多继承
多继承:一个子类可能有多个父类(基类)。
多继承可能存在二义性问题:即如果继承的父类中出现同样的方法或者数据的时候,那么当子类去调用的时候会存在不知道调用谁的问题。
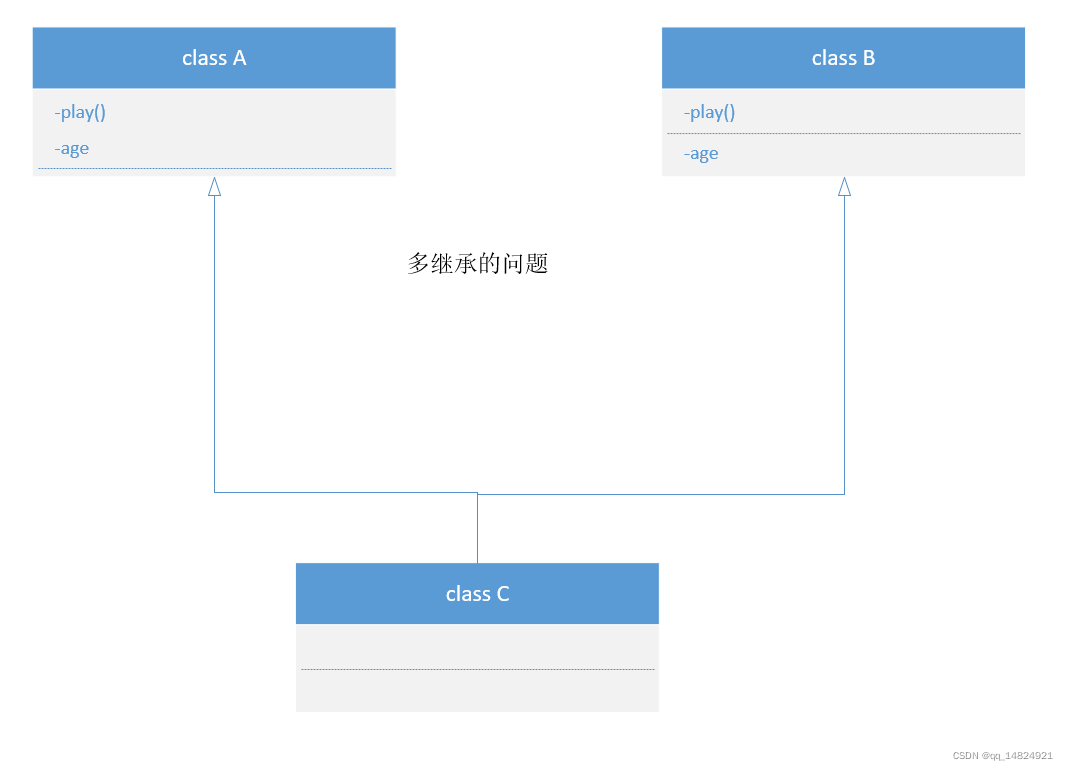
有问题的代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() {
}
~A() {
}
void play() {
cout << "AAA" << endl;
}
protected:
int age = 12;
};
class B {
public:
B() {
}
~B() {
}
void play() {
cout << "BBB" << endl;
}
protected:
int age = 13;
};
class C: public A, public B {
public:
C() {
}
~C() {
}
void test() {
cout << age << endl; // 存在二义性问题,编译器不知道该调用那个父类的
}
};
int main() {
C c1;
c1.play(); // 存在二义性问题,编译器不知道该调用那个父类的
}
多继承二义性的解决方法:
1、子类访问父类成员数据可以指定父类名
2、子类访问父类方法可以指定父类名或者重写方法再调用父类方法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() {
}
~A() {
}
void play() {
cout << "AAA" << endl;
}
protected:
int age = 12;
};
class B {
public:
B() {
}
~B() {
}
void play() {
cout << "BBB" << endl;
}
protected:
int age = 13;
};
class C: public A, public B {
public:
C() {
}
~C() {
}
// 优雅的访问父类方法
void play() {
A::play();
B::play();
}
void test() {
cout << A::age << endl; // 访问父类成员可以指定父类名
}
};
int main() {
C c1;
c1.test();
c1.play(); // 存在二义性问题,编译器不知道该调用那个父类的
c1.A::play(); // 这种方法也可以不推荐
return 0;
}
输入、输出:
多重继承
多重继承:A的派生类B和C,B和C的派生类为D类。
