上一章我们讲了多头注意力机制的原理,并且使用了“我请李雷帮我订了去北京的机票“这句话进行了模拟推演。本章配上具体的python代码实现,加深理解。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ====================== 1. 准备数据 ======================
# 设置中文字体(根据系统安装的字体选择,以下是常见兼容字体)
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"] # 支持中文显示
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示异常的问题(可选)
tokens = ["我", "请", "李雷", "帮", "我", "订了", "去", "北京", "的", "机票"]
N = len(tokens) # token 数量
embedding_dim = 8
num_heads = 4
head_dim = embedding_dim // num_heads
# 模拟 embedding 层输出 (N, D) 10 8
embeddings = torch.randn(N, embedding_dim) * 0.5
# ====================== 2. 定义线性层参数 ======================
# 8*8
W_q = torch.randn(embedding_dim, embedding_dim) * 0.3
W_k = torch.randn(embedding_dim, embedding_dim) * 0.3
W_v = torch.randn(embedding_dim, embedding_dim) * 0.3
W_o = torch.randn(embedding_dim, embedding_dim) * 0.3
# ====================== 3. 计算 Q / K / V ======================
Q = embeddings @ W_q # (N, D)
# print(Q)
K = embeddings @ W_k
V = embeddings @ W_v
# print(Q.size(), K.size(), V.size())
# print(Q)
# 拆分多头
def split_heads(x, num_heads):
"""把 (N, D) → (num_heads, N, D/num_heads)"""
N, D = x.shape
# # 第二步:交换维度 0 和 1,得到 (num_heads, N, D//num_heads)
return x.view(N, num_heads, D // num_heads).transpose(0, 1)
# 10*8 10个token 每个被编码为8维向量 多头注意力 4头 每个8维向量被拆成4个2维向量
Q_heads = split_heads(Q, num_heads)
# torch.Size([4, 10, 2])
# print(Q_heads.shape)
K_heads = split_heads(K, num_heads)
V_heads = split_heads(V, num_heads)
# ====================== 4. 计算每个 Head 的注意力 ======================
attention_outputs = []
attention_weights = []
scale = head_dim ** 0.5
# exit()
for h in range(num_heads):
q, k, v = Q_heads[h], K_heads[h], V_heads[h] # (N, head_dim)
# QK^T → (N, N) 自注意力(Self-Attention)矩阵。
scores = (q @ k.T) / scale
# print(scores.shape)
# print(scores)
# Softmax
weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
