1.高级应用
1.安全性(给redis.conf增加requirepass密码)
vi redis.conf
requirepass mima
pkill redis-server
redis-server redis.conf
两张启动方式
a1 redis-cli -a mima
a2 1 redis-cli
a2 2 auth mima
2.主从复制(master与slave数据库同步)
1.slave与master 建立连接,slave发送同步命令
2.master会启动一个进程将数据库快照保存到文件,同时master也会执行其他的存储命令并缓存
3.完成保存后,将文件发送到slave
4.slave将文件保存到磁盘
设置主从:
从机的redis.conf需要配置主机的ip、端口及密码
1.slaveof 192.168.88.89 6379
2.masterauth mima
查看主从关系:info
role:master
slave0:192.168.88.90,6379,online
默认情况下redis数据库充当slave角色时是只读的不能进行写操作。slave-read-only yes
3.哨兵机制(略)
redis哨兵监控,主从切换
具体见文档
4.事务处理multi
multi 打开事物
exec 开始按顺序执行事物
discard 取消事物,清空事物队列
例1:
get age
100
multi
set age 10
set age 20
exec
get age
20
例2:
get age
100
multi
set age 10
set age 20
discard
get age
100
与mysql的事物不同,redis的事物若有一条指令发生错误,实物不会回滚(redis需要改进的地方)
乐观锁:watch 若使用watch监控一个Key,这个元素从调用watch后发生过变化,整个事物会失败。断开连接或使用exec、discard、unwatch都会清除监控。
例:
session1:
get age
10
watch age
multi
session2:
set age 30
get age
30
session1:
set age 20
exec
nil(执行失败)
get age
30
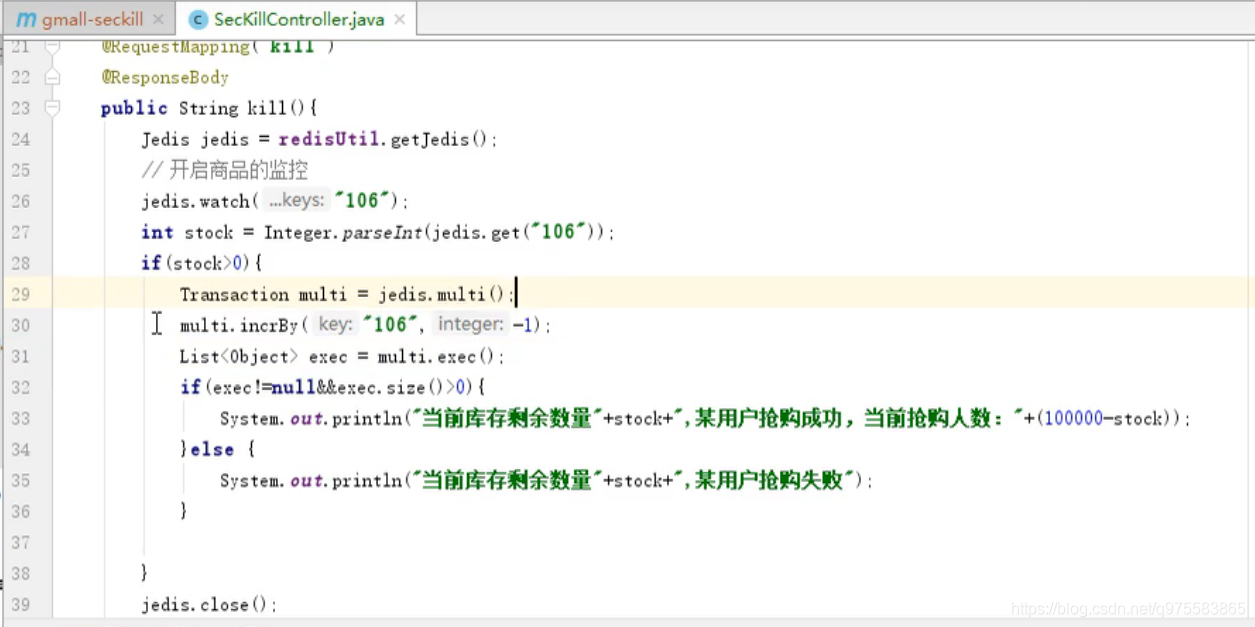
商品秒杀1:基于multi和 watch实现的 (并发时,只有一个人能抢到,随机拼运气)

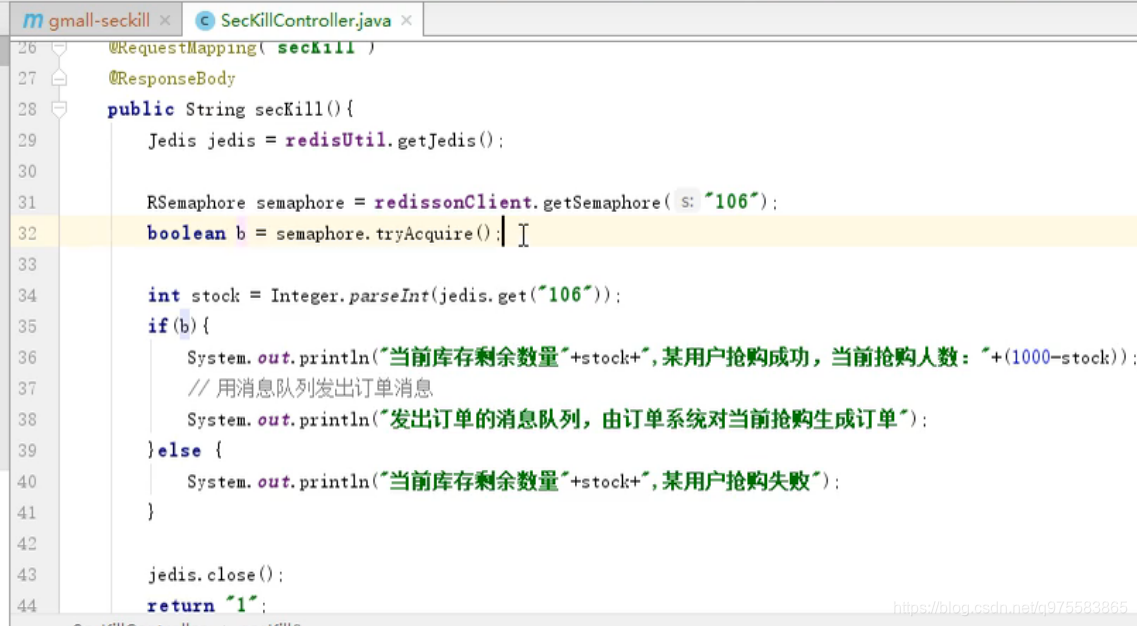
商品秒杀2:基于redission (先到先得)
秒杀限流
1.漏桶算法 以流量为界限进行计算
long timeStamp = getNowTime();
int capacity = 10000;// 桶的容量,即最大承载值
int rate = 1;//水漏出的速度,即服务器的处理请求的能力
int water = 100;//当前水量,即当前的即时请求压力
//当前请求线程进入漏桶方法,true则不被拒绝,false则说明当前服务器负载水量不足,则被拒绝
public static bool control() {
long now = getNowTime();//当前请求时间
//先执行漏水代码
//rate是固定的代表服务器的处理能力,所以可以认为“时间间隔*rate”即为漏出的水量
water = Math.max(0, water - (now - timeStamp) * rate);//请求时间-上次请求时间=时间间隔
timeStamp = now;//更新时间,为下次请求计算间隔做准备
if (water < capacity) { // 执行漏水代码后,发现漏桶未满,则可以继续加水,即没有到服务器可以承担的上线
water ++;
return true;
} else {
return false;//水满,拒绝加水,到服务器可以承担的上线,拒绝请求
}
}
2.令牌桶算法 系统会以一个恒定的速度往桶里放入令牌,而如果请求需要被处理,则需要先从桶里获取一个令牌,当桶里没有令牌可取时,则拒绝服务
long timeStamp=getNowTime();
int capacity; // 桶的容量
int rate ;//令牌放入速度
int tokens;//当前水量
bool control() {
//先执行添加令牌的操作
long now = getNowTime();
tokens = max(capacity, tokens+ (now - timeStamp)*rate);
timeStamp = now;
if(tokens<1){
return false; //令牌已用完,拒绝访问
}else{
tokens--;
retun true; //还有令牌,领取令牌
}
