文章目录
一、CountDownLatch 核心概念解析
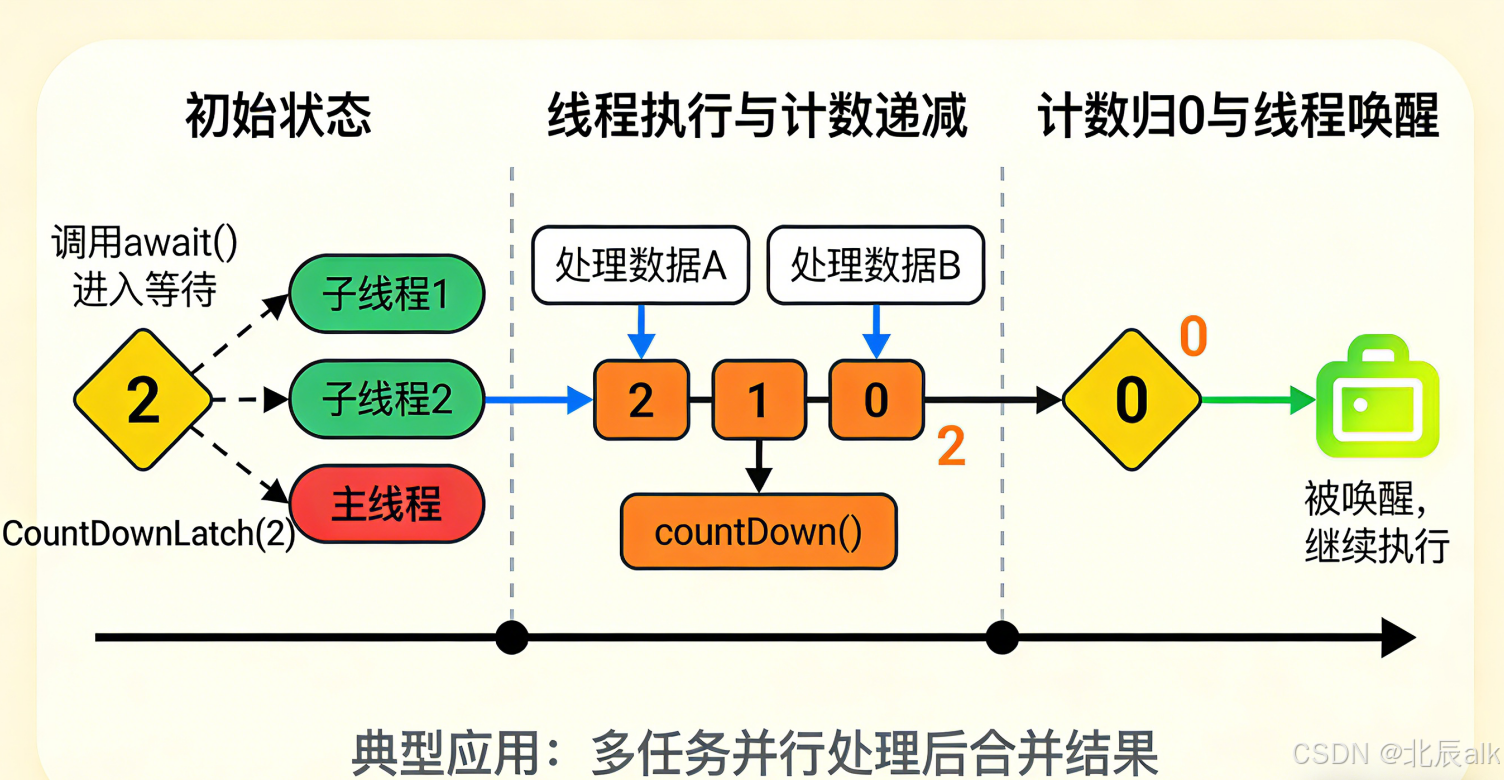
1.1 什么是 CountDownLatch?
CountDownLatch 是 Java 并发包(java.util.concurrent)中的一个同步辅助类,它允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程完成操作后再继续执行。可以将其理解为一个倒计时门闩,当计数器减到零时,等待的线程才会被释放。
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* CountDownLatch 基本结构示例
*
* 核心特性:
* 1. 一次性使用:计数器归零后无法重置
* 2. 不可逆性:计数器只能递减,不能递增
* 3. 线程安全:内部使用AQS实现,保证线程安全
* 4. 等待机制:支持多个线程同时等待
*/
public class CountDownLatchStructure {
// CountDownLatch 的内部状态
class LatchState {
private int count; // 计数器
public LatchState(int count) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
}
this.count = count;
}
public void countDown() {
synchronized (this) {
if (count > 0) {
count--;
}
}
}
public boolean await() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this) {
while (count > 0) {
this.wait(); // 等待计数器归零
}
return true;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 CountDownLatch,初始化计数器为3
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
System.out.println("CountDownLatch 创建完成,初始计数器 = " + 3);
System.out.println("等待线程将阻塞,直到计数器归零");
}
}
1.2 CountDownLatch 与相关工具对比
| 特性 | CountDownLatch | CyclicBarrier | Semaphore | Phaser |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 核心功能 | 等待其他线程完成 | 线程互相等待 | 控制并发数 | 更灵活的同步 |
| 重用性 | 一次性 | 可重用 | 可重用 | 可重用 |
| 计数器方向 | 递减 | 递增 | 增减 | 复杂状态 |
| 线程角色 | 主从模式 | 对等模式 | 资源控制 | 多阶段 |
| 典型场景 | 启动准备、任务分片 | 并行计算 | 连接池、限流 | 多阶段任务 |
二、CountDownLatch 工作原理深度剖析
2.1 内部实现机制
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
/**
* CountDownLatch 内部 AQS 实现解析
*
* CountDownLatch 内部使用 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer (AQS) 实现,
* 这是一个基于 CLH 队列锁的框架。
*/
public class CountDownLatchInternal {
// 简化版 AQS 实现,展示 CountDownLatch 核心逻辑
static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
Sync(int count) {
setState(count); // 使用 AQS 的 state 存储计数器
}
int getCount() {
return getState();
}
/**
* 尝试获取共享锁
* 当 state == 0 时返回 1,表示获取成功
* 否则返回 -1,表示需要加入等待队列
*/
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
/**
* 尝试释放共享锁(countDown 操作)
* 通过 CAS 递减 state,当 state 减到 0 时返回 true
*/
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// 自旋 CAS 操作
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0)
return false; // 计数器已为 0,无需操作
int nextc = c - 1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
return nextc == 0; // 返回是否减到 0
}
}
}
/**
* 完整工作流程演示
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== CountDownLatch 内部工作流程 ===");
System.out.println("1. 初始化: state = N (N > 0)");
System.out.println("2. await(): 调用 tryAcquireShared,如果 state != 0,线程进入等待队列");
System.out.println("3. countDown(): 调用 tryReleaseShared,CAS 递减 state");
System.out.println("4. 当 state 减到 0 时,唤醒所有等待线程");
System.out.println("5. 被唤醒的线程从 await() 返回,继续执行");
// 实际使用示例
final int THREAD_COUNT = 3;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_COUNT);
System.out.println("\n实际演示:");
System.out.println("初始化 CountDownLatch,计数器 = " + THREAD_COUNT);
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; i++) {
final int threadId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("线程 " + threadId + " 开始工作");
Thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟工作
System.out.println("线程 " + threadId + " 完成工作,调用 countDown()");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println("线程 " + threadId + " countDown 后,当前计数: " + (THREAD_COUNT - threadId - 1));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
System.out.println("\n主线程调用 await(),等待所有线程完成...");
latch.await();
System.out.println("所有线程完成,主线程继续执行");
}
}
2.2 工作流程详解
三、核心 API 详解与示例
3.1 构造函数
/**
* CountDownLatch 构造函数详解
*/
public class ConstructorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 示例 1: 基本用法
System.out.println("=== 构造函数示例 ===");
// 创建 CountDownLatch,指定初始计数值
int initialCount = 5;
CountDownLatch latch1 = new CountDownLatch(initialCount);
System.out.println("创建 CountDownLatch,初始计数: " + initialCount);
// 示例 2: 边界条件测试
testBoundaryConditions();
// 示例 3: 实际应用场景
demonstrateRealWorldUsage();
}
private static void testBoundaryConditions() {
System.out.println("\n=== 边界条件测试 ===");
try {
// 测试 1: 计数为 0
CountDownLatch zeroLatch = new CountDownLatch(0);
System.out.println("创建计数为 0 的 latch");
zeroLatch.await(); // 应该立即返回
System.out.println("计数为 0 的 latch await() 立即返回");
// 测试 2: 计数为负数(应该抛出异常)
try {
CountDownLatch negativeLatch = new CountDownLatch(-1);
System.out.println("ERROR: 应该抛出 IllegalArgumentException");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("正确捕获 IllegalArgumentException: " + e.getMessage());
}
// 测试 3: 大计数
int largeCount = 10000;
CountDownLatch largeLatch = new CountDownLatch(largeCount);
System.out.println("创建大计数 latch: " + largeCount);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
private static void demonstrateRealWorldUsage() {
System.out.println("\n=== 实际应用场景演示 ===");
// 场景: 并行加载多个模块,主线程等待所有模块加载完成
String[] modules = {"用户模块", "订单模块", "支付模块", "库存模块", "日志模块"};
CountDownLatch moduleLatch = new CountDownLatch(modules.length);
System.out.println("开始并行加载 " + modules.length + " 个模块:");
for (int i = 0; i < modules.length; i++) {
final String moduleName = modules[i];
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 模拟模块加载时间
long loadTime = (long) (Math.random() * 2000) + 500;
Thread.sleep(loadTime);
System.out.println("✓ " + moduleName + " 加载完成 (" + loadTime + "ms)");
moduleLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("✗ " + moduleName + " 加载被中断");
moduleLatch.countDown(); // 确保减少计数
}
}, "ModuleLoader-" + moduleName).start();
}
try {
System.out.println("\n主线程等待所有模块加载完成...");
long startWait = System.currentTimeMillis();
moduleLatch.await();
long endWait = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("\n✅ 所有模块加载完成!");
System.out.println("等待时间: " + (endWait - startWait) + "ms");
System.out.println("应用程序启动完成,可以接收请求");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("主线程等待被中断");
}
}
}
3.2 await() 方法详解
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* await() 方法深度解析
*
* CountDownLatch 提供了多种 await 方法:
* 1. await(): 无限期等待
* 2. await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit): 超时等待
* 3. 组合使用模式
*/
public class AwaitMethodsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== await() 方法详解 ===");
// 演示 1: 基本 await()
demonstrateBasicAwait();
// 演示 2: 超时 await()
demonstrateTimeoutAwait();
// 演示 3: 多个线程同时 await()
demonstrateMultipleAwait();
// 演示 4: 中断处理
demonstrateInterruption();
}
private static void demonstrateBasicAwait() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 1: 基本 await() ---");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("线程A 完成任务,countDown");
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
System.out.println("线程B 完成任务,countDown");
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
try {
System.out.println("主线程调用 await(),开始等待...");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
latch.await();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("主线程等待结束,耗时: " + (end - start) + "ms");
System.out.println("所有任务完成,继续执行主流程");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("主线程等待被中断");
}
}
private static void demonstrateTimeoutAwait() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 2: 超时 await() ---");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
// 启动两个线程,但第三个永远不会启动(模拟超时场景)
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {
final int id = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(id * 1000);
System.out.println("任务" + id + " 完成");
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
try {
