传统 RAG 存在以下限制… 👇
1)检索一次,生成一次。
↳这意味着如果检索到的上下文不够或不正确,LLM 就无法动态搜索更多信息。
2)无法通过复杂的查询进行推理。
↳如果查询需要多个检索步骤或 CoT(思路链),传统的 RAG 就不够了。
3)适应性有限
↳系统无法根据当前问题修改其策略。例如,是否进行向量搜索、网页搜索或调用 API。
Agentic RAG 解决了传统 RAG 的以上问题
核心思想是在RAG的每个阶段引入代理行为。
代理可以积极思考任务——规划、调整和迭代以找到最佳解决方案,而不仅仅是遵循一组指令,而 LLM 可以实现这一点。
下图说明了Agentic RAG 的工作流程。继续阅读时请参考它…
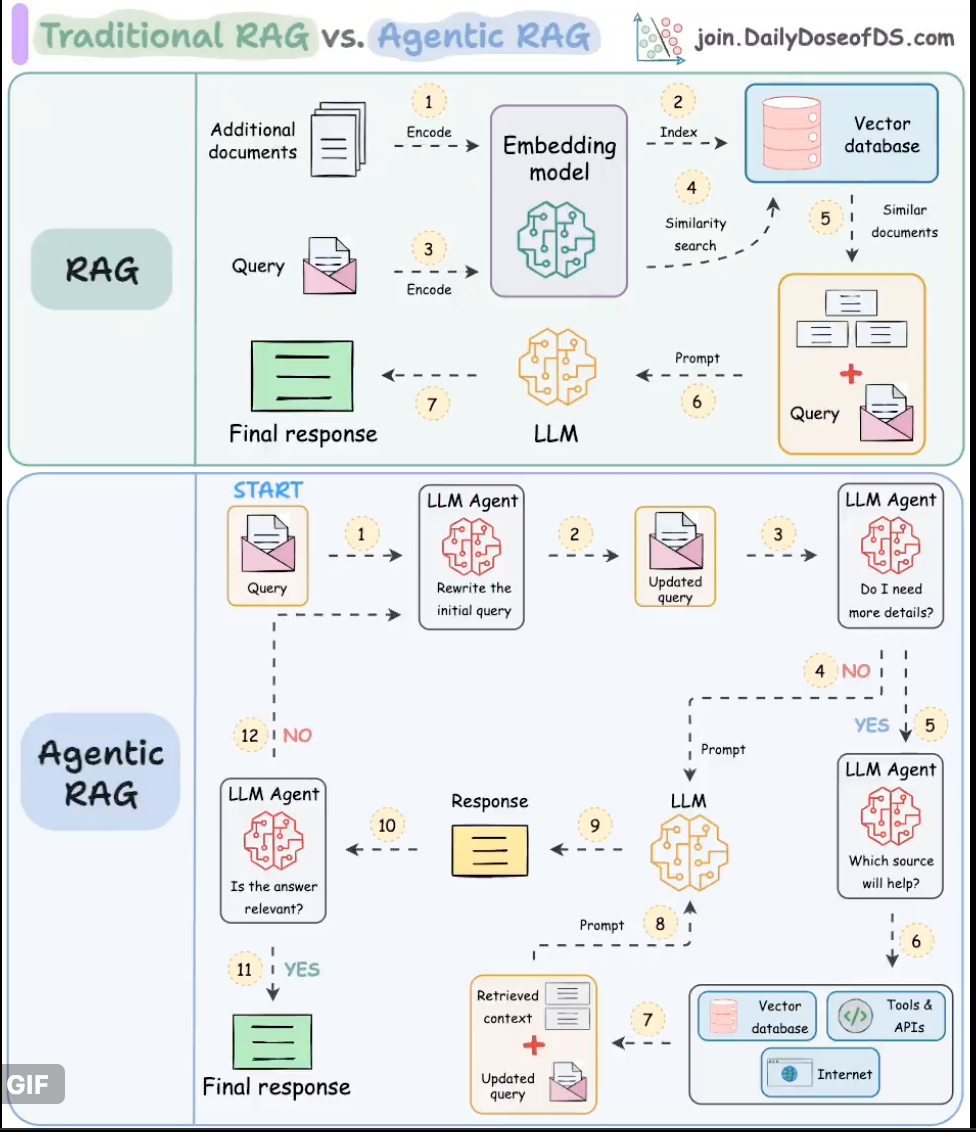
步骤1-2)用户输入查询,代理对其进行细化(纠正拼写、简化嵌入等)
步骤3)另一个代理决定是否需要更多详细信息。
↳步骤 4)如果不是,则将细化查询发送到 LLM。
↳步骤5-8)如果是,代理选择相关来源(矢量数据库、工具/API、互联网),检索上下文,并将其发送给 LLM。
步骤9)生成响应。
步骤 10)最后一个代理检查答案是否相关。
↳步骤 11)如果是,则返回响应。
↳步骤 12)如果没有,则从步骤 1 重新开始。此过程重复,直到系统提供可接受的答案或承认它无法响应。
这使得 RAG 更加动态和稳健。
然而,值得注意的是,构建 RAG 系统通常取决于设计偏好和选择。
上图只是Agentic RAG 系统可能拥有的众多蓝图之一。
您可以对其进行调整以适合您的特定用例。
Agentic RAG 架构图
传统 RAG:
用户输入触发一次数据库调用来检索其他信息。
Agentic RAG:
代理可以推理从哪个来源检索给定查询的信息。
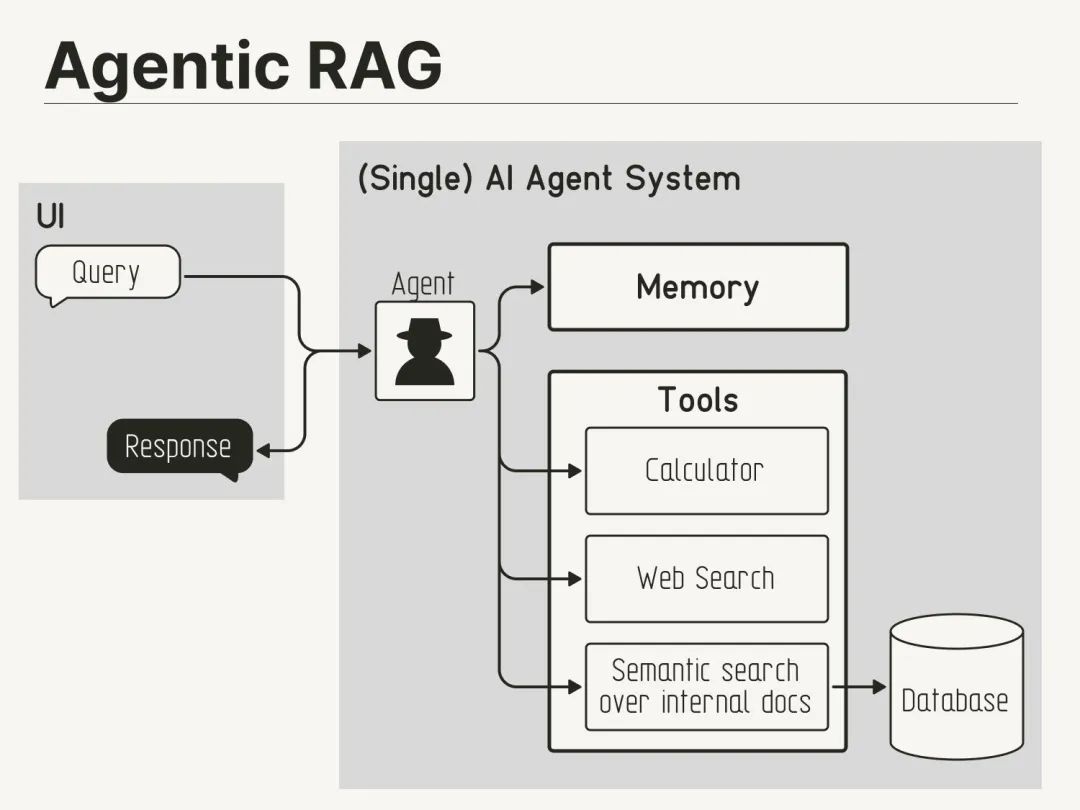
实现框架
以下介绍几个主流的Agentic RAG实现框架:
LangChain
最受欢迎的Agent框架之一
提供了完整的RAG和Agent工具链
主要组件:
Agents: 支持多种Agent类型,如ReAct、Plan-and-Execute等
Tools: 丰富的工具集成,包括搜索、计算、API调用等
Chains: 可组合的处理流程
Memory: 支持对话历史和状态管理
AutoGPT
专注于自主Agent系统
特点:
多Agent协作
长期记忆管理
自主规划能力
工具使用能力
Microsoft Semantic Kernel
微软开源的AI开发框架
核心特性:
Planner: 智能任务规划
Skills: 可扩展的能力模块
Memory: 语义记忆系统
Connectors: 丰富的集成能力
Haystack
专注于文档处理和问答的框架
主要功能:
Pipeline: 灵活的处理流程
Agent: 智能检索和处理
Reader: 深度文档理解
Generator: 答案生成
CAMEL (Communicative Agents for Mind Exploration and Learning)
注重Agent间的交互和协作
特色:
Role-Playing: 基于角色的交互
Task Decomposition: 任务分解
Multi-Agent Communication: 多Agent协作
选择建议:
