引子
前面已经讲了mybatis的二级缓存的实现方式和ehcache框架的利用,现在来看一看mybati二级缓存的实现基础
首先我们知道二级缓存是mapper级别的数据域,那么二级缓存到底是如何创建,保存以及是如何获取的呢?其实二级缓的cahce在SqlSessionFactoryBuilder解析mmaper的时候就已经开始创建了只是没有数据而已,这也说明了为什么二级缓存不是session级别的。现在要了解二级缓存那么就要来看是二级缓存是如何创建的。
创建:
首先解析mapper的xml文件是利用XMLMapperBuilder方法,在前面的解析中我们会利用接口的类名找到相应的mapper的xml文件然后开始解析:
这个方法便是XMLMapperBuilder读取mapper下的各种标签
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
//创建二级缓存
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}cacheElement(context.evalNode(“cache”));方法:
private void cacheElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//这里如果cache的type有这个属性那么便会用外部的cache缓存方式,否则便默认是PrePetual的简单的map缓存
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
//这里是设置缓存的管理算法,默认是LRU算法
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
//设置缓存刷新时间
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
// 设置缓存存储的大小
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
//设置是否只读,默认为false
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//利用builderAssistant来创建缓存对象
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
可以看到这里通过读取cache标签的属性来设置缓存的类型和参数
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
//设置并创建缓存,同时这里currentNamespace便是mapper的namespace,也就说明了为什么二级缓存是mapper级别
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
//将这个mapper缓存放到configuration中在之后将这个缓存的引用赋值给该mapper的sql(mappedStatement)
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}这里主要看CacheBuilder的builde方法:
public Cache build() {
setDefaultImplementations();
//设置基础的缓存,默认是PerpetualCache
Cache cache = newBaseCacheInstance(implementation, id);
setCacheProperties(cache);
// issue #352, do not apply decorators to custom caches
// 缓存清除的算法初始化,并将其装饰到基础缓存中
if (PerpetualCache.class.equals(cache.getClass())) {
for (Class<? extends Cache> decorator : decorators) {
cache = newCacheDecoratorInstance(decorator, cache);
setCacheProperties(cache);
}
// 利用装饰器模式对缓存设置,如LoggingCache,SerializedCache等等,同样这些装饰代理至基础缓存中
cache = setStandardDecorators(cache);
} else if (!LoggingCache.class.isAssignableFrom(cache.getClass())) {
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
}
return cache;
}这里就形成一个mapper的二级缓存,通过debug可以清楚的看到这个是多层次的装饰,体现了一条责任链:
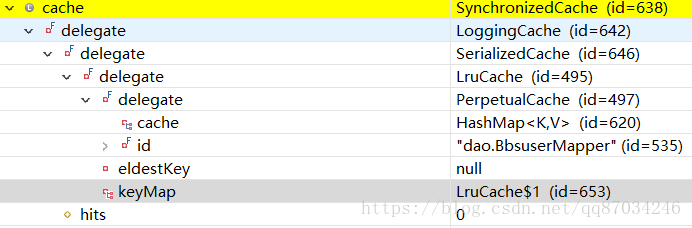
可以看到这是一个清晰的责任链,包括线程的安全,日志的输出,序列化以及缓存的清除算法到最底层的PerpetualCache缓存
然后在回到读取mapper文件的语句:
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));在这个语句中会将为每个sql语句创建mappedStatement对象,在这个对象中就会持有自己mapper的缓存对象的引用,同时将mappedStatement对象以hasMap的形式放到Configruation当中,这里同样利用debug可以看到:
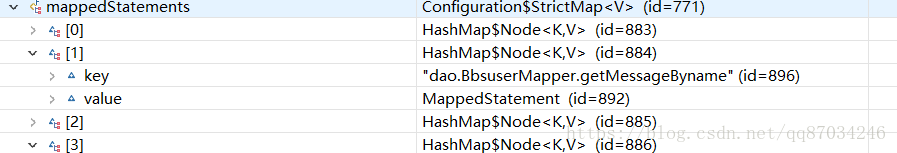
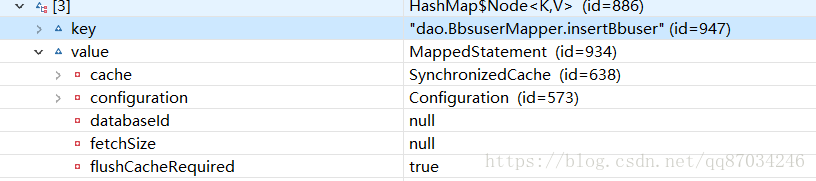
可以看到持有的缓存对象是一个对象。而这也就是mybatis自带的二级缓存的创建机制





 本文详细介绍了MyBatis中二级缓存的创建过程,包括解析mapper XML文件时二级缓存的初始化、缓存类型的配置及缓存管理算法的设置。
本文详细介绍了MyBatis中二级缓存的创建过程,包括解析mapper XML文件时二级缓存的初始化、缓存类型的配置及缓存管理算法的设置。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








