写在前面
这是NLP保姆级教程的第二篇----基于RNN的文本分类实现(Text RNN)
参考的的论文是来自2016年复旦大学IJCAI上的发表的关于循环神经网络在多任务文本分类上的应用:Recurrent Neural Network for Text Classification with Multi-Task Learning[1]
论文概览
在先前的许多工作中,模型的学习都是基于单任务,对于复杂的问题,也可以分解为简单且相互独立的子问题来单独解决,然后再合并结果,得到最初复杂问题的结果。这样做看似合理,其实是不正确的,因为现实世界中很多问题不能分解为一个一个独立的子问题,即使可以分解,各个子问题之间也是相互关联的,通过一些共享因素或「共享表示(share representation)」 联系在一起。把现实问题当做一个个独立的单任务处理,往往会忽略了问题之间所富含的丰富的关联信息。
上面的问题引出了本文的重点——「多任务学习(Multi-task learning)」,把多个相关(related)的任务(task)放在一起学习。多个任务之间共享一些因素,它们可以在学习过程中,共享它们所学到的信息,这是单任务学习没有具备的。相关联的多任务学习比单任务学习能去的更好的泛化(generalization)效果。本文基于 RNN 循环神经网络,提出三种不同的信息共享机制,整体网络是基于所有的任务共同学习得到。
下图展示的是单任务学习和多任务学习的流程图,可以对比一下区别。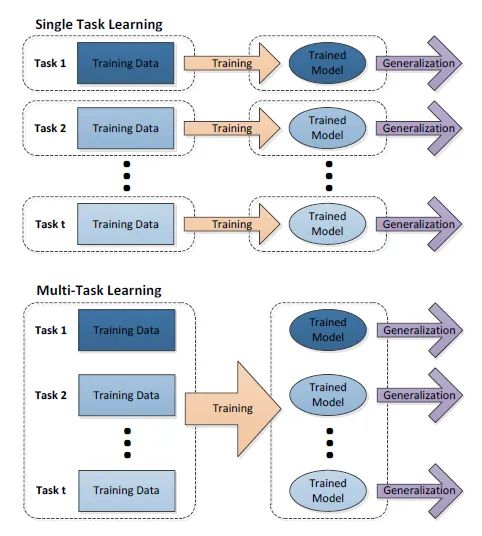
下面具体介绍一下文章中的三个模型。
Model I: Uniform-Layer Architecture
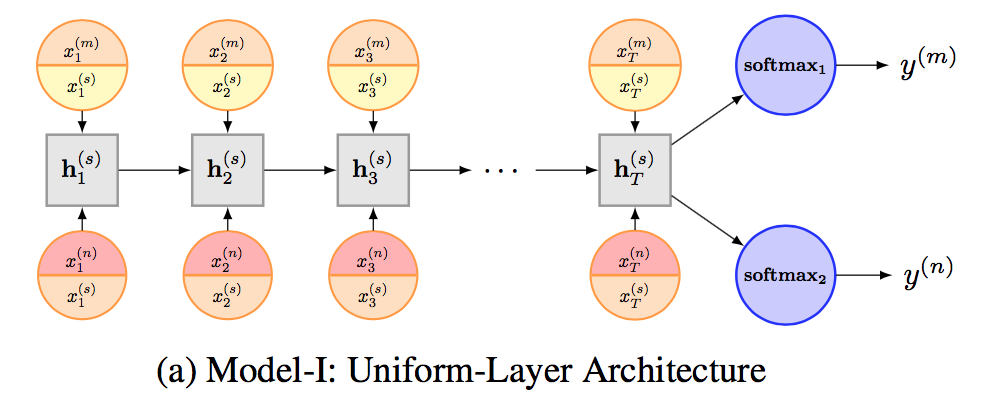 在他们提出的第一个模型中,不同的任务共享一个LSTM网络层和一个embedding layer,此外每个任务还有其自己的embedding layer。所以对于上图中的任务m,输入x包括了两个部分:
在他们提出的第一个模型中,不同的任务共享一个LSTM网络层和一个embedding layer,此外每个任务还有其自己的embedding layer。所以对于上图中的任务m,输入x包括了两个部分:

