在上一章节中,我们讨论了模型参数的加载,本文主要讨论,如何基于加载的模型实现模型的推理。
如果对于yolov3的模型结构感兴趣,那么你可能需要至少看三篇论文 【4】【5】【6】
模型架构可视化
首先,梳理一下YOLOV3Tiny的模型结构,从模型结构可以看出,yolov3TIny的模型结构非常简洁。
Backbone包含卷积层,pooling层,残差链接,以及上采样层。没有其他的多余操作。
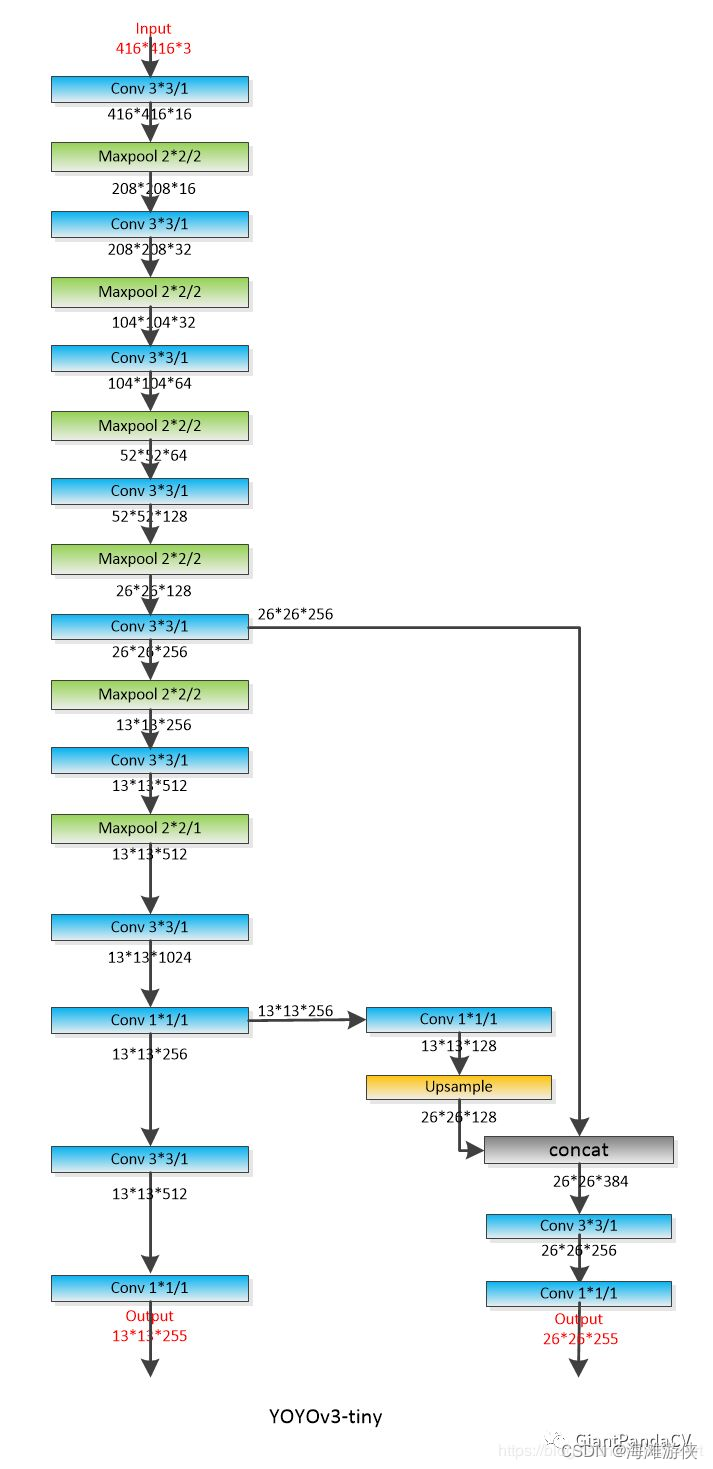
模型推理代码解读
模型推理主要调用的函数是detect(),所以,虽然这个函数很长,我们也把它展示在最后面。
const int64_t t_start_ms = ggml_time_ms();
detect(img, model, params.thresh, labels, alphabet);
const int64_t t_detect_ms = ggml_time_ms() - t_start_ms;
if (!save_image(img, params.fname_out.c_str(), 80)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: failed to save image to '%s'\n", __func__, params.fname_out.c_str());
return 1;
}
printf("Detected objects saved in '%s' (time: %f sec.)\n", params.fname_out.c_str(), t_detect_ms / 1000.0f);
ggml_free(model.ctx);
return 0;在函数detect中,可以看到,通过ggml_init() 函数的调用,首先进行了heap上buffer的分配。然后,通过ggml_init的调用,我们进行内存的分配,并且,我们可以根据编译选项,选择是否基于cublas或者clblast或者metal进行加速。所以,目前看来,ggml_init可以实现内存的获取,以及cublas等加速器的初始化。
接下来,调用的是ggml_new_graph()。 这里从名字就可以看出,涉及到图(graph)的生成,而ggml_cgraph的声明如下,网络中重要的节点会放置在其中。
在get_yolo_detections中,可以看到获得candidates 的objectness等参数的过程。
// computation graph
struct ggml_cgraph {
int size;
int n_nodes;
int n_leafs;
struct ggml_tensor ** nodes;
s




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 512
512

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