System.out.println("主线程调用 await(2500ms),带超时等待...");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean completed = latch.await(2500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (completed) {
System.out.println("✅ 所有任务在规定时间内完成");
} else {
System.out.println("⏰ 等待超时,仍有 " + latch.getCount() + " 个任务未完成");
}
System.out.println("实际等待时间: " + (end - start) + "ms");
// 即使超时,也可以继续执行(但可能状态不完整)
System.out.println("继续执行后续逻辑(可能基于不完整状态)");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("等待被中断");
}
}
private static void demonstrateMultipleAwait() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 3: 多个线程同时 await() ---");
final int WAITER_COUNT = 5;
final int TASK_COUNT = 3;
CountDownLatch startLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); // 统一开始
CountDownLatch completionLatch = new CountDownLatch(TASK_COUNT); // 任务完成
AtomicInteger waitersReady = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 创建多个等待线程
for (int i = 0; i < WAITER_COUNT; i++) {
final int waiterId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
waitersReady.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("等待线程 " + waiterId + " 准备就绪,调用 await()");
startLatch.await(); // 等待开始信号
System.out.println("等待线程 " + waiterId + " 被唤醒,开始工作...");
Thread.sleep(500); // 模拟工作
completionLatch.countDown(); // 完成任务
System.out.println("等待线程 " + waiterId + " 完成任务");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
// 等待所有等待线程就绪
while (waitersReady.get() < WAITER_COUNT) {
Thread.yield();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); // 给线程一些时间进入等待状态
System.out.println("\n所有 " + WAITER_COUNT + " 个等待线程已进入 await 状态");
System.out.println("主线程释放开始门闩...");
startLatch.countDown(); // 释放所有等待线程
System.out.println("主线程等待所有任务完成...");
completionLatch.await();
System.out.println("\n✅ 所有 " + WAITER_COUNT + " 个线程都完成了工作");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
private static void demonstrateInterruption() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 4: 中断处理 ---");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);
Thread waitingThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("等待线程: 调用 await()");
latch.await();
System.out.println("等待线程: await() 返回,继续执行");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("等待线程: 在 await() 中被中断,中断状态: " +
Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 恢复中断状态
}
});
waitingThread.start();
try {
// 给等待线程时间进入等待状态
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("主线程: 中断等待线程");
waitingThread.interrupt();
// 等待线程结束
waitingThread.join(1000);
// 测试 latch 是否还能使用
System.out.println("\n中断后 latch 状态:");
System.out.println("当前计数: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("尝试 countDown...");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println("countDown 后计数: " + latch.getCount());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
3.3 countDown() 方法详解
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
/**
* countDown() 方法深度解析
*
* 关键特性:
* 1. 线程安全:使用 CAS 操作保证线程安全
* 2. 幂等性:计数为 0 后多次调用无效果
* 3. 无阻塞:立即返回,不会阻塞调用线程
*/
public class CountDownMethodDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== countDown() 方法详解 ===");
// 演示 1: 基本 countDown()
demonstrateBasicCountDown();
// 演示 2: 多线程并发 countDown()
demonstrateConcurrentCountDown();
// 演示 3: 计数为 0 后的行为
demonstrateZeroCountBehavior();
// 演示 4: countDown() 的性能特性
demonstratePerformance();
}
private static void demonstrateBasicCountDown() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 1: 基本 countDown() ---");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
System.out.println("初始状态:");
System.out.println(" 计数器: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println(" 是否归零: " + (latch.getCount() == 0));
System.out.println("\n执行 countDown() 1:");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 计数器: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("执行 countDown() 2:");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 计数器: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("执行 countDown() 3:");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 计数器: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println(" 是否归零: " + (latch.getCount() == 0));
System.out.println("\n尝试在归零后 await():");
try {
latch.await(); // 应该立即返回
System.out.println(" await() 立即返回");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
private static void demonstrateConcurrentCountDown() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 2: 多线程并发 countDown() ---");
final int THREAD_COUNT = 100;
final int INITIAL_COUNT = THREAD_COUNT;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(INITIAL_COUNT);
AtomicLong completedThreads = new AtomicLong(0);
System.out.println("启动 " + THREAD_COUNT + " 个线程并发执行 countDown()");
System.out.println("初始计数: " + latch.getCount());
// 启动多个线程同时执行 countDown
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; i++) {
final int threadId = i;
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 随机睡眠,模拟不同的执行时间
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));
long before = latch.getCount();
latch.countDown();
long after = latch.getCount();
completedThreads.incrementAndGet();
System.out.printf("线程 %03d: 计数 %d -> %d%n",
threadId, before, after);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
threads[i].start();
}
// 等待所有线程启动
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.join();
}
System.out.println("\n最终状态:");
System.out.println(" 完成 countDown 的线程数: " + completedThreads.get());
System.out.println(" 最终计数器值: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println(" 计数器是否归零: " + (latch.getCount() == 0));
// 验证线程安全性
if (completedThreads.get() == THREAD_COUNT && latch.getCount() == 0) {
System.out.println("✅ 并发 countDown() 测试通过:线程安全");
} else {
System.out.println("❌ 并发 countDown() 测试失败");
}
}
private static void demonstrateZeroCountBehavior() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 3: 计数为 0 后的行为 ---");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
System.out.println("初始状态: 计数 = " + latch.getCount());
// 第一次 countDown,计数归零
System.out.println("执行 countDown() 1:");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 计数: " + latch.getCount());
// 第二次 countDown,计数已为 0
System.out.println("执行 countDown() 2 (计数已为 0):");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 计数: " + latch.getCount());
// 第三次 countDown,计数仍为 0
System.out.println("执行 countDown() 3 (计数已为 0):");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 计数: " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("\n结论: countDown() 在计数为 0 后调用是安全的,但无实际效果");
// 测试 await() 在计数归零后的行为
System.out.println("\n测试计数归零后 await() 的行为:");
try {
System.out.println(" 调用 await()...");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
latch.await();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(" await() 立即返回,耗时: " + (end - start) + "ms");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
private static void demonstratePerformance() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 4: countDown() 性能特性 ---");
final int ITERATIONS = 1000000; // 100万次
final int LATCH_COUNT = 1000000;
System.out.println("性能测试: " + ITERATIONS + " 次 countDown() 调用");
// 测试 1: 单个线程连续调用
System.out.println("\n测试 1: 单个线程连续调用");
CountDownLatch latch1 = new CountDownLatch(LATCH_COUNT);
long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < ITERATIONS; i++) {
latch1.countDown();
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(" 耗时: " + (end1 - start1) + "ms");
System.out.println(" 平均每次调用: " +
((double)(end1 - start1) / ITERATIONS * 1000000) + "ns");
// 测试 2: 多线程并发调用
System.out.println("\n测试 2: 多线程并发调用");
final int THREAD_COUNT = 10;
final int COUNT_PER_THREAD = ITERATIONS / THREAD_COUNT;