如果需要快速开发和原型验证,建议使用LangChain
如果需要更强的自主性,可以考虑AutoGPT
如果在企业环境中使用,Microsoft Semantic Kernel是个不错的选择
如果主要处理文档,Haystack比较专业
如果研究Agent协作,CAMEL值得关注
每个框架都有其特点和适用场景,选择时需要考虑:
项目需求和复杂度、开发团队的技术栈、系统的可扩展性要求、部署和维护成本、社区活跃度和支持。
基于LangChain的 Agentic RAG 实现,供参考👇
from langchain.agents import Tool, AgentExecutor, LLMSingleActionAgent
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import StringPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import AgentAction, AgentFinish
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
import re
from typing import List, Union, Tuple
# Define custom prompt template
class CustomPromptTemplate(StringPromptTemplate):
template = """Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
{tools}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
Question: {input}
{agent_scratchpad}"""
def format(self, **kwargs) -> str:
# Get the intermediate steps (AgentAction, Observation tuples)
intermediate_steps = kwargs.pop("intermediate_steps")
thoughts = ""
for action, observation in intermediate_steps:
thoughts += action.log
thoughts += f"\nObservation: {observation}\nThought: "
kwargs["agent_scratchpad"] = thoughts
tools = kwargs["tools"]
kwargs["tool_names"] = ", ".join([tool.name for tool in tools])
return self.template.format(**kwargs)
# Define tools
def search_docs(query: str) -> str:
return f"Searched documents for: {query}"
def analyze_text(text: str) -> str:
return f"Analyzed text: {text}"
tools = [
Tool(
name="SearchDocs",