其中等号右侧第一项和第二项分别表示该任务「特有」的word embedding和该模型中「共享」的word embedding,两者做一个concatenation。
LSTM网络层是所有任务所共享的,对于任务m的最后sequence representation为LSTM的输出:

Model II: Coupled-Layer Architecture
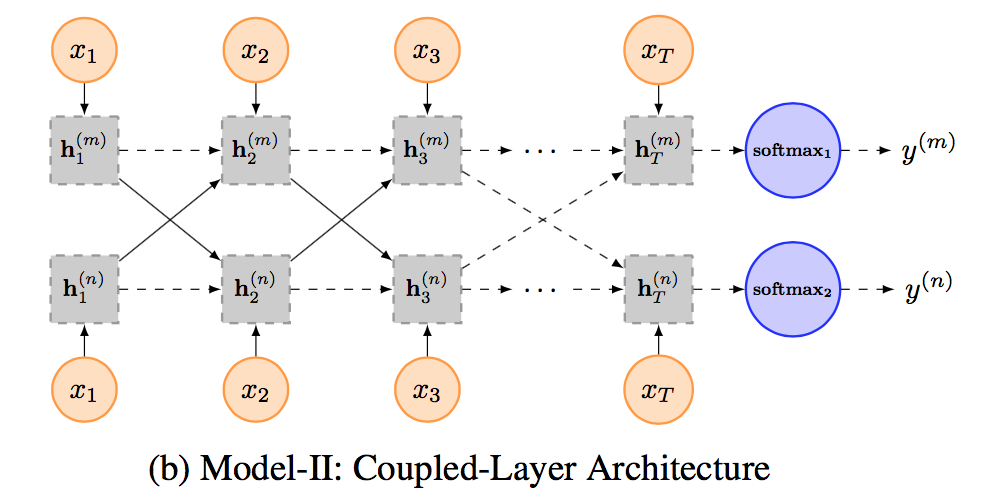 在第二个模型中,为每个任务都指定了「特定」的LSTM layer,但是不同任务间的LSTM layer可以共享信息。
在第二个模型中,为每个任务都指定了「特定」的LSTM layer,但是不同任务间的LSTM layer可以共享信息。
为了更好地控制在不同LSTM layer之间的信息流动,作者提出了一个global gating unit,使得模型具有决定信息流动程度的能力。
为此,他们改写了LSTM中的表达式:

