -
int numMoved = size - index - 1; -
if (numMoved > 0) -
//向左挪一位,index位置原来的数据已经被覆盖了 -
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, -
numMoved); -
//多出来的最后一位删掉 -
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work -
return oldValue; -
} -
//删除ArrayList中指定的元素 -
public boolean remove(Object o) { -
if (o == null) { -
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) -
if (elementData[index] == null) { -
fastRemove(index); -
return true; -
} -
} else { -
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) -
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { -
fastRemove(index); -
return true; -
} -
} -
return false; -
} -
//private的快速删除与上面的public普通删除区别在于,没有进行边界判断以及不返回删除值 -
private void fastRemove(int index) { -
modCount++; -
int numMoved = size - index - 1; -
if (numMoved > 0) -
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, -
numMoved); -
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work -
} -
//清空ArrayList,将全部元素置为null -
public void clear() { -
modCount++; -
// clear to let GC do its work -
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) -
elementData[i] = null; -
size = 0; -
} -
//将集合C中所有的元素添加到ArrayList中 -
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { -
Object[] a = c.toArray(); -
int numNew = a.length; -
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount -
//在原来数组的后面添加c中所有的元素 -
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); -
size += numNew; -
return numNew != 0; -
} -
//从index位置开始,将集合C中所欲的元素添加到ArrayList中 -
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { -
rangeCheckForAdd(index); -
Object[] a = c.toArray(); -
int numNew = a.length; -
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount -
int numMoved = size - index; -
if (numMoved > 0) -
//将index开始向后的所有数据,向后移动numNew个位置,给新插入的数据腾出空间 -
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, -
numMoved); -
//将集合C中的数据插到刚刚腾出的位置 -
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); -
size += numNew; -
return numNew != 0; -
} -
//删除从fromIndex到toIndex之间的数据,不包括toIndex位置的数据 -
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { -
modCount++; -
int numMoved = size - toIndex; -
System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, -
numMoved); -
// clear to let GC do its work -
int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); -
for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { -
elementData[i] = null; -
} -
size = newSize; -
} -
//范围检测 -
private void rangeCheck(int index) { -
if (index >= size) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); -
} -
//add和addAll方法中的范围检测 -
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { -
if (index > size || index < 0) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); -
} -
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { -
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size; -
} -
//删除ArrayList中所有集合C中包含的数据 -
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { -
return batchRemove(c, false); -
} -
//删除ArrayList中除了集合C中包含的数据外的其他所有数据 -
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { -
return batchRemove(c, true); -
} -
//批量删除 -
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { -
final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; -
int r = 0, w = 0; -
boolean modified = false; -
try { -
for (; r < size; r++) -
if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) -
elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; -
} finally { -
// Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, -
// even if c.contains() throws. -
//官方的注释是为了保持和AbstractCollection的兼容性 -
//我的理解是上面c.contains抛出了异常,导致for循环终止,那么必然会导致r != size -
//所以0-w之间是需要保留的数据,同时从w索引开始将剩下没有循环的数据(也就是从r开始的)拷贝回来,也保留 -
if (r != size) { -
System.arraycopy(elementData, r, -
elementData, w, -
size - r); -
w += size - r; -
} -
//for循环完毕,检测了所有的元素 -
//0-w之间保存了需要留下的数据,w开始以及后面的数据全部清空 -
if (w != size) { -
// clear to let GC do its work -
for (int i = w; i < size; i++) -
elementData[i] = null; -
modCount += size - w; -
size = w; -
modified = true; -
} -
} -
return modified; -
} -
/***************************** Writer and Read Object *************************/ -
//java.io.Serializable的写入函数 -
//将ArrayList的“容量、所有的元素值”都写入到输出流中 -
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) -
throws java.io.IOException{ -
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff -
int expectedModCount = modCount; -
s.defaultWriteObject(); -
// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() -
//写入“数组的容量”,保持与clone()的兼容性 -
s.writeInt(size); -
//写入“数组的每一个元素” -
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { -
