智能股票分析预测系统是一个基于机器学习的股票分析与预测平台,集成了数据获取、特征工程、模型训练和可视化分析等功能。系统通过多种机器学习算法对股票历史数据进行分析,预测未来走势,并提供直观的可视化图表展示分析结果。
项目结构
- 📁 IntelligentStockAnalysisSystem/
- 📄 data_fetcher.py # 股票数据获取模块
- 📄 data_processor.py # 数据处理与特征工程
- 📄 feature_selector.py # 特征选择模块
- 📄 app.py # 程序入口
- 📄 model_trainer.py # 模型训练与评估
- 📄 visualizer.py # 可视化图表生成
- 📁 templates/ # HTML模板
- 📄 dashboard.html # 主仪表盘页面
- 📄 error.html # 错误页面
- 📁 static/ # 静态资源(CSS/JS/图片)
- 📄 README.md # 项目说明文档
功能特性
- 数据源支持:通过AKShare获取实时股票数据
- 高级特征工程:计算20+技术指标(MA、RSI、MACD、波动率等)
- 集成机器学习模型:随机森林、XGBoost、Lasso回归
- 时间序列验证:时间序列交叉验证
- 特征选择:基于相关性的特征筛选
- 可视化图表:生成8种专业分析图表
- 响应式Web界面:适配各种设备尺寸
快速开始
环境要求
- Python 3.8+
安装步骤
- 安装依赖
pip install flask akshare pandas numpy scikit-learn xgboost matplotlib seaborn
- 运行项目
python app.py
在实现项目核心功能时,可以按照项目的运行流程来逐步实现对应的模块功能,其主要流程如图所示:
![]()
一、项目构建
开发项目前,需要完成项目初始化的设置,主要是项目运行所需的一些依赖库的安装。诸如,Flask、AkShare、Pandas、Scikit-learnFlask等。进行依赖的安装时,可以通过pip命令进行统一的安装。
# 统一安装项目运行所需的依赖
pip install flask akshare pandas numpy scikit-learn xgboost matplotlib seaborn
1.数据采集
股票数据采集函数完整的实现代码如下所示:
def get_stock_data(stock_code="600519", start_date="20000101", end_date=None):
"""
获取股票历史数据
"""
if end_date is None:
# 默认结束日期为今天
end_date = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d")
try:
df = ak.stock_zh_a_hist(
symbol=stock_code,
period="daily",
start_date=start_date,
end_date=end_date,
adjust="qfq"
)
# 如果数据为空,尝试其他数据源(并对备选数据源中的数据进行处理,使其列名与结构与主数据保持一致)
if df.empty:
df = ak.stock_zh_a_daily(symbol=stock_code, adjust="qfq")
df = df.reset_index()
df = df.rename(columns={'date': '日期', 'open': '开盘', 'close': '收盘',
'high': '最高', 'low': '最低', 'volume': '成交量'})
df = df[['日期', '开盘', '收盘', '最高', '最低', '成交量']]
return df
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取数据失败: {e}")
# 尝试备选数据源
try:
df = ak.stock_zh_a_daily(symbol=stock_code, adjust="qfq")
df = df.reset_index()
df = df.rename(columns={'date': '日期', 'open': '开盘', 'close': '收盘',
'high': '最高', 'low': '最低', 'volume': '成交量'})
df = df[['日期', '开盘', '收盘', '最高', '最低', '成交量']]
return df
except:
# 返回空DataFrame
return pd.DataFrame()
调用get_stock_data()函数,测试是否能正常获取股票数据,测试代码如下所示:
if __name__ == "__main__":
code="600519"
start_date="20000101"
# 获取股票数据
stock_data = get_stock_data(stock_code=code, start_date=start_date)
print(stock_data)
运行效果如下所示:
日期 股票代码 开盘 收盘 ... 振幅 涨跌幅 涨跌额 换手率
0 2020-01-02 600519 920.72 922.72 ... 2.98 -5.43 -53.00 1.18
1 2020-01-03 600519 909.72 871.28 ... 4.35 -5.57 -51.44 1.04
2 2020-01-06 600519 863.58 870.71 ... 2.94 -0.07 -0.57 0.50
3 2020-01-07 600519 870.22 887.25 ... 2.60 1.90 16.54 0.38
4 2020-01-08 600519 877.77 880.86 ... 1.46 -0.72 -6.39 0.20
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
1329 2025-07-01 600519 1409.00 1405.10 ... 0.61 -0.31 -4.42 0.16