CountDownLatch latch2 = new CountDownLatch(ITERATIONS);
CountDownLatch startLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch finishLatch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_COUNT);
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int t = 0; t < THREAD_COUNT; t++) {
final int threadId = t;
threads[t] = new Thread(() -> {
try {
startLatch.await(); // 等待开始信号
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT_PER_THREAD; i++) {
latch2.countDown();
}
finishLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
threads[t].start();
}
// 所有线程准备就绪后同时开始
startLatch.countDown();
try {
finishLatch.await(); // 等待所有线程完成
long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(" 耗时: " + (end2 - start2) + "ms");
System.out.println(" 平均每次调用: " +
((double)(end2 - start2) / ITERATIONS * 1000000) + "ns");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
System.out.println("\n性能结论:");
System.out.println("1. countDown() 是非常轻量级的操作");
System.out.println("2. 多线程并发调用有很好的扩展性");
System.out.println("3. 在计数归零后调用几乎无开销");
}
}
3.4 getCount() 方法详解
/**
* getCount() 方法详解
*
* getCount() 返回当前的计数值,常用于调试和状态监控。
* 注意:getCount() 的返回值只是一个快照,可能立即过时。
*/
public class GetCountMethodDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== getCount() 方法详解 ===");
// 演示 1: 基本使用
demonstrateBasicUsage();
// 演示 2: 监控和调试
demonstrateMonitoring();
// 演示 3: 竞态条件演示
demonstrateRaceCondition();
// 演示 4: 实际应用场景
demonstrateRealWorldUsage();
}
private static void demonstrateBasicUsage() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 1: 基本使用 ---");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);
System.out.println("初始状态:");
System.out.println(" getCount() = " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("\n执行 countDown() 后:");
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" getCount() = " + latch.getCount());
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" getCount() = " + latch.getCount());
latch.countDown();
latch.countDown();
latch.countDown();
System.out.println(" 执行3次 countDown() 后:");
System.out.println(" getCount() = " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("\n重要提示:");
System.out.println("1. getCount() 返回的是调用瞬间的快照值");
System.out.println("2. 在多线程环境中,返回值可能立即过时");
System.out.println("3. 不要基于 getCount() 的返回值做业务决策");
}
private static void demonstrateMonitoring() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 2: 监控和调试 ---");
final int TASK_COUNT = 10;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(TASK_COUNT);
System.out.println("启动 " + TASK_COUNT + " 个任务");
System.out.println("初始计数: " + latch.getCount());
// 启动监控线程
Thread monitorThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (latch.getCount() > 0) {
System.out.printf("监控: 剩余任务数 = %d%n", latch.getCount());
Thread.sleep(200); // 每200ms监控一次
}
System.out.println("监控: 所有任务完成!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
monitorThread.setDaemon(true);
monitorThread.start();
// 启动工作线程
for (int i = 0; i < TASK_COUNT; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 模拟任务执行时间
long duration = (long) (Math.random() * 1000) + 500;
Thread.sleep(duration);
latch.countDown();
System.out.printf("任务 %d 完成,耗时 %dms%n", taskId, duration);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
latch.await();
System.out.println("\n主线程: 所有任务完成确认");
// 给监控线程一点时间输出最后一条信息
Thread.sleep(300);
}
private static void demonstrateRaceCondition() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 3: 竞态条件演示 ---");
final int THREAD_COUNT = 50;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_COUNT);
System.out.println("演示 getCount() 的竞态条件");
System.out.println("启动 " + THREAD_COUNT + " 个线程快速执行 countDown()");
// 创建快速执行的线程
Thread[] threads = new Thread[THREAD_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; i++) {
final int threadId = i;
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
// 尽可能快地执行 countDown
latch.countDown();
});
}
// 同时启动所有线程
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.start();
}
// 在主线程中连续调用 getCount()
System.out.println("\n主线程连续调用 getCount():");
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
long count = latch.getCount();
System.out.printf(" getCount() 调用 %2d: 计数 = %2d%n", i + 1, count);
if (count == 0) {
System.out.println(" 注意: 计数已归零,但其他线程可能仍在运行");
}
Thread.yield(); // 让出CPU,增加竞态条件概率
}
// 等待所有线程完成
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.join();
}
System.out.println("\n最终 getCount(): " + latch.getCount());
System.out.println("\n竞态条件总结:");
System.out.println("1. getCount() 返回的是瞬时值");
System.out.println("2. 在调用 getCount() 和实际使用返回值之间,状态可能已改变");
System.out.println("3. 适合用于监控和调试,不适合用于同步控制");
}
private static void demonstrateRealWorldUsage() {
System.out.println("\n--- 演示 4: 实际应用场景 ---");
// 场景: 批量处理任务,显示进度
final int BATCH_SIZE = 100;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(BATCH_SIZE);
System.out.println("批量处理 " + BATCH_SIZE + " 个任务");
System.out.println("显示处理进度:\n");
// 进度显示线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
long total = BATCH_SIZE;
while (true) {
long remaining = latch.getCount();
long completed = total - remaining;
// 计算进度百分比
double percent = (double) completed / total * 100;
// 显示进度条
int barWidth = 50;
int progress = (int) (barWidth * completed / total);
System.out.printf("\r进度: [%-" + barWidth + "s] %6.2f%% (%d/%d)",
"=".repeat(progress), percent, completed, total);
if (remaining == 0) {
System.out.println("\n\n✅ 批量处理完成!");
break;
}
Thread.sleep(100); // 每100ms更新一次进度
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
// 模拟批量处理任务
for (int i = 0; i < BATCH_SIZE; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 模拟任务处理时间
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
latch.countDown(); // 确保计数减少
}
}).start();
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
四、高级应用场景与实战
4.1 复杂并发模式实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* CountDownLatch 高级应用场景
*
* 1. 并行任务分片与聚合
* 2. 多阶段工作流
* 3. 资源初始化协调
* 4. 测试并发场景
*/
public class AdvancedUsageDemo {
/**
* 场景 1: 并行计算 Map-Reduce 模式
*/
static class ParallelMapReduce {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== 场景 1: 并行 Map-Reduce ===");
// 模拟数据
List<Integer> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
data.add(i);
}
// 将数据分成4个分片
int sliceCount = 4;
int sliceSize = data.size() / sliceCount;
CountDownLatch mapLatch = new CountDownLatch(sliceCount);
List<Future<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(sliceCount);
System.out.println("开始并行 Map 阶段...");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Map 阶段:并行处理每个分片
for (int i = 0; i < sliceCount; i++) {
final int sliceIndex = i;
final int fromIndex = i * sliceSize;
final int toIndex = (i == sliceCount - 1) ? data.size() : (i + 1) * sliceSize;
Callable<Integer> task = () -> {
try {
// 模拟计算密集型任务
int sum = 0;
for (int j = fromIndex; j < toIndex; j++) {
sum += data.get(j);
// 模拟处理时间
Thread.sleep(1);
}
System.out.printf("分片 %d 计算完成: sum = %d%n", sliceIndex, sum);
return sum;
} finally {
mapLatch.countDown();
}
};
results.add(executor.submit(task));
}
// 等待所有 Map 任务完成
mapLatch.await();
System.out.println("Map 阶段完成,开始 Reduce 阶段...");
// Reduce 阶段:聚合结果
int finalResult = 0;
for (Future<Integer> future : results) {
try {
finalResult += future.get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("最终结果: " + finalResult);
System.out.println("总耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
// 验证结果
int expected = data.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).sum();
System.out.println("预期结果: " + expected);
System.out.println("结果验证: " + (finalResult == expected ? "✅ 正确" : "❌ 错误"));
executor.shutdown();
}
}
/**