多重继承(菱形继承)存在的问题也是二义性,当D类同时继承B和C的时候,那么该类中会同时存在两个同名的数据成员,分别属于B类和C类的。
解决法:
1、指定父类名
2、通过虚继承的方式解决
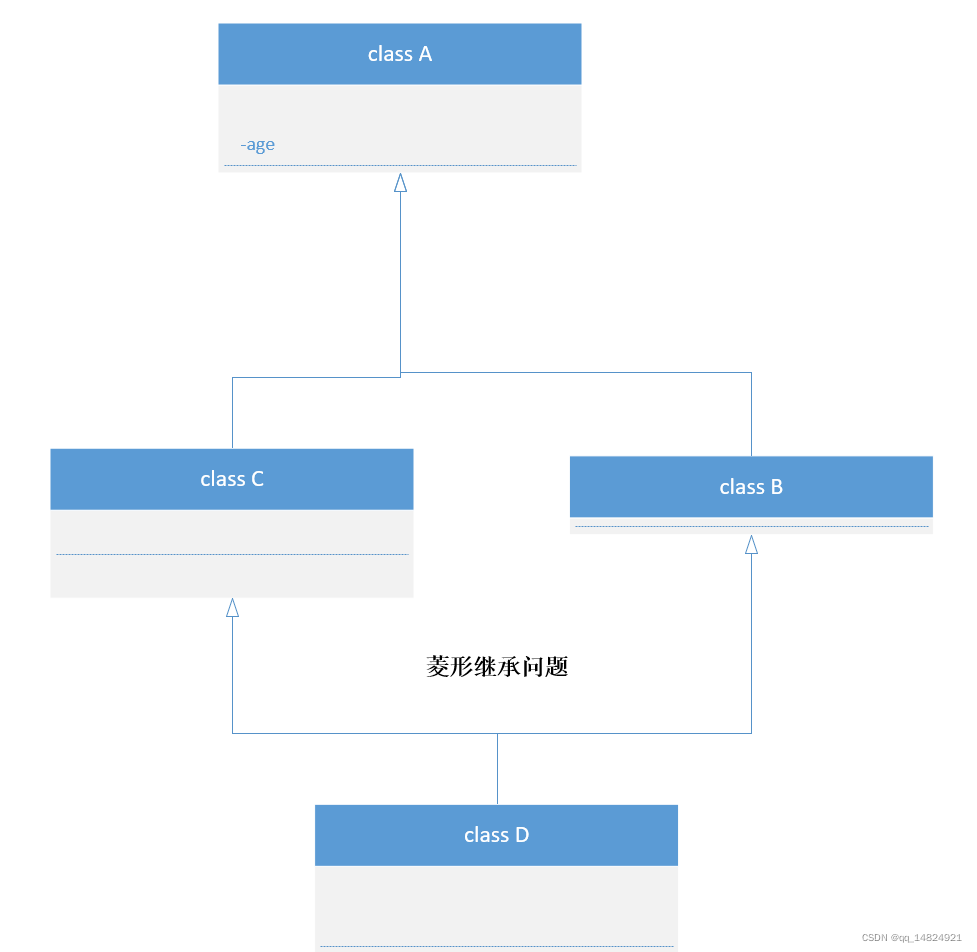
问题代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A() {
}
~A() {
}
protected:
int age = 12;
};
class B : public A {
};
class C : public A {
};
class D : public B, public C {
public:
void test() {
age = 12; // 问题代码,存在歧义
}
};
int main() {
D d1;
d1.test();
return 0;
}
通过VS命令行参数查看对象的内存分布:
命令参数:/d1 reportSingleClassLayoutD
输出的内存分布:
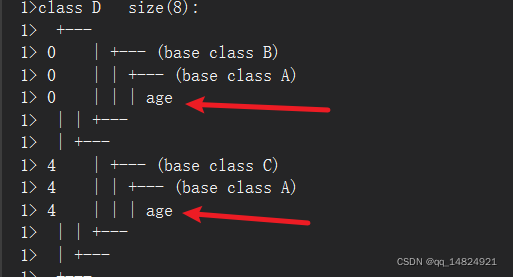
可以看到内存分布中存在两个age
使用虚基类解决:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A { // 虚基类
public:
A() {
}
~A() {
}
protected:
int age = 12;
};
class B: virtual public A { // 虚继承
};
class C : virtual public A { // 虚继承
};
class D : public B, public C {
public:
void test() {
age = 13;
cout << age << endl;
}
};
int main() {
D d1;
d1.test();
return 0;
}
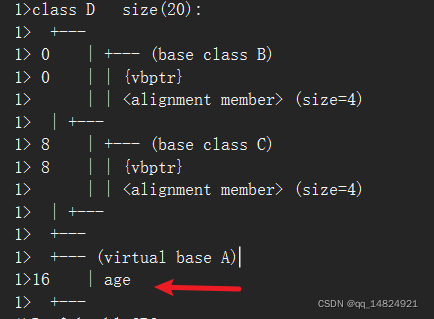
再次查看内存分布图其中只有一个数据





 本文探讨了多继承在C++中的应用及其可能导致的二义性问题,如成员方法和数据成员的冲突。通过实例展示了如何通过指定父类名来解决这种问题,并解释了虚继承在解决菱形继承二义性中的作用。此外,还介绍了使用虚基类如何优化内存布局,消除数据冗余。
本文探讨了多继承在C++中的应用及其可能导致的二义性问题,如成员方法和数据成员的冲突。通过实例展示了如何通过指定父类名来解决这种问题,并解释了虚继承在解决菱形继承二义性中的作用。此外,还介绍了使用虚基类如何优化内存布局,消除数据冗余。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