attention_weights.append(weights)
# 加权求和
out = weights @ v # (N, head_dim)
attention_outputs.append(out)
print(f"\n--- Head {h+1} ---")
print("注意力权重 (softmax 后):\n", torch.round(weights, decimals=3))
# ====================== 5. 拼接多头输出 ======================
concat = torch.cat(attention_outputs, dim=-1) # (N, D)
final_output = concat @ W_o # (N, D)
print("\n=== 最终输出 ===\n", torch.round(final_output, decimals=3))
# exit()
# ====================== 6. 可视化注意力 ======================
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, num_heads, figsize=(4 * num_heads, 3))
for h in range(num_heads):
ax = axes[h]
im = ax.imshow(attention_weights[h].detach().numpy(), cmap='Blues', aspect='auto')
ax.set_title(f"Head {h+1}")
ax.set_xticks(range(N))
ax.set_yticks(range(N))
ax.set_xticklabels(tokens, rotation=45)
ax.set_yticklabels(tokens)
plt.colorbar(im, ax=ax, fraction=0.046, pad=0.04)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# ====================== 7. 打印每个 token 的 Top-3 注意力 ======================
print("\n=== 每个 token 在各 head 的 Top-3 注意力对象 ===")
for h in range(num_heads):
weights = attention_weights[h]
print(f"\n-- Head {h+1} --")
for i in range(N):
top3 = torch.topk(weights[i], 3)
idxs = top3.indices.tolist()
vals = top3.values.tolist()
print(f"{tokens[i]} → {[f'{tokens[idx]}({val:.3f})' for idx, val in zip(idxs, vals)]}")
以上代码会输出:
-
每个头(head)的注意力权重矩阵(数值 + 可视化 heatmap)
-
每个 token 的前 3 个最关注对象
-
每个 token 的最终向量输出(融合了上下文语义)
=== 每个 token 在各 head 的 Top-3 注意力对象 ===
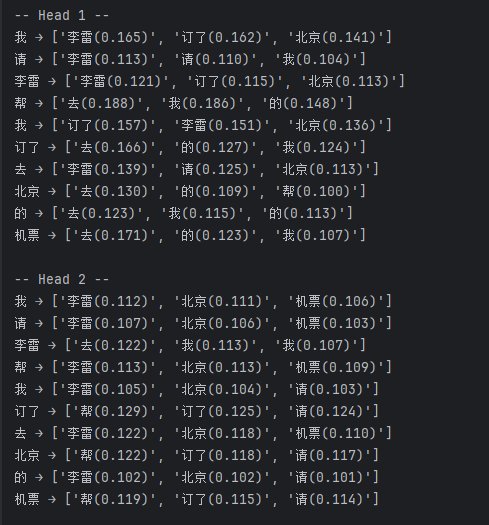
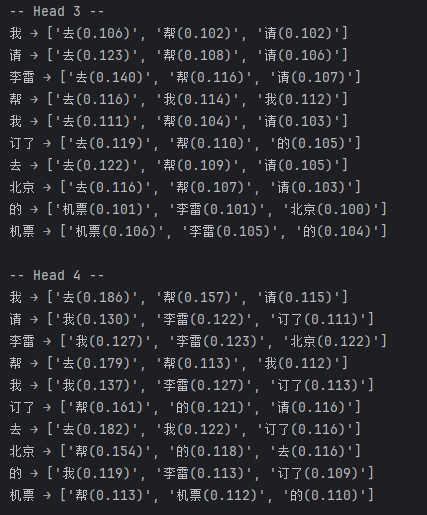
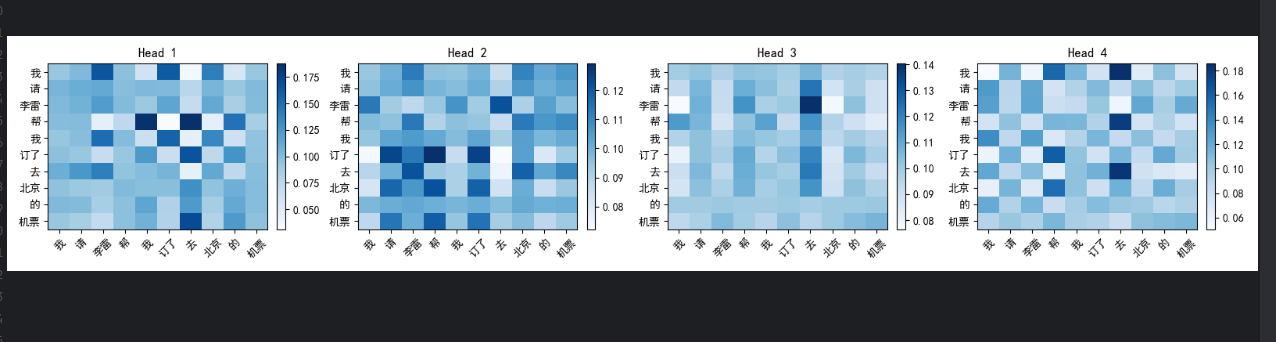
从图中我们可以非常直观的看出来每一个token和其他token之间的关注度权重,能够明白模型是如何理解语义信息的,也可以从结果中看出来,头的侧重点不一样,token之间关注的权重会有一些细微的变化,但句子、段落表达出的总体的意思都是大差不差的。都是--我请李雷帮我订了去北京的机票
希望结合代码能够帮助你更好的理解多头注意力机制。




















 5453
5453

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