* 场景 2: 多阶段工作流协调
*/
static class MultiStageWorkflow {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n=== 场景 2: 多阶段工作流 ===");
// 定义三个阶段
CountDownLatch stage1Latch = new CountDownLatch(3); // 数据加载
CountDownLatch stage2Latch = new CountDownLatch(2); // 数据处理
CountDownLatch stage3Latch = new CountDownLatch(1); // 结果汇总
System.out.println("开始三阶段工作流执行...\n");
// 阶段1:数据加载
System.out.println("【阶段1】数据加载(3个并行任务)");
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.printf(" 数据加载任务 %d 开始...%n", taskId);
Thread.sleep(500 + taskId * 100);
System.out.printf(" ✓ 数据加载任务 %d 完成%n", taskId);
stage1Latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
// 阶段2:数据处理(等待阶段1完成后开始)
new Thread(() -> {
try {
stage1Latch.await();
System.out.println("\n【阶段2】数据处理(2个并行任务)");
CountDownLatch processLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.printf(" 数据处理任务 %d 开始...%n", taskId);
Thread.sleep(800 + taskId * 100);
System.out.printf(" ✓ 数据处理任务 %d 完成%n", taskId);
processLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
processLatch.await();
System.out.println(" → 阶段2完成,触发阶段3");
stage2Latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
// 阶段3:结果汇总(等待阶段2完成后开始)
new Thread(() -> {
try {
stage2Latch.await();
System.out.println("\n【阶段3】结果汇总");
System.out.println(" 开始汇总所有处理结果...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(" ✓ 结果汇总完成");
stage3Latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
// 主线程等待整个工作流完成
stage3Latch.await();
System.out.println("\n🎉 整个工作流执行完成!");
}
}
/**
* 场景 3: 服务启动协调
*/
static class ServiceInitializationCoordinator {
static class Service {
private final String name;
private final int initTime;
private volatile boolean initialized = false;
public Service(String name, int initTime) {
this.name = name;
this.initTime = initTime;
}
public void initialize(CountDownLatch latch) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.printf("服务 '%s' 开始初始化(预计 %dms)...%n",
name, initTime);
Thread.sleep(initTime);
initialized = true;
System.out.printf("✅ 服务 '%s' 初始化完成%n", name);
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.printf("❌ 服务 '%s' 初始化被中断%n", name);
latch.countDown(); // 确保计数减少
}
}).start();
}
public boolean isInitialized() {
return initialized;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n=== 场景 3: 服务启动协调 ===");
// 定义需要初始化的服务
Service[] services = {
new Service("数据库连接池", 2000),
new Service("Redis缓存", 1500),
new Service("消息队列", 2500),
new Service("配置中心", 800),
new Service("监控系统", 1200)
};
CountDownLatch initLatch = new CountDownLatch(services.length);
System.out.println("开始并行初始化 " + services.length + " 个服务...\n");
// 并行初始化所有服务
for (Service service : services) {
service.initialize(initLatch);
}
// 显示初始化进度
new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (initLatch.getCount() > 0) {
long remaining = initLatch.getCount();
System.out.printf("\r等待服务初始化... 剩余 %d 个服务 ", remaining);
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
// 等待所有服务初始化完成
initLatch.await();
System.out.println("\n\n🎉 所有服务初始化完成!");
System.out.println("应用程序可以正常启动...");
// 验证所有服务状态
boolean allReady = true;
for (Service service : services) {
if (!service.isInitialized()) {
System.out.printf("警告: 服务 '%s' 未正确初始化%n", service.name);
allReady = false;
}
}
if (allReady) {
System.out.println("✅ 所有服务状态验证通过");
} else {
System.out.println("⚠️ 部分服务可能有问题,建议检查");
}
}
}
/**
* 场景 4: 并发测试工具
*/
static class ConcurrentTestHarness {
public static long timeTasks(int nThreads, final Runnable task)
throws InterruptedException {
// 起始门:确保所有线程同时开始
final CountDownLatch startGate = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 结束门:等待所有线程完成
final CountDownLatch endGate = new CountDownLatch(nThreads);
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 等待开始信号
startGate.await();
try {
task.run();
} finally {
// 通知任务完成
endGate.countDown();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
t.start();
}
long start = System.nanoTime();
// 释放起始门,所有线程同时开始执行
startGate.countDown();
// 等待所有线程完成
endGate.await();
long end = System.nanoTime();
return end - start;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n=== 场景 4: 并发测试工具 ===");
// 测试任务:模拟一些工作
Runnable testTask = () -> {
// 模拟一些计算工作
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
sum += i % 3;
}
// 模拟一些IO等待
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
};
// 测试不同线程数下的性能
int[] threadCounts = {1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32};
System.out.println("并发性能测试(每个线程执行相同任务)");
System.out.println("线程数 | 耗时(ns) | 加速比");
System.out.println("------|----------|------");
long singleThreadTime = 0;
for (int nThreads : threadCounts) {
long duration = timeTasks(nThreads, testTask);
if (nThreads == 1) {
singleThreadTime = duration;
}
double speedup = (double) singleThreadTime / duration;
System.out.printf("%6d | %9d | %.2fx%n",
nThreads, duration, speedup);
}
System.out.println("\n测试说明:");
System.out.println("1. 使用 CountDownLatch 确保所有线程同时开始");
System.out.println("2. 使用 CountDownLatch 等待所有线程完成");
System.out.println("3. 可以准确测量并发执行时间");
System.out.println("4. 适用于性能基准测试和并发问题复现");
}
}
}
4.2 生产环境最佳实践
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
/**
* CountDownLatch 生产环境最佳实践
*
* 包括错误处理、资源管理、性能优化等
*/
public class ProductionBestPractices {
/**
* 实践 1: 异常安全的使用模式
*/
static class ExceptionSafePattern {
public static void executeWithWorkers(int workerCount)
throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch completionLatch = new CountDownLatch(workerCount);
AtomicBoolean hasError = new AtomicBoolean(false);
for (int i = 0; i < workerCount; i++) {
final int workerId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 执行工作任务
doWork(workerId);
// 只有成功完成才减少计数
if (!hasError.get()) {
completionLatch.countDown();
System.out.printf("Worker %d completed successfully%n", workerId);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 发生异常,设置错误标志
hasError.set(true);
System.err.printf("Worker %d failed: %s%n", workerId, e.getMessage());
// 立即减少计数,让主线程可以继续处理
while (completionLatch.getCount() > 0) {
completionLatch.countDown();
}
}
}).start();
}
// 等待所有工作完成或发生错误
completionLatch.await();
if (hasError.get()) {
System.out.println("任务执行过程中发生错误,进行错误处理...");
handleError();
} else {
System.out.println("所有任务成功完成");
}
}
private static void doWork(int workerId) throws Exception {
// 模拟工作,随机失败
if (Math.random() < 0.2) {
throw new Exception("模拟的工作错误");
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
private static void handleError() {
// 错误处理逻辑
System.out.println("执行错误恢复操作...");
}
}
/**
* 实践 2: 超时与中断处理
*/
static class TimeoutAndInterruption {
public static class TaskExecutor {
private final CountDownLatch latch;
private final AtomicBoolean cancelled;
public TaskExecutor(int taskCount) {
this.latch = new CountDownLatch(taskCount);
this.cancelled = new AtomicBoolean(false);
}
public void executeTask(Runnable task) {
new Thread(() -> {
if (cancelled.get()) {
System.out.println("任务已取消,跳过执行");
latch.countDown();
return;
}
try {
task.run();
System.out.println("任务执行完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("任务执行异常: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
public boolean awaitCompletion(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return latch.await(timeout, unit);
}
public void cancelAll() {
cancelled.set(true);
// 快速释放所有等待
while (latch.getCount() > 0) {
latch.countDown();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TaskExecutor executor = new TaskExecutor(5);
// 添加任务
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
executor.executeTask(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); // 模拟长时间任务
