本文系《pytest源码剖析》系列内容
正在连载,欢迎关注

插件路径:_pytest.unittest
实现的 hook
| hook | tryfirst | trylast | optionalhook | hookwrapper | wrapper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pytest_pycollect_makeitem | False | False | False | False | False |
| pytest_runtest_makereport | False | False | False | True | False |
| pytest_runtest_protocol | False | True | False | False | False |
调用的 hook
-
无
插件功能
-
搜集
unittest.TestCase的子类,作为测试用例 -
将
setUpClass/ tearDownClass方法转为类级 fixture -
将
setup_method / teardown_method转为方法级 fixture -
创建兼容 unittest 测试报告对象,
_pytest.unittest.TestCaseFunction -
将
unittest.skip的结果改为pytest.skip
代码片段
def pytest_pycollect_makeitem(
collector: Union[Module, Class], name: str, obj: object
) -> Optional["UnitTestCase"]:
# Has unittest been imported and is obj a subclass of its TestCase?
try:
ut = sys.modules["unittest"]
# Type ignored because `ut` is an opaque module.
if not issubclass(obj, ut.TestCase): # type: ignore
return None
except Exception:
return None
# Yes, so let's collect it.
item: UnitTestCase = UnitTestCase.from_parent(collector, name=name, obj=obj)
return item
class UnitTestCase(Class):
# Marker for fixturemanger.getfixtureinfo()
# to declare that our children do not support funcargs.
nofuncargs = True
def collect(self) -> Iterable[Union[Item, Collector]]:
from unittest import TestLoader
cls = self.obj
if not getattr(cls, "__test__", True):
return
skipped = _is_skipped(cls)
if not skipped:
self._inject_setup_teardown_fixtures(cls)
self._inject_setup_class_fixture()
self.session._fixturemanager.parsefactories(self, unittest=True)
loader = TestLoader()
foundsomething = False
for name in loader.getTestCaseNames(self.obj):
x = getattr(self.obj, name)
if not getattr(x, "__test__", True):
continue
funcobj = getimfunc(x)
yield TestCaseFunction.from_parent(self, name=name, callobj=funcobj)
class TestCaseFunction(Function):
def setup(self) -> None:
...
self._testcase = self.parent.obj(self.name) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
self._obj = getattr(self._testcase, self.name)
def runtest(self) -> None:
...
setattr(self._testcase, self.name, self.obj)
try:
self._testcase(result=self) # type: ignore[arg-type]
finally:
delattr(self._testcase, self.name)
def addSkip(self, testcase: "unittest.TestCase", reason: str) -> None:
...
def addSuccess(self, testcase: "unittest.TestCase") -> None:
...
-
被 unittest 插件处理的前提条件
-
是 python 文件
-
有 unittest 模块
-
是 TestCase 子类
-
-
收集用例是使用了 unittest 自己的用例加载器
-
遍历用例名称
-
根据名称得到方法对象
funcobj -
后续会读取
funcobj的属性,但不会直接调用
-
-
用例执行是使用
unittest自己的运行协议-
检查是否有跳过标记
-
实例化
TestCase类,并指定测试方法 -
调用
TestCase类的实例对象,执行用例 -
执行结果由 pytest 收集,所以实现了 result 方法
-
简评
这个插件实现了 hook,却没有调用什么 hook,说明此插件纯纯是为了 pytest 增加额外的功能
...
插件把 unittest 的 setUpClass/ tearDownClass 方法转为类级 fixture,
却没有将 setUp / tearDown 方法转为方法级别 fixture
...
在从 unittest.TestCase 子类中收集用例方法时,没有自己写代码实现,
而是复用 unittest 的 TestLoader,这样可以尽可能的兼容 unittest 原生的规则
...
同样的,在执行用例时,也是重用 unittest 的 TestCase,这么做有几个好处:
-
兼容 unittest 原生机制,如 doCleanups
-
兼容类中实例属性的传递
-
自动调用 setUp 和 tearDown(所以就不需要转成 fixture 了)
...
如下图所示 unittest 有五个核心组件
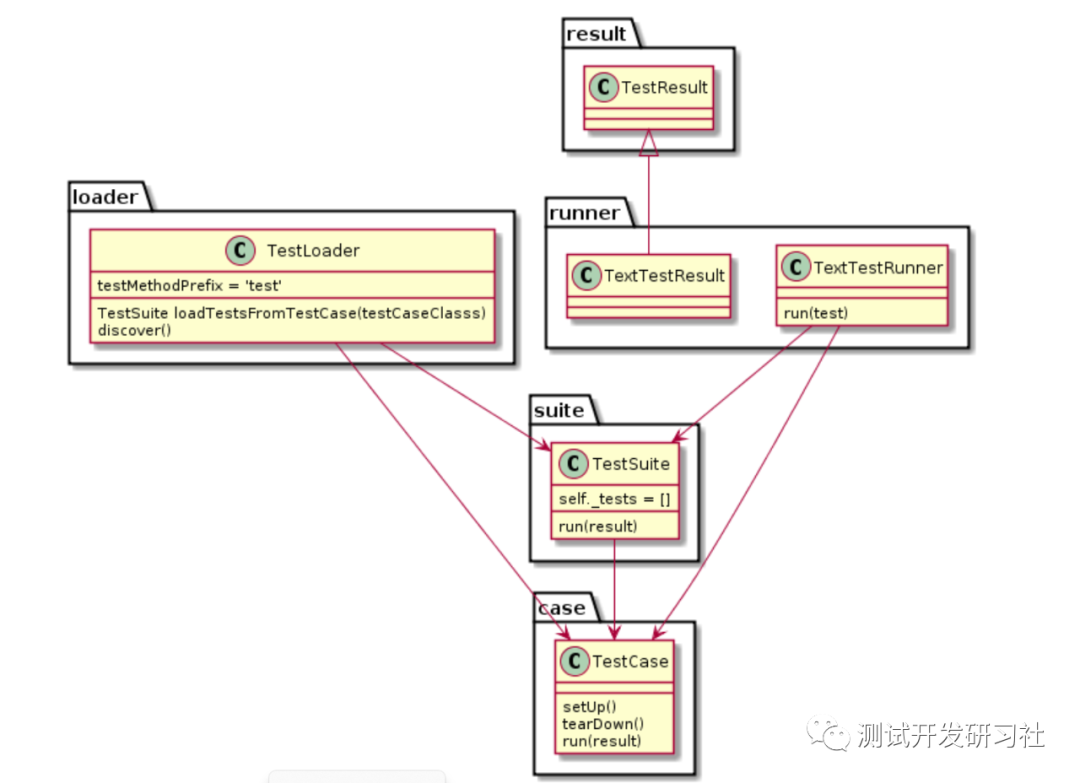
pytest 复用了其中的 loader 和 case,用来收集和执行类中的用例。
除此之外的功能,均由 pytest 自行实现





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