func=search_docs,
description="useful for searching documents"
),
Tool(
name="AnalyzeText",
func=analyze_text,
description="useful for analyzing text content"
)
]
# Define output parser
class CustomOutputParser:
def parse(self, llm_output: str) -> Union[AgentAction, AgentFinish]:
if "Final Answer:" in llm_output:
return AgentFinish(
return_values={"output": llm_output.split("Final Answer:")[-1].strip()},
log=llm_output,
)
regex = r"Action: (.*?)[\n]*Action Input: (.*)"
match = re.search(regex, llm_output, re.DOTALL)
if not match:
raise ValueError(f"Could not parse LLM output: `{llm_output}`")
action = match.group(1).strip()
action_input = match.group(2).strip()
return AgentAction(tool=action, tool_input=action_input, log=llm_output)
# Initialize the agent
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
prompt = CustomPromptTemplate(
template=CustomPromptTemplate.template,
tools=tools,
input_variables=["input", "intermediate_steps"]
)
output_parser = CustomOutputParser()
llm_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
agent = LLMSingleActionAgent(
llm_chain=llm_chain,
output_parser=output_parser,
stop=["\nObservation:"],
allowed_tools=[tool.name for tool in tools]
)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor.from_agent_and_tools(
agent=agent,
tools=tools,
verbose=True,
memory=ConversationBufferMemory()
)
# Example usage
response = agent_executor.run("Search for documents about AI and analyze them.")