System.out.println("Task " + taskId + " finished");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
}
// 监控线程:超时后取消任务
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000); // 3秒后超时
System.out.println("超时,取消所有任务");
executor.cancelAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
try {
boolean completed = executor.awaitCompletion(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (completed) {
System.out.println("所有任务正常完成");
} else {
System.out.println("任务执行超时或被取消");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("等待被中断");
executor.cancelAll();
}
}
}
/**
* 实践 3: 资源清理模式
*/
static class ResourceCleanupPattern {
static class ResourceManager {
private final CountDownLatch shutdownLatch;
private final List<AutoCloseable> resources;
public ResourceManager() {
this.shutdownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
this.resources = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addResource(AutoCloseable resource) {
resources.add(resource);
}
public void shutdown() {
System.out.println("开始关闭资源...");
// 使用 CountDownLatch 协调资源关闭
CountDownLatch cleanupLatch = new CountDownLatch(resources.size());
for (AutoCloseable resource : resources) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
resource.close();
System.out.println("资源关闭成功: " + resource.getClass().getSimpleName());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("资源关闭失败: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
cleanupLatch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
try {
// 等待所有资源关闭完成
cleanupLatch.await(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("所有资源关闭完成");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("资源关闭被中断");
} finally {
// 通知主线程可以继续
shutdownLatch.countDown();
}
}
public void awaitShutdown() throws InterruptedException {
shutdownLatch.await();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ResourceManager manager = new ResourceManager();
// 模拟添加资源
manager.addResource(() -> {
System.out.println("关闭数据库连接");
Thread.sleep(500);
});
manager.addResource(() -> {
System.out.println("关闭网络连接");
Thread.sleep(300);
});
manager.addResource(() -> {
System.out.println("关闭文件句柄");
Thread.sleep(200);
});
// 启动关闭过程
new Thread(manager::shutdown).start();
// 等待关闭完成
manager.awaitShutdown();
System.out.println("应用程序安全退出");
}
}
/**
* 实践 4: 性能监控与调试
*/
static class PerformanceMonitoring {
static class MonitoredLatch extends CountDownLatch {
private final String name;
private final long creationTime;
private volatile long lastCountDownTime;
private final AtomicLong countDownCount = new AtomicLong();
public MonitoredLatch(String name, int count) {
super(count);
this.name = name;
this.creationTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastCountDownTime = creationTime;
}
@Override
public void countDown() {
super.countDown();
countDownCount.incrementAndGet();
lastCountDownTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public void printStats() {
long currentCount = getCount();
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - creationTime;
long timeSinceLastCountDown = System.currentTimeMillis() - lastCountDownTime;
System.out.println("\n=== Latch 统计信息 ===");
System.out.println("名称: " + name);
System.out.println("初始计数: " + countDownCount.get() + currentCount);
System.out.println("当前剩余计数: " + currentCount);
System.out.println("已执行 countDown 次数: " + countDownCount.get());
System.out.println("创建时间: " + elapsed + "ms 前");
System.out.println("距离上次 countDown: " + timeSinceLastCountDown + "ms");
if (currentCount == 0) {
System.out.println("状态: 已完成");
} else if (timeSinceLastCountDown > 10000) {
System.out.println("警告: 超过10秒没有 countDown 活动");
} else {
System.out.println("状态: 进行中");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MonitoredLatch latch = new MonitoredLatch("数据处理门闩", 5);
// 启动任务
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 + taskId * 500);
latch.countDown();
System.out.println("任务 " + taskId + " 完成");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
// 监控线程
new Thread(() -> {
while (latch.getCount() > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
latch.printStats();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}).start();
latch.await();
System.out.println("\n最终统计:");
latch.printStats();
}
}
}
五、常见问题与解决方案
5.1 典型错误与陷阱
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* CountDownLatch 常见错误与解决方案
*/
public class CommonPitfallsAndSolutions {
/**
* 陷阱 1: 忘记调用 countDown()
*/
static class Pitfall1_ForgetCountDown {
public static void wrongWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== 陷阱 1: 忘记调用 countDown() ===");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
// 只启动两个线程,但 latch 需要三个 countDown
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
latch.countDown(); // 这里只调用两次
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
System.out.println("主线程等待...");
latch.await(); // 这里会永远等待!
System.out.println("这行永远不会执行");
}
public static void correctWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n✅ 正确做法: 确保 countDown() 被调用");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
AtomicInteger completedTasks = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 使用 try-finally 确保 countDown 被调用
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 模拟可能失败的任务
if (Math.random() < 0.3) {
throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败");
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
completedTasks.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("任务异常: " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
// 确保无论成功失败都减少计数
latch.countDown();
System.out.println("countDown 被调用,剩余: " + latch.getCount());
}
}).start();
}
// 设置超时,防止永久等待
boolean completed = latch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (completed) {
System.out.println("所有任务完成,成功数: " + completedTasks.get());
} else {
System.out.println("等待超时,剩余任务: " + latch.getCount());
}
}
}
/**
* 陷阱 2: 在 countDown() 之前 await()
*/
static class Pitfall2_AwaitBeforeCountDown {
public static void wrongWay() {
System.out.println("\n=== 陷阱 2: 线程启动顺序问题 ===");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 先 await 再启动线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("等待线程开始等待...");
latch.await(); // 这会阻塞
System.out.println("等待线程被唤醒");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
// 主线程直接继续执行
System.out.println("主线程继续执行...");
// 忘记启动 countDown 线程!
}
public static void correctWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n✅ 正确做法: 确保线程启动顺序");
CountDownLatch startLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch finishLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 工作线程
Thread worker = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("工作线程: 等待开始信号...");
startLatch.await(); // 等待开始信号
System.out.println("工作线程: 开始工作...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("工作线程: 工作完成");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
finishLatch.countDown(); // 通知完成
}
});
// 启动工作线程
worker.start();
// 给工作线程时间进入等待状态
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("主线程: 发送开始信号");
startLatch.countDown(); // 释放工作线程
System.out.println("主线程: 等待工作完成");
finishLatch.await(); // 等待工作完成
System.out.println("主线程: 所有任务完成");
}
}
/**
* 陷阱 3: 错误的重用尝试
*/
static class Pitfall3_ReuseAttempt {
public static void wrongWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n=== 陷阱 3: 错误的重用尝试 ===");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 第一次使用
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
latch.await();
System.out.println("第一次等待完成");
// 错误地尝试重用
System.out.println("尝试重用 latch...");
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
latch.countDown(); // 这不会生效!