Model III: Shared-Layer Architecture
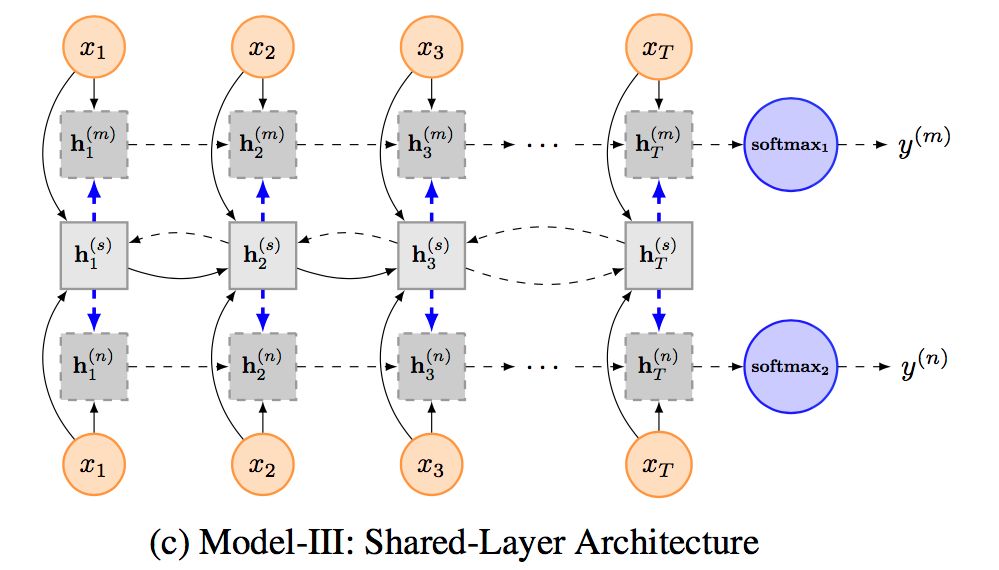 与模型二相似,作者也为每个单独的任务指派了特定的LSTM层,但是对于整体的模型使用了双向的LSTM,这样可以使得信息共享更为准确。
与模型二相似,作者也为每个单独的任务指派了特定的LSTM层,但是对于整体的模型使用了双向的LSTM,这样可以使得信息共享更为准确。
模型表现
论文作者在4个数据集上对上述模型做了评价,并和其他state-of-the-art的网络模型进行了对比,均显示最好的效果。
代码实现
RNN的代码框架和上一篇介绍的CNN类似,首先定义一个RNN类来实现论文中的模型
class RNN(BaseModel):
"""
A RNN class for sentence classification
With an embedding layer + Bi-LSTM layer + FC layer + softmax
"""
def __init__(self, sequence_length, num_classes, vocab_size,
embed_size, learning_rate, decay_steps, decay_rate,
hidden_size, is_training, l2_lambda, grad_clip,
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1)):
这里的模型包括了一层embedding,一层双向LSTM,一层全连接层最后接上一个softmax分类函数。
然后依次定义模型,训练,损失等函数在后续调用。
def inference(self):
"""
1. embedding layer
2. Bi-LSTM layer
3. concat Bi-LSTM output
4. FC(full connected) layer
5. softmax layer
"""
# embedding layer
with tf.name_scope('embedding'):
self.embedded_words = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.Embedding, self.input_x)
# Bi-LSTM layer
with tf.name_scope('Bi-LSTM'):
lstm_fw_cell = rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.hidden_size)
lstm_bw_cell = rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.hidden_size)
if self.dropout_keep_prob is not None:
lstm_fw_cell = rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_fw_cell, output_keep_prob=self.dropout_keep_prob)
lstm_bw_cell = rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_bw_cell, output_keep_prob=self.dropout_keep_prob)
outputs, output_states = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(lstm_fw_cell, lstm_bw_cell,
self.embedded_words,
dtype=tf.float32)
output = tf.concat(outputs, axis=2)
output_last = tf.reduce_mean(output, axis=1)
# FC layer
with tf.name_scope('output'):
self.score = tf.matmul(output_last, self.W_projection) + self.b_projection
return self.score
def loss(self):
# loss
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=self.input_y, logits=self.score)
data_loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses)
l2_loss = tf.add_n([tf.nn.l2_loss(cand_v) for cand_v in tf.trainable_variables()
if 'bias' not in cand_v.name]) * self.l2_lambda
data_loss += l2_loss
return data_loss
def train(self):
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(self.learning_rate, self.global_step,
self.decay_steps, self.decay_rate, staircase=True)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate)
grads_and_vars = optimizer.compute_gradients(self.loss_val)
grads_and_vars = [(tf.clip_by_norm(grad, self.grad_clip), val) for grad, val in grads_and_vars]
train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars, global_step=self.global_step)
return train_op
训练部分的数据集这里就直接采用CNN那篇文章相同的数据集(懒…),预处理的方式与函数等都是一样的,,,
def train(x_train, y_train, vocab_processor, x_dev, y_dev):
with tf.Graph().as_default():
session_conf = tf.ConfigProto(
# allows TensorFlow to fall back on a device with a certain operation implemented
allow_soft_placement= FLAGS.allow_soft_placement,
# allows TensorFlow log on which devices (CPU or GPU) it places operations
log_device_placement=FLAGS.log_device_placement
)
sess = tf.Session(config=session_conf)
with sess.as_default():
# initialize cnn
rnn = RNN(sequence_length=x_train.shape[1],
num_classes=y_train.shape[1],