s.writeObject(elementData[i]); -
} -
if (modCount != expectedModCount) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
//java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出 -
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) -
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { -
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; -
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff -
s.defaultReadObject(); -
//从输入流中读取ArrayList的“容量” -
s.readInt(); // ignored -
if (size > 0) { -
// be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity -
ensureCapacityInternal(size); -
Object[] a = elementData; -
//从输入流中将“所有元素值”读出 -
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { -
a[i] = s.readObject(); -
} -
} -
} -
/******************************** Iterators ************************************/ -
/** -
* 该部分的方法重写了AbstractList抽象类中Iterator部分的方法,因为ArrayList继承 -
* 了AbstractList,基本大同小异,只是这里针对本类的数组,思想与AbstractList一致 -
* 可以参照上一章Collection架构与源码分析的AbatractList部分 -
*/ -
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) { -
if (index < 0 || index > size) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index); -
return new ListItr(index); -
} -
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { -
return new ListItr(0); -
} -
public Iterator<E> iterator() { -
return new Itr(); -
} -
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { -
int cursor; // index of next element to return -
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such -
int expectedModCount = modCount; -
public boolean hasNext() { -
return cursor != size; -
} -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
public E next() { -
checkForComodification(); -
int i = cursor; -
if (i >= size) -
throw new NoSuchElementException(); -
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; -
if (i >= elementData.length) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
cursor = i + 1; -
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; -
} -
public void remove() { -
if (lastRet < 0) -
throw new IllegalStateException(); -
checkForComodification(); -
try { -
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet); -
cursor = lastRet; -
lastRet = -1; -
expectedModCount = modCount; -
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
final void checkForComodification() { -
if (modCount != expectedModCount) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { -
ListItr(int index) { -
super(); -
cursor = index; -
} -
public boolean hasPrevious() { -
return cursor != 0; -
} -
public int nextIndex() { -
return cursor; -
} -
public int previousIndex() { -
return cursor - 1; -
} -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
public E previous() { -
checkForComodification(); -
int i = cursor - 1; -
if (i < 0) -
throw new NoSuchElementException(); -
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; -
if (i >= elementData.length) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
cursor = i; -
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; -
} -
public void set(E e) { -
if (lastRet < 0) -
throw new IllegalStateException(); -
checkForComodification(); -
try { -
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e); -
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
public void add(E e) { -
checkForComodification(); -
try { -
int i = cursor; -
ArrayList.this.add(i, e); -
cursor = i + 1; -
lastRet = -1; -
expectedModCount = modCount; -
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
} -
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { -
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); -
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex); -
} -
static void subListRangeCheck(int fromIndex, int toIndex, int size) { -
if (fromIndex < 0) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex); -
if (toIndex > size) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex); -
if (fromIndex > toIndex) -
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex + -
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")"); -
} -
private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess { -
private final AbstractList<E> parent; -
private final int parentOffset; -
private final int offset; -
int size; -
SubList(AbstractList<E> parent, -
int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { -
this.parent = parent; -
this.parentOffset = fromIndex; -
this.offset = offset + fromIndex; -
this.size = toIndex - fromIndex; -
this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; -
} -
public E set(int index, E e) { -
rangeCheck(index); -