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
// 这里会立即返回,但并不是因为新线程完成了
latch.await();
System.out.println("第二次等待完成(但可能是错误的!)");
}
public static void correctWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n✅ 正确做法: 使用 CyclicBarrier 或创建新实例");
// 方案1: 使用 CyclicBarrier(如果需要重用)
System.out.println("方案1: 使用 CyclicBarrier 替代");
java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier barrier =
new java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { // 重用两次
final int round = i + 1;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("第" + round + "轮: 线程工作...");
Thread.sleep(500);
barrier.await(); // 等待另一个线程
System.out.println("第" + round + "轮: 同步完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(100); // 错开启动时间
}
Thread.sleep(1500);
// 方案2: 每次都创建新的 CountDownLatch
System.out.println("\n方案2: 创建新的 CountDownLatch 实例");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
CountDownLatch newLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
final int round = i + 1;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("第" + round + "轮: 新线程工作...");
Thread.sleep(500);
newLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
newLatch.await();
System.out.println("第" + round + "轮: 等待完成");
}
}
}
/**
* 陷阱 4: 计数不匹配
*/
static class Pitfall4_CountMismatch {
public static void wrongWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n=== 陷阱 4: 计数不匹配 ===");
// 动态任务列表
List<Runnable> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
tasks.add(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("任务 " + taskId + " 完成");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
}
// 错误:硬编码计数
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5); // 硬编码为5
for (Runnable task : tasks) {
new Thread(() -> {
task.run();
latch.countDown();
}).start();
}
latch.await(); // 会永远等待额外的2个 countDown
System.out.println("这行可能不会执行");
}
public static void correctWay() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("\n✅ 正确做法: 动态计算计数");
// 动态任务列表
List<Runnable> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
tasks.add(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("任务 " + taskId + " 完成");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
}
// 正确:根据任务数量动态设置计数
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(tasks.size());
for (Runnable task : tasks) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
task.run();
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
boolean completed = latch.await(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (completed) {
System.out.println("所有任务完成");
} else {
System.out.println("等待超时,剩余任务: " + latch.getCount());
}
// 更好的做法:使用 ExecutorService
System.out.println("\n更好的做法: 使用 ExecutorService");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
List<Future<?>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (Runnable task : tasks) {
futures.add(executor.submit(task));
}
// 等待所有任务完成
for (Future<?> future : futures) {
try {
future.get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.err.println("任务执行异常: " + e.getCause().getMessage());
}
}
System.out.println("所有任务完成(使用 ExecutorService)");
executor.shutdown();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 演示各种陷阱和解决方案
Pitfall1_ForgetCountDown.correctWay();
Pitfall2_AwaitBeforeCountDown.correctWay();
Pitfall3_ReuseAttempt.correctWay();
Pitfall4_CountMismatch.correctWay();
// 注意:wrongWay() 方法可能导致死锁,这里不实际执行
System.out.println("\n⚠️ 注意:错误的用法可能导致死锁,实际使用时要小心");
}
}
5.2 调试技巧与工具
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.ThreadInfo;
import java.lang.management.ThreadMXBean;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
/**
* CountDownLatch 调试技巧与工具
*/
public class DebuggingTechniques {
/**
* 技巧 1: 线程转储分析
*/
static class ThreadDumpAnalyzer {
public static void analyzeDeadlock() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== 调试技巧 1: 线程转储分析 ===");
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 创建可能死锁的场景
Thread waitingThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("等待线程: 开始等待 latch");
latch.await(); // 这会阻塞
System.out.println("等待线程: 被唤醒");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("等待线程: 被中断");
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}, "WaitingThread");
waitingThread.start();
// 给线程时间进入等待状态
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("\n当前线程状态:");
printThreadDump();
// 模拟忘记调用 countDown
System.out.println("\n模拟死锁场景:忘记调用 countDown()");
System.out.println("等待 3 秒后检查线程状态...");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("\n3秒后的线程状态:");
printThreadDump();
// 最后释放 latch 避免永久阻塞
latch.countDown();
waitingThread.join();
}
private static void printThreadDump() {
ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
// 检测死锁
long[] deadlockedThreads = threadMXBean.findDeadlockedThreads();
if (deadlockedThreads != null && deadlockedThreads.length > 0) {
System.out.println("⚠️ 检测到死锁线程:");
for (long threadId : deadlockedThreads) {
ThreadInfo threadInfo = threadMXBean.getThreadInfo(threadId);
System.out.println(" - " + threadInfo.getThreadName());
}
} else {
System.out.println("未检测到死锁");
}
// 打印所有线程状态
System.out.println("\n所有线程状态:");
ThreadInfo[] threadInfos = threadMXBean.dumpAllThreads(false, false);
for (ThreadInfo threadInfo : threadInfos) {
if (threadInfo.getThreadName().contains("Thread") ||
threadInfo.getThreadName().equals("main")) {
System.out.printf(" %-20s: %s%n",
threadInfo.getThreadName(),
threadInfo.getThreadState());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 技巧 2: 自定义监控 Latch
*/
static class DebuggableCountDownLatch extends CountDownLatch {
private final String name;
private final StackTraceElement[] creationStackTrace;
private final List<StackTraceElement[]> awaitStackTraces =
Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
private final List<Long> countDownTimestamps =
Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
public DebuggableCountDownLatch(String name, int count) {
super(count);
this.name = name;
this.creationStackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
}
@Override
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 记录谁在等待
awaitStackTraces.add(Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace());
System.out.printf("[DEBUG] %s: 线程 '%s' 开始等待%n",
name, Thread.currentThread().getName());
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
super.await();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("[DEBUG] %s: 线程 '%s' 等待结束,耗时 %dms%n",
name, Thread.currentThread().getName(), end - start);
}
@Override
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
awaitStackTraces.add(Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace());
System.out.printf("[DEBUG] %s: 线程 '%s' 开始超时等待 (%d %s)%n",
name, Thread.currentThread().getName(),
timeout, unit);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean result = super.await(timeout, unit);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("[DEBUG] %s: 线程 '%s' 超时等待结束,结果=%s,耗时 %dms%n",
name, Thread.currentThread().getName(),
result, end - start);
return result;
}
@Override
public void countDown() {
countDownTimestamps.add(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.printf("[DEBUG] %s: countDown 调用,剩余计数=%d%n",
name, getCount() - 1);
super.countDown();
}
public void printDebugInfo() {
System.out.println("\n=== " + name + " 调试信息 ===");
System.out.println("创建位置:");
for (int i = 2; i < Math.min(creationStackTrace.length, 6); i++) {
System.out.println(" " + creationStackTrace[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n等待线程栈追踪 (" + awaitStackTraces.size() + " 个):");
for (int i = 0; i < awaitStackTraces.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(" 等待 #" + (i + 1) + ":");
StackTraceElement[] trace = awaitStackTraces.get(i);
for (int j = 2; j < Math.min(trace.length, 5); j++) {
System.out.println(" " + trace[j]);
}
}
System.out.println("\ncountDown 时间戳 (" + countDownTimestamps.size() + " 次):");
if (!countDownTimestamps.isEmpty()) {
long first = countDownTimestamps.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < countDownTimestamps.size(); i++) {
long timestamp = countDownTimestamps.get(i);
System.out.printf(" #%d: +%dms%n",
i + 1, timestamp - first);
}
}
System.out.println("\n当前状态: 计数=" + getCount());
}
}
/**
* 技巧 3: 使用 JMX 监控
*/
static class JMXMonitor {
static class MonitoredService implements MonitoredServiceMBean {
private final CountDownLatch latch;
private final String serviceName;
private volatile long startTime;
private volatile long lastActivityTime;
public MonitoredService(String name, int taskCount) {
this.serviceName = name;
this.latch = new CountDownLatch(taskCount);
this.startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastActivityTime = startTime;
}
public void countDown() {
latch.countDown();
lastActivityTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
latch.await();
}
// JMX 属性
@Override
public String getServiceName() {
return serviceName;
}
@Override
public long getRemainingCount() {
return latch.getCount();
}
@Override
public long getUptime() {
return System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
}
@Override
public long getTimeSinceLastActivity() {
return System.currentTimeMillis() - lastActivityTime;
}
@Override
public boolean isCompleted() {
return latch.getCount() == 0;
}
}