print(response)
如何学习大模型
现在社会上大模型越来越普及了,已经有很多人都想往这里面扎,但是却找不到适合的方法去学习。
作为一名资深码农,初入大模型时也吃了很多亏,踩了无数坑。现在我想把我的经验和知识分享给你们,帮助你们学习AI大模型,能够解决你们学习中的困难。
下面这些都是我当初辛苦整理和花钱购买的资料,现在我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括市面上AI大模型各大白皮书、AGI大模型系统学习路线、AI大模型视频教程、实战学习,等录播视频免费分享出来,需要的小伙伴可以扫取。

一、AGI大模型系统学习路线
很多人学习大模型的时候没有方向,东学一点西学一点,像只无头苍蝇乱撞,我下面分享的这个学习路线希望能够帮助到你们学习AI大模型。
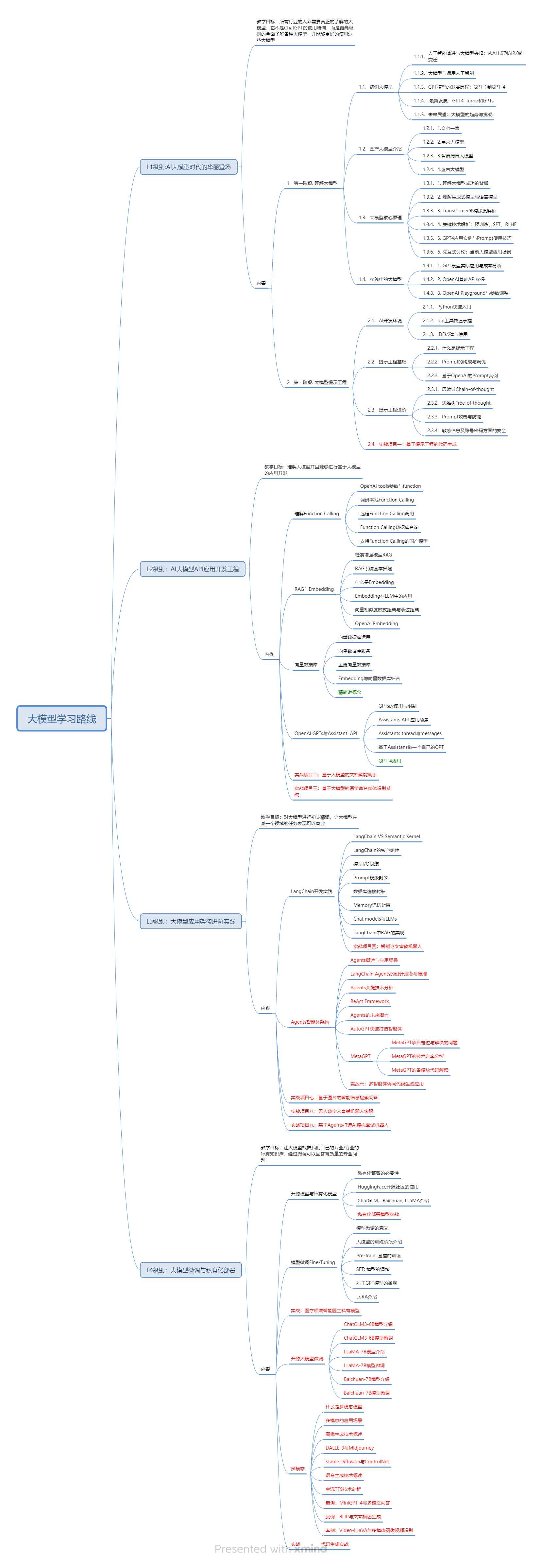
二、AI大模型视频教程
三、AI大模型各大学习书籍
四、AI大模型各大场景实战案例

五、结束语
学习AI大模型是当前科技发展的趋势,它不仅能够为我们提供更多的机会和挑战,还能够让我们更好地理解和应用人工智能技术。通过学习AI大模型,我们可以深入了解深度学习、神经网络等核心概念,并将其应用于自然语言处理、计算机视觉、语音识别等领域。同时,掌握AI大模型还能够为我们的职业发展增添竞争力,成为未来技术领域的领导者。
再者,学习AI大模型也能为我们自己创造更多的价值,提供更多的岗位以及副业创收,让自己的生活更上一层楼。
因此,学习AI大模型是一项有前景且值得投入的时间和精力的重要选择。




















 380
380

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