checkForComodification(); -
E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); -
ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e; -
return oldValue; -
} -
public E get(int index) { -
rangeCheck(index); -
checkForComodification(); -
return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); -
} -
public int size() { -
checkForComodification(); -
return this.size; -
} -
public void add(int index, E e) { -
rangeCheckForAdd(index); -
checkForComodification(); -
parent.add(parentOffset + index, e); -
this.modCount = parent.modCount; -
this.size++; -
} -
public E remove(int index) { -
rangeCheck(index); -
checkForComodification(); -
E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index); -
this.modCount = parent.modCount; -
this.size--; -
return result; -
} -
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { -
checkForComodification(); -
parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex, -
parentOffset + toIndex); -
this.modCount = parent.modCount; -
this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex; -
} -
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { -
return addAll(this.size, c); -
} -
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { -
rangeCheckForAdd(index); -
int cSize = c.size(); -
if (cSize==0) -
return false; -
checkForComodification(); -
parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c); -
this.modCount = parent.modCount; -
this.size += cSize; -
return true; -
} -
public Iterator<E> iterator() { -
return listIterator(); -
} -
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) { -
checkForComodification(); -
rangeCheckForAdd(index); -
final int offset = this.offset; -
return new ListIterator<E>() { -
int cursor = index; -
int lastRet = -1; -
int expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; -
public boolean hasNext() { -
return cursor != SubList.this.size; -
} -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
public E next() { -
checkForComodification(); -
int i = cursor; -
if (i >= SubList.this.size) -
throw new NoSuchElementException(); -
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; -
if (offset + i >= elementData.length) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
cursor = i + 1; -
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; -
} -
public boolean hasPrevious() { -
return cursor != 0; -
} -
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") -
public E previous() { -
checkForComodification(); -
int i = cursor - 1; -
if (i < 0) -
throw new NoSuchElementException(); -
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; -
if (offset + i >= elementData.length) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
cursor = i; -
return (E) elementData[offset + (lastRet = i)]; -
} -
public int nextIndex() { -
return cursor; -
} -
public int previousIndex() { -
return cursor - 1; -
} -
public void remove() { -
if (lastRet < 0) -
throw new IllegalStateException(); -
checkForComodification(); -
try { -
SubList.this.remove(lastRet); -
cursor = lastRet; -
lastRet = -1; -
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; -
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
public void set(E e) { -
if (lastRet < 0) -
throw new IllegalStateException(); -
checkForComodification(); -
try { -
ArrayList.this.set(offset + lastRet, e); -
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
public void add(E e) { -
checkForComodification(); -
try { -
int i = cursor; -
SubList.this.add(i, e); -
cursor = i + 1; -
lastRet = -1; -
expectedModCount = ArrayList.this.modCount; -
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
final void checkForComodification() { -
if (expectedModCount != ArrayList.this.modCount) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
}; -
} -
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { -
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size); -
return new SubList(this, offset, fromIndex, toIndex); -
} -
private void rangeCheck(int index) { -
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); -
} -
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { -
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) -
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); -
} -
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) { -
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+this.size; -
} -
private void checkForComodification() { -
if (ArrayList.this.modCount != this.modCount) -
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); -
} -
} -
}
总结一下:
1). ArrayList实际上是通过一个数组去保存数据的,当我们构造ArrayList时,如果使用默认构造函数,最后ArrayList的默认容量大小是10。