interface MonitoredServiceMBean {
String getServiceName();
long getRemainingCount();
long getUptime();
long getTimeSinceLastActivity();
boolean isCompleted();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=== 调试技巧 3: JMX 监控 ===");
MonitoredService service = new MonitoredService("数据处理服务", 5);
// 注册 JMX MBean(简化版,实际需要完整的 JMX 注册代码)
System.out.println("服务已创建,可通过 JMX 监控:");
System.out.println(" 服务名称: " + service.getServiceName());
System.out.println(" 初始计数: " + service.getRemainingCount());
System.out.println(" 运行时间: " + service.getUptime() + "ms");
// 模拟任务执行
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int taskId = i;
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 + taskId * 500);
service.countDown();
System.out.printf("任务 %d 完成,剩余计数: %d%n",
taskId, service.getRemainingCount());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
// 监控线程
new Thread(() -> {
while (service.getRemainingCount() > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.printf("\r监控: 剩余=%d, 最后活动=%dms前",
service.getRemainingCount(),
service.getTimeSinceLastActivity());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
System.out.println("\n监控: 服务完成");
}).start();
service.await();
System.out.println("\n✅ 所有任务完成");
}
}
/**
* 技巧 4: 单元测试模式
*/
static class UnitTestPatterns {
static class LatchTestUtils {
/**
* 测试 CountDownLatch 是否正常工作的工具方法
*/
public static boolean testLatchFunctionality(
int threadCount,
long timeout,
TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
AtomicInteger completedCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 启动工作线程
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 模拟工作
Thread.sleep(100);
completedCount.incrementAndGet();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
// 等待完成
boolean completed = latch.await(timeout, unit);
// 验证结果
if (completed && completedCount.get() == threadCount) {
System.out.println("✅ Latch 功能测试通过");
return true;
} else {
System.out.printf("❌ Latch 功能测试失败: completed=%s, count=%d/%d%n",
completed, completedCount.get(), threadCount);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 测试超时功能
*/
public static boolean testTimeoutFunctionality()
throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
// 只启动2个线程,故意制造超时
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
}
// 应该超时
boolean completed = latch.await(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!completed && latch.getCount() == 1) {
System.out.println("✅ 超时功能测试通过");
return true;
} else {
System.out.printf("❌ 超时功能测试失败: completed=%s, remaining=%d%n",
completed, latch.getCount());
return false;
}
}
/**
* 测试中断处理
*/
public static boolean testInterruptionHandling()
throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
AtomicBoolean wasInterrupted = new AtomicBoolean(false);
Thread waitingThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
wasInterrupted.set(true);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
waitingThread.start();
// 给线程时间进入等待状态
Thread.sleep(100);
// 中断等待线程
waitingThread.interrupt();
waitingThread.join(1000);
// 验证中断状态
boolean interrupted = wasInterrupted.get() ||
waitingThread.isInterrupted();
if (interrupted) {
System.out.println("✅ 中断处理测试通过");
return true;
} else {
System.out.println("❌ 中断处理测试失败");
return false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== 调试技巧 4: 单元测试模式 ===");
System.out.println("\n测试 1: 基本功能测试");
boolean test1 = LatchTestUtils.testLatchFunctionality(5, 2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println("\n测试 2: 超时功能测试");
boolean test2 = LatchTestUtils.testTimeoutFunctionality();
System.out.println("\n测试 3: 中断处理测试");
boolean test3 = LatchTestUtils.testInterruptionHandling();
System.out.println("\n=== 测试结果汇总 ===");
System.out.println("测试 1 (基本功能): " + (test1 ? "✅ 通过" : "❌ 失败"));
System.out.println("测试 2 (超时功能): " + (test2 ? "✅ 通过" : "❌ 失败"));
System.out.println("测试 3 (中断处理): " + (test3 ? "✅ 通过" : "❌ 失败"));
if (test1 && test2 && test3) {
System.out.println("\n🎉 所有测试通过!");
} else {
System.out.println("\n⚠️ 部分测试失败,需要检查实现");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CountDownLatch 调试技巧演示");
System.out.println("=" .repeat(50));
// 注意:ThreadDumpAnalyzer.analyzeDeadlock() 会模拟死锁场景
// 在实际调试时才运行
System.out.println("运行调试工具演示...");
// 演示可调试的 Latch
System.out.println("\n1. 可调试的 CountDownLatch 演示:");
DebuggableCountDownLatch debugLatch =
new DebuggableCountDownLatch("测试Latch", 2);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
debugLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}, "测试线程1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
debugLatch.countDown();
Thread.sleep(500);
debugLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}).start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
debugLatch.printDebugInfo();
// 演示单元测试
System.out.println("\n2. 单元测试演示:");
UnitTestPatterns.main(new String[0]);
}
}
六、总结与最佳实践
6.1 CountDownLatch 核心要点总结
/**
* CountDownLatch 使用总结
*/
public class CountDownLatchSummary {
/**
* 适用场景
*/
static class UseCases {
// 1. 服务启动协调
// 2. 并行任务分片聚合
// 3. 测试并发场景
// 4. 多阶段工作流协调
// 5. 资源初始化同步
}
/**
* 最佳实践
*/
static class BestPractices {
// 1. 总是在 finally 块中调用 countDown()
// 2. 设置合理的超时时间
// 3. 根据实际任务数量动态设置计数
// 4. 考虑使用 ExecutorService 替代手动线程管理
// 5. 添加适当的监控和日志
}
/**
* 常见陷阱
*/
static class CommonPitfalls {
// 1. 忘记调用 countDown() - 导致永久等待
// 2. 计数不匹配 - 多计数或少计数
// 3. 尝试重用 - CountDownLatch 是一次性的
// 4. 没有处理中断 - await() 可能被中断
// 5. 依赖 getCount() 做业务逻辑 - 返回值是快照
}
/**
* 替代方案
*/
static class Alternatives {
// 1. CyclicBarrier - 可重用的屏障
// 2. Phaser - 更灵活的同步器
// 3. CompletableFuture - 更现代的异步编程
// 4. ExecutorService.invokeAll() - 批量任务执行
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== CountDownLatch 总结 ===");
System.out.println("\n🎯 核心价值:");
System.out.println(" 1. 简单的线程协调机制");
System.out.println(" 2. 高效的并发控制");
System.out.println(" 3. 清晰的等待/通知语义");
System.out.println("\n🔧 适用场景:");
System.out.println(" ✅ 并行任务分片聚合");
System.out.println(" ✅ 服务/资源初始化");
System.out.println(" ✅ 并发测试和基准测试");
System.out.println(" ✅ 简单的多阶段工作流");
System.out.println("\n⚠️ 注意事项:");
System.out.println(" 1. 一次性使用,不能重置");
System.out.println(" 2. 确保 countDown() 被调用");
System.out.println(" 3. 考虑设置超时时间");
System.out.println(" 4. 处理可能的中断");
System.out.println("\n🚀 性能特点:");
System.out.println(" 1. 基于 AQS,性能优秀");
System.out.println(" 2. countDown() 是轻量级操作");
System.out.println(" 3. 支持大量线程同时等待");
System.out.println("\n📊 监控建议:");
System.out.println(" 1. 记录 latch 的创建和销毁");
System.out.println(" 2. 监控 await() 的等待时间");
System.out.println(" 3. 跟踪 countDown() 的调用频率");
System.out.println("\n💡 进阶建议:");
System.out.println(" 1. 考虑使用 CompletableFuture 处理复杂异步流程");
System.out.println(" 2. 使用 ExecutorService 管理线程生命周期");
System.out.println(" 3. 为生产环境添加监控和告警");
System.out.println("\n🎉 总结:");
System.out.println("CountDownLatch 是 Java 并发工具箱中的瑞士军刀之一。");
System.out.println("正确使用时,它可以简化复杂的线程协调问题;");
System.out.println("错误使用时,可能导致难以调试的死锁。");
System.out.println("理解其原理和最佳实践是成为并发编程专家的关键一步。");
}
}
6.2 完整示例:电商订单处理系统
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.*;
/**
* 完整示例:电商订单处理系统
* 演示 CountDownLatch 在实际业务场景中的应用
*/
public class ECommerceOrderSystem {
/**
* 订单处理服务
*/
static class OrderProcessingService {
private final ExecutorService executor;
private final InventoryService inventoryService;
private final PaymentService paymentService;
private final ShippingService shippingService;
private final NotificationService notificationService;
public OrderProcessingService(int threadPoolSize) {
this.executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadPoolSize);
this.inventoryService = new InventoryService();
this.paymentService = new PaymentService();
this.shippingService = new ShippingService();
this.notificationService = new NotificationService();
}
/**
* 处理单个订单
*/
public CompletableFuture<OrderResult> processOrder(Order order) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.printf("开始处理订单: %s%n", order.getId());
// 使用 CountDownLatch 协调并行检查
CountDownLatch validationLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);
AtomicBoolean inventoryAvailable = new AtomicBoolean(false);
AtomicBoolean paymentValid = new AtomicBoolean(false);
// 并行检查库存和支付
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
boolean available = inventoryService.checkInventory(
order.getProductId(), order.getQuantity());
inventoryAvailable.set(available);
} finally {
validationLatch.countDown();
}
});
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
boolean valid = paymentService.validatePayment(
order.getPaymentMethod(), order.getAmount());
paymentValid.set(valid);
} finally {
validationLatch.countDown();
}
});
try {
// 等待验证完成
if (!validationLatch.await(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
return OrderResult.failed(order.getId(),
"验证超时");
}
// 检查验证结果
if (!inventoryAvailable.get()) {
return OrderResult.failed(order.getId(),
"库存不足");
}
if (!paymentValid.get()) {
return OrderResult.failed(order.getId(),
"支付验证失败");
}
// 并行执行后续步骤
CountDownLatch processingLatch = new CountDownLatch(3);
AtomicReference<String> inventoryResult = new AtomicReference<>();
AtomicReference<String> paymentResult = new AtomicReference<>();
AtomicReference<String> shippingResult = new AtomicReference<>();
// 扣减库存
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
String result = inventoryService.deductInventory(