}
5.持久化机制
redis需要经常将内存里的数据同步到磁盘实现持久化。
1.快照(默认方式)
快照是将内存中的数据写入到二进制文件,默认文件名dump.rdb。可redis.conf配置发起快照的条件:
save 900 1 (900秒内超过1个key被修改发起)
save 300 10 (300秒内超过10个key被修改发起)
900/300 秒内只会发起一次快照,这样的持久化可能导致数据丢失,所以有aop的方式持久化。
2.aof
aof有更好的持久性,redis会将每一个收到的写命令通过write追加到文件中,重启时,会重新执行文件中的写命令在内存中重建整个数据库
由于os会在内核中缓存write做的修改,所以可能不是立即写入到磁盘,可能导致数据丢失。所以需要redis.conf配置强制os写入磁盘的时机:
appendonly yes
appendfsync always //收到的写命令立即写入磁盘,性能差,持久化最好
appendfsnc everysec //每秒写入磁盘一次,性能与持久化折中
appendfsyc no //完全依赖os,性能最好,持久化差
6.发布与订阅信息
订阅者可通过subscribe订阅自己感兴趣的消息类型,redis将消息类型称为通道。发布者可通过publish发送特定类型的消息时,订阅该消息类型的全部client会收到此信息
client1 subscribe tv1
client2 subscribe tv1 tv2
client3或主机 publish tv2 hello
client2
1) message
2)tv2
3)hello
7.虚拟内存
把不经常访问的数据交换到磁盘上,节约内存开销。
redis.conf配置
vm-enabled yes 开启vm功能
vm-swap-file /tmp/redis.swap value保存的路径
vm-max-memory 1000000 redis使用的最大内存上限
vm-page-size 32 每个页面32字节
vm-pages 134217728 最多使用多少个页面
vm-max-threads 用于value对象换入工作线程的数量
启动redis时会提示如果确认要使用vm功能需要在redis.conf里加入 really-user-vm yes
2.其他功能
1.批量插入pipeline
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
@ActiveProfiles("pipeline") // 设置profile
public class PipelineTests {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void test1() throws InterruptedException {
// 普通模式和pipeline模式
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("queue_1", i);
}
System.out.println("操作完毕:" + redisTemplate.opsForList().size("queue_1"));
System.out.println("普通模式一万次操作耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
redisTemplate.executePipelined(new RedisCallback<String>() {
@Override
public String doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
connection.lPush("queue_2".getBytes(), String.valueOf(i).getBytes());
}
return null;
}
});
System.out.println("操作完毕:" + redisTemplate.opsForList().size("queue_2"));
System.out.println("pipeline一万次操作耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
}
}
2.根据经纬度计算距离 (附近的人等)
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.geo.GeoResult;
import org.springframework.data.geo.GeoResults;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisGeoCommands;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