vocab_size=len(vocab_processor.vocabulary_),
embed_size=FLAGS.embed_size,
l2_lambda=FLAGS.l2_reg_lambda,
is_training=True,
grad_clip=FLAGS.grad_clip,
learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate,
decay_steps=FLAGS.decay_steps,
decay_rate=FLAGS.decay_rate,
hidden_size=FLAGS.hidden_size
)
# output dir for models and summaries
timestamp = str(time.time())
out_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.curdir, 'run', timestamp))
if not os.path.exists(out_dir):
os.makedirs(out_dir)
print('Writing to {} \n'.format(out_dir))
# checkpoint dir. checkpointing – saving the parameters of your model to restore them later on.
checkpoint_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(out_dir, FLAGS.ckpt_dir))
checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, 'model')
if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=FLAGS.num_checkpoints)
# Write vocabulary
vocab_processor.save(os.path.join(out_dir, 'vocab'))
# Initialize all
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
def train_step(x_batch, y_batch):
"""
A single training step
:param x_batch:
:param y_batch:
:return:
"""
feed_dict = {
rnn.input_x: x_batch,
rnn.input_y: y_batch,
rnn.dropout_keep_prob: FLAGS.dropout_keep_prob
}
_, step, loss, accuracy = sess.run(
[rnn.train_op, rnn.global_step, rnn.loss_val, rnn.accuracy],
feed_dict=feed_dict
)
time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat()
print("{}: step {}, loss {:g}, acc {:g}".format(time_str, step, loss, accuracy))
def dev_step(x_batch, y_batch):
"""
Evaluate model on a dev set
Disable dropout
:param x_batch:
:param y_batch:
:param writer:
:return:
"""
feed_dict = {
rnn.input_x: x_batch,
rnn.input_y: y_batch,
rnn.dropout_keep_prob: 1.0
}
step, loss, accuracy = sess.run(
[rnn.global_step, rnn.loss_val, rnn.accuracy],
feed_dict=feed_dict
)
time_str = datetime.datetime.now().isoformat()
print("dev results:{}: step {}, loss {:g}, acc {:g}".format(time_str, step, loss, accuracy))
# generate batches
batches = data_process.batch_iter(list(zip(x_train, y_train)), FLAGS.batch_size, FLAGS.num_epochs)
# training loop
for batch in batches:
x_batch, y_batch = zip(*batch)
train_step(x_batch, y_batch)
current_step = tf.train.global_step(sess, rnn.global_step)
if current_step % FLAGS.validate_every == 0:
print('\n Evaluation:')
dev_step(x_dev, y_dev)
print('')
path = saver.save(sess, checkpoint_prefix, global_step=current_step)
print('Save model checkpoint to {} \n'.format(path))
def main(argv=None):
x_train, y_train, vocab_processor, x_dev, y_dev = prepocess()
train(x_train, y_train, vocab_processor, x_dev, y_dev)
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
如何学习AI大模型?
作为一名热心肠的互联网老兵,我决定把宝贵的AI知识分享给大家。 至于能学习到多少就看你的学习毅力和能力了 。我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

一、全套AGI大模型学习路线
AI大模型时代的学习之旅:从基础到前沿,掌握人工智能的核心技能!

二、640套AI大模型报告合集
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。

三、AI大模型经典PDF籍
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点。这些大型预训练模型,如GPT-3、BERT、XLNet等,以其强大的语言理解和生成能力,正在改变我们对人工智能的认识。 那以下这些PDF籍就是非常不错的学习资源。
四、AI大模型商业化落地方案

作为普通人,入局大模型时代需要持续学习和实践,不断提高自己的技能和认知水平,同时也需要有责任感和伦理意识,为人工智能的健康发展贡献力量。
 基于RNN的文本分类及AI大模型学习资料分享
基于RNN的文本分类及AI大模型学习资料分享




















 1677
1677

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