order.getProductId(), order.getQuantity());
inventoryResult.set(result);
} finally {
processingLatch.countDown();
}
});
// 处理支付
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
String result = paymentService.processPayment(
order.getPaymentMethod(), order.getAmount());
paymentResult.set(result);
} finally {
processingLatch.countDown();
}
});
// 安排发货
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
String result = shippingService.arrangeShipping(
order.getShippingAddress());
shippingResult.set(result);
} finally {
processingLatch.countDown();
}
});
// 等待所有处理完成
if (!processingLatch.await(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
return OrderResult.failed(order.getId(),
"处理超时");
}
// 检查处理结果
if (inventoryResult.get() == null ||
paymentResult.get() == null ||
shippingResult.get() == null) {
return OrderResult.failed(order.getId(),
"处理失败");
}
// 发送通知(异步,不阻塞)
notificationService.sendOrderConfirmation(order);
return OrderResult.success(order.getId(),
Arrays.asList(
inventoryResult.get(),
paymentResult.get(),
shippingResult.get()
));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return OrderResult.failed(order.getId(), "处理被中断");
}
}, executor);
}
/**
* 批量处理订单
*/
public CompletableFuture<BatchResult> processBatch(List<Order> orders) {
System.out.printf("开始批量处理 %d 个订单%n", orders.size());
CountDownLatch batchLatch = new CountDownLatch(orders.size());
AtomicInteger successCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
AtomicInteger failureCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
List<OrderResult> results =
Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// 并行处理所有订单
for (Order order : orders) {
processOrder(order).whenComplete((result, error) -> {
if (error != null) {
failureCount.incrementAndGet();
results.add(OrderResult.failed(order.getId(),
error.getMessage()));
} else if (result.isSuccess()) {
successCount.incrementAndGet();
results.add(result);
} else {
failureCount.incrementAndGet();
results.add(result);
}
batchLatch.countDown();
});
}
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
// 等待所有订单处理完成
batchLatch.await(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return new BatchResult(
orders.size(),
successCount.get(),
failureCount.get(),
results
);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return BatchResult.failed("批量处理被中断");
}
});
}
public void shutdown() {
executor.shutdown();
try {
if (!executor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
executor.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
executor.shutdownNow();
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
// 模拟的服务类
static class InventoryService {
boolean checkInventory(String productId, int quantity) {
// 模拟检查库存
return Math.random() > 0.1; // 90% 有库存
}
String deductInventory(String productId, int quantity) {
// 模拟扣减库存
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 100));
return "库存扣减成功";
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return "库存扣减被中断";
}
}
}
static class PaymentService {
boolean validatePayment(String method, double amount) {
// 模拟支付验证
return Math.random() > 0.05; // 95% 验证通过
}
String processPayment(String method, double amount) {
// 模拟支付处理
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 200));
return String.format("支付成功: %.2f via %s", amount, method);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return "支付处理被中断";
}
}
}
static class ShippingService {
String arrangeShipping(String address) {
// 模拟安排发货
try {
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random() * 300));
return "发货安排成功,地址: " + address;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return "发货安排被中断";
}
}
}
static class NotificationService {
void sendOrderConfirmation(Order order) {
// 模拟发送通知(异步)
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.printf("已发送订单确认通知: %s%n", order.getId());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
});
}
}
// 数据模型
static class Order {
private final String id;
private final String productId;
private final int quantity;
private final String paymentMethod;
private final double amount;
private final String shippingAddress;
public Order(String id, String productId, int quantity,
String paymentMethod, double amount, String shippingAddress) {
this.id = id;
this.productId = productId;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.paymentMethod = paymentMethod;
this.amount = amount;
this.shippingAddress = shippingAddress;
}
// getters
public String getId() { return id; }
public String getProductId() { return productId; }
public int getQuantity() { return quantity; }
public String getPaymentMethod() { return paymentMethod; }
public double getAmount() { return amount; }
public String getShippingAddress() { return shippingAddress; }
}
static class OrderResult {
private final String orderId;
private final boolean success;
private final String message;
private final List<String> details;
private OrderResult(String orderId, boolean success,
String message, List<String> details) {
this.orderId = orderId;
this.success = success;
this.message = message;
this.details = details;
}
public static OrderResult success(String orderId, List<String> details) {
return new OrderResult(orderId, true, "处理成功", details);
}
public static OrderResult failed(String orderId, String message) {
return new OrderResult(orderId, false, message, null);
}
// getters
public boolean isSuccess() { return success; }
public String getOrderId() { return orderId; }
public String getMessage() { return message; }
public List<String> getDetails() { return details; }
}
static class BatchResult {
private final int total;
private final int success;
private final int failure;
private final List<OrderResult> details;
private final String error;
public BatchResult(int total, int success, int failure,
List<OrderResult> details) {
this.total = total;
this.success = success;
this.failure = failure;
this.details = details;
this.error = null;
}
public static BatchResult failed(String error) {
return new BatchResult(0, 0, 0, null, error);
}
private BatchResult(int total, int success, int failure,
List<OrderResult> details, String error) {
this.total = total;
this.success = success;
this.failure = failure;
this.details = details;
this.error = error;
}
// getters
public int getTotal() { return total; }
public int getSuccess() { return success; }
public int getFailure() { return failure; }
public double getSuccessRate() {
return total > 0 ? (double) success / total * 100 : 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("=== 电商订单处理系统演示 ===");
System.out.println("演示 CountDownLatch 在实际业务中的应用\n");
// 创建订单处理服务
OrderProcessingService service = new OrderProcessingService(10);
// 生成测试订单
List<Order> orders = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
orders.add(new Order(
"ORD" + String.format("%04d", i),
"PROD" + (i % 5 + 1),
(i % 3 + 1) * 2,
i % 2 == 0 ? "信用卡" : "支付宝",
99.99 * (i % 4 + 1),
"地址" + i
));
}
System.out.printf("生成 %d 个测试订单%n", orders.size());
// 批量处理订单
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
BatchResult result = service.processBatch(orders).get();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 输出结果
System.out.println("\n=== 处理结果 ===");
System.out.printf("总订单数: %d%n", result.getTotal());
System.out.printf("成功: %d%n", result.getSuccess());
System.out.printf("失败: %d%n", result.getFailure());
System.out.printf("成功率: %.1f%%%n", result.getSuccessRate());
System.out.printf("总耗时: %dms%n", endTime - startTime);
// 输出部分订单详情
System.out.println("\n=== 部分订单详情 ===");
if (result.getDetails() != null) {
int count = 0;
for (OrderResult orderResult : result.getDetails()) {
if (count++ < 5) { // 只显示前5个
System.out.printf("订单 %s: %s%n",
orderResult.getOrderId(),
orderResult.getMessage());
}
}
if (result.getDetails().size() > 5) {
System.out.printf("... 还有 %d 个订单%n",
result.getDetails().size() - 5);
}
}
// 关闭服务
service.shutdown();
System.out.println("\n=== 系统总结 ===");
System.out.println("CountDownLatch 在本系统中的应用:");
System.out.println("1. 订单验证阶段: 并行检查库存和支付");
System.out.println("2. 订单处理阶段: 并行扣库存、支付、发货");
System.out.println("3. 批量处理阶段: 协调多个订单的并发处理");
System.out.println("4. 超时控制: 防止单个环节阻塞整个系统");
System.out.println("\n🎉 演示完成!");
}
}
6.3 学习路径建议
# CountDownLatch 学习路径
## 阶段 1:基础掌握(1-2天)
1. 理解基本概念和原理
2. 掌握 await() 和 countDown() 方法
3. 完成简单的示例代码
4. 理解一次性使用的特点
## 阶段 2:应用实践(3-5天)
1. 在项目中实际应用 CountDownLatch
2. 处理各种边界条件和异常
3. 学习与 ExecutorService 结合使用
4. 实现并行任务分片模式
## 阶段 3:深入理解(1-2周)
1. 研究 AQS 实现原理
2. 理解内存模型和 happens-before
3. 学习性能优化技巧
4. 掌握调试和监控方法
## 阶段 4:扩展应用(持续学习)
1. 学习其他同步工具对比
2. 掌握 CompletableFuture 等现代并发工具
3. 理解分布式系统中的同步问题
4. 参与开源项目,学习最佳实践
## 推荐资源
1. 《Java并发编程实战》
2. Java官方文档:java.util.concurrent 包
3. 相关开源项目源码
4. 并发编程相关的技术博客和视频教程
七、总结
CountDownLatch 是 Java 并发编程中的基础且强大的工具,它的核心价值在于:
- 简单性:API 简单易懂,学习成本低
- 高效性:基于 AQS 实现,性能优秀
- 可靠性:经过充分测试和验证
- 灵活性:适用于多种并发协调场景
关键要点回顾:
- CountDownLatch 是一次性使用的,不能重置
- 总是使用 try-finally 确保 countDown() 被调用
- 设置合理的超时时间,避免永久等待
- 理解其底层基于 AQS 的实现原理
- 在生产环境中添加适当的监控和日志
进阶方向:
- 学习 CyclicBarrier 和 Phaser 等其他同步工具
- 掌握 CompletableFuture 进行异步编程
- 理解分布式系统中的同步协调机制
- 参与复杂并发系统的设计和优化
掌握 CountDownLatch 不仅是学习一个工具,更是理解并发编程思想的重要一步。它在简单的 API 背后,体现了并发控制的核心原则:协调、同步和通信。


























 253
253


 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?