@ActiveProfiles("geo") // 设置profile
public class GeoTests {
@Autowired
GeoExampleService geoExampleService;
@Test
public void test1() throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟三个人位置上报
geoExampleService.add(new Point(116.405285, 39.904989), "allen");
geoExampleService.add(new Point(116.405265, 39.904969), "mike");
geoExampleService.add(new Point(116.405315, 39.904999), "tony");
// tony查找附近的人
GeoResults<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation> geoResults = geoExampleService.near(new Point(116.405315, 39.904999));
for (GeoResult<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation> geoResult : geoResults) {
RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation content = geoResult.getContent();
System.out.println(content.getName() + " :" + geoResult.getDistance().getValue());
}
}
}import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.data.geo.*;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisGeoCommands;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@Profile("geo")
public class GeoExampleService {
// 参数可以是任何对象,默认由JDK序列化
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 上传位置
*/
public void add(Point point, String userId) {
redisTemplate.opsForGeo().add("user_geo", new RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<>(userId, point));
}
/**
* 附近的人
*
* @param point 用户自己的位置
*/
public GeoResults<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation> near(Point point) {
// 半径 100米
Distance distance = new Distance(100, RedisGeoCommands.DistanceUnit.METERS);
Circle circle = new Circle(point, distance);
// 附近5个人
RedisGeoCommands.GeoRadiusCommandArgs geoRadiusCommandArgs = RedisGeoCommands.GeoRadiusCommandArgs.newGeoRadiusArgs().includeDistance().limit(5);
GeoResults<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation> user_geo = redisTemplate.opsForGeo().radius("user_geo", circle, geoRadiusCommandArgs);
return user_geo;
}
}3.发布订阅
4.流(类似mq)





















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