2). 当ArrayList容量不足以容纳全部元素时,ArrayList会自动扩张容量,新的容量 = 原始容量 + 原始容量 / 2。
3). ArrayList的克隆函数,即是将全部元素克隆到一个数组中。
4. ArrayList实现java.io.Serializable的方式。当写入到输出流时,先写入“容量”,再依次写出“每一个元素”;当读出输入流时,先读取“容量”,再依次读取“每一个元素”。
3. ArrayList遍历方式
ArrayList支持三种遍历方式,下面我们逐个讨论:
1). 通过迭代器遍历。即Iterator迭代器。
-
Integer value = null; -
Iterator it = list.iterator(); -
while (it.hasNext()) { -
value = (Integer)it.next(); -
}
2). 随机访问,通过索引值去遍历。由于ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,所以它支持通过索引值去随机访问元素。
-
Integer value = null; -
int size = list.size(); -
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { -
value = (Integer)list.get(i); -
}
3). 通过for循环遍历。
-
Integer value = null; -
for (Integer integ : list) { -
value = integ; -
}
下面写了一个测试用例,比较这三种遍历方式的效率:
-
import java.util.*; -
/* -
* @description ArrayList三种遍历方式效率的测试 -
* @author eson_15 -
*/ -
public class ArrayListRandomAccessTest { -
public static void main(String[] args) { -
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); -
for (int i=0; i<500000; i++) -
list.add(i); -
isRandomAccessSupported(list);//判断是否支持RandomAccess -
iteratorThroughRandomAccess(list) ; -
iteratorThroughIterator(list) ; -
iteratorThroughFor(list) ; -
} -
private static void isRandomAccessSupported(List<Integer> list) { -
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) { -
System.out.println("RandomAccess implemented!"); -
} else { -
System.out.println("RandomAccess not implemented!"); -
} -
} -
public static void iteratorThroughRandomAccess(List<Integer> list) { -
long startTime; -
long endTime; -
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); -
for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) { -
list.get(i); -
} -
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); -
long interval = endTime - startTime; -
System.out.println("RandomAccess遍历时间:" + interval+" ms"); -
} -
public static void iteratorThroughIterator(List<Integer> list) { -
long startTime; -
long endTime; -
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); -
for(Iterator<Integer> it = list.iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) { -
it.next(); -
} -
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); -
long interval = endTime - startTime; -
System.out.println("Iterator遍历时间:" + interval+" ms"); -
} -
@SuppressWarnings("unused") -
public static void iteratorThroughFor(List<Integer> list) { -
long startTime; -
long endTime; -
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); -
for(Object obj : list) -
; -
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); -
long interval = endTime - startTime; -
System.out.println("For循环遍历时间:" + interval+" ms"); -
} -
}
每次执行的结果会有一点点区别,在这里我统计了6次执行结果,见下表:
|
|
RandomAccess(ms) |
Iterator(ms) |
For(ms) |
|
第一次 |
5 |
8 |
7 |
|
第二次 |
4 |
7 |
7 |
|
第三次 |
5 |
8 |
10 |
|
第四次 |
5 |
7 |
6 |
|
第五次 |
5 |
8 |
7 |
|
第六次 |
5 |
7 |
6 |
|
平均 |
4.8 |
7.5 |
7.1 |
由此可见,遍历ArrayList时,使用随机访问(即通过索引号访问)效率最高,而使用迭代器的效率最低。
4. toArray()异常问题
当我们调用ArrayList中的toArray()方法时,可能会遇到"java.lang.ClassCastException"异常的情况,下面来讨论下出现的原因:
ArrayList中提供了2个toArray()方法:
-
Object[] toArray() -
<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)
调用toArray()函数会抛出"java.lang.ClassCastException"异常,但是调用toArray(T[] contents)能正常返回T[]。toArray()会抛出异常是因为toArray()返回的是Object[]数组,将Object[]转换为其它类型(比如将Object[]转换为Integer[])则会抛出"java.lang.ClassCastException"异常,因为java不支持向下转型。解决该问题的办法是调用<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents),而不是Object[] toArray()。
调用<T> T[] toArray(T[] contents)返回T[]可以通过以下几种方式实现:
-
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式一 -
public static Integer[] vectorToArray1(ArrayList<Integer> v) { -
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()]; -
v.toArray(newText); -
return newText; -
} -
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式二。<span style="color:#FF6666;">最常用!</span> -
public static Integer[] vectorToArray2(ArrayList<Integer> v) { -
Integer[] newText = (Integer[])v.toArray(new Integer[v.size()]); -
return newText; -
} -
// toArray(T[] contents)调用方式三 -
public static Integer[] vectorToArray3(ArrayList<Integer> v) { -
Integer[] newText = new Integer[v.size()]; -
Integer[] newStrings = (Integer[])v.toArray(newText); -
return newStrings; -
}
三种方式都大同小异。
ArrayList源码就讨论这么多,如有错误,欢迎留言指正~








 本文详细介绍了ArrayList,它是List中常用的动态数组,操作非线程安全。分析了其基于JDK1.7的源码,包括默认容量、自动扩容等。还探讨了三种遍历方式,随机访问效率最高。此外,指出调用toArray()可能出现的异常及解决办法。
本文详细介绍了ArrayList,它是List中常用的动态数组,操作非线程安全。分析了其基于JDK1.7的源码,包括默认容量、自动扩容等。还探讨了三种遍历方式,随机访问效率最高。此外,指出调用toArray()可能出现的异常及解决办法。
















 573
573

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