1330 2025-07-02 600519 1409.50 1409.60 ... 1.05 0.32 4.50 0.21
1331 2025-07-03 600519 1412.00 1415.60 ... 1.04 0.43 6.00 0.19
1332 2025-07-04 600519 1415.70 1422.22 ... 1.55 0.47 6.62 0.23
1333 2025-07-07 600519 1422.28 1410.70 ... 0.95 -0.81 -11.52 0.19
[1334 rows x 12 columns]
2.数据处理与特征工程
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def process_data(df, prediction_window=5):
"""数据清洗与特征工程"""
# 重命名列
df = df.rename(columns={
'日期': 'date',
'开盘': 'open',
'收盘': 'close',
'最高': 'high',
'最低': 'low',
'成交量': 'volume'
})
# 转换日期类型并设置索引
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'])
df.set_index('date', inplace=True)
# 添加基本技术指标
df['ma5'] = df['close'].rolling(5, min_periods=1).mean()
df['ma20'] = df['close'].rolling(20, min_periods=1).mean()
df['ma60'] = df['close'].rolling(60, min_periods=1).mean()
# 添加波动率指标
df['daily_return'] = df['close'].pct_change()
df['volatility_5d'] = df['daily_return'].rolling(5).std() * np.sqrt(252)
df['volatility_20d'] = df['daily_return'].rolling(20).std() * np.sqrt(252)
# 添加RSI和MACD
df['rsi'] = compute_rsi(df['close'])
df['macd'], df['signal'] = compute_macd(df['close'])
# 添加成交量相关指标
df['volume_ma5'] = df['volume'].rolling(5).mean()
df['volume_ma20'] = df['volume'].rolling(20).mean()
df['volume_ratio'] = df['volume'] / df['volume_ma20']
# 添加时间特征
df['year'] = df.index.year
df['month'] = df.index.month
df['day_of_week'] = df.index.dayofweek
df['day_of_month'] = df.index.day
# 添加滞后特征 计算当前时刻与过去 lag 天之间的收益率
for lag in [1, 2, 3, 5, 10]:
df[f'return_lag{lag}'] = df['close'].pct_change(lag)
# 修改目标变量计算(未来几天的收益率) -计算当前时刻与未来 prediction_window 天之后的收盘价之间的收益率
future_returns = df['close'].pct_change(prediction_window).shift(-prediction_window)
# 使用滚动平均平滑目标变量
smoothed_returns = future_returns.rolling(5, min_periods=1).mean()
# 添加滞后特征作为目标变量
df['future_return'] = smoothed_returns
# 添加方向目标变量(用于分类)
df['future_direction'] = np.where(df['future_return'] > 0, 1, 0)
# 清理无效数据
df.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan, inplace=True)
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# 验证数据
validate_data(df)
return df
def validate_data(df):
"""验证数据是否包含无效值"""
# 首先检查空值
if df.isnull().any().any():
print(f"警告: 数据包含 {df.isnull().sum().sum()} 个空值")
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# 只检查数值列中的无穷值
numeric_cols = df.select_dtypes(include=[np.number]).columns
for col in numeric_cols:
# 检查无穷值
if np.isinf(df[col]).any():
print(f"警告: 列 '{col}' 包含无穷值")
# 替换无穷值为NaN
df[col] = df[col].replace([np.inf, -np.inf], np.nan)
# 再次检查空值(替换无穷值后可能产生新的空值)
if df.isnull().any().any():
print(f"警告: 数据替换后包含 {df.isnull().sum().sum()} 个空值")
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# 检查异常大值
for col in numeric_cols:
if (df[col].abs() > 1e10).any():
print(f"警告: 列 '{col}' 包含异常大的数值")
return df
3.MACD指标与RSI指标函数完整的实现代码如下所示:
def compute_rsi(series, period=14):
"""计算相对强弱指数RSI(添加边界条件处理)"""
delta = series.diff()
gain = delta.where(delta > 0, 0)
loss = -delta.where(delta < 0, 0)
# 避免除零错误
avg_gain = gain.rolling(period, min_periods=1).mean()
avg_loss = loss.rolling(period, min_periods=1).mean()
# 添加额外保护:当avg_loss为0时直接返回100
rs = avg_gain / avg_loss
rs = np.where(avg_loss == 0, 100, rs) # 当损失为0时,RS设为100
rsi = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
# 替换无效值
rsi = pd.Series(rsi, index=series.index)
rsi = rsi.fillna(50) # 当数据不足时设为中性值50
rsi.replace([np.inf, -np.inf], 50, inplace=True)
return rsi
def compute_macd(series, fast=12, slow=26, signal=9):
"""计算MACD指标"""
ema_fast = series.ewm(span=fast, min_periods=1).mean()
ema_slow = series.ewm(span=slow, min_periods=1).mean()
macd = ema_fast - ema_slow
signal_line = macd.ewm(span=signal, min_periods=1).mean()
return macd, signal_line
4.关键特征的筛选
在前面股票特征的构建过程中,设置了许多的特征,例如收盘价均线(ma5、ma20、ma60等)、成交量均线(volume_ma5、volume_ma20等)、MACD指标、RSI指标等。但是在模型的训练预测阶段,并不是所有的特征都能产生作用,可能有些特征对最终的预测结果影响较大,而一些特征对最终的预测结果影响较小。因此为了提高模型的性能,需要对特征进行筛选,尽量选取一些对最终预测结果影响较大的特征。
def select_features(df):
"""选择相关性高的特征"""
# 计算特征与目标的相关性
corr_matrix = df.corr()
target_corr = corr_matrix['future_return'].abs().sort_values(ascending=False)
# 选择相关性大于0.05的特征
selected_features = target_corr[target_corr > 0.05].index.tolist()
# 确保包含关键特征
essential_features = [
'close', 'volatility_20d', 'rsi', 'macd', 'volume_ratio',
'year', 'ma5', 'ma20', 'daily_return', 'volume_ma5'
]
for feat in essential_features:
if feat not in selected_features and feat in df.columns:
selected_features.append(feat)
# 如果目标变量存在于筛选出的特征中移除目标变量
if 'future_return' in selected_features:
selected_features.remove('future_return')
if 'future_direction' in selected_features:
selected_features.remove('future_direction')
return selected_features
5.模型的构建与训练
构建了随机森林、XGBoost和Lasso三种模型进行训练,并对它们的性能进行评估,从中确定性能最好的模型。
def train_and_evaluate_models(X, y):
"""训练多个模型并评估性能"""
# 时间序列交叉验证
tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=5)
# 构建模型字典
models = {
'RandomForest': RandomForestRegressor(
n_estimators=200,
max_depth=8,
min_samples_leaf=15,
max_features=0.7,
random_state=42,
n_jobs=-1
),
'XGBoost': XGBRegressor(
n_estimators=300,
max_depth=5,
learning_rate=0.03,
subsample=0.7,
colsample_bytree=0.8,
random_state=42,
n_jobs=-1
),
'Lasso': LassoCV(cv=5, random_state=42, max_iter=10000)
}
#记录模型训练结果的字典
results = {
'model': [],
'train_score': [],
'test_score': [],
'mae': []
}
# 记录最佳模型及其得分
best_model = None
best_score = -np.inf
for model_name, model in models.items():
fold_scores = []
fold_mae = []
for train_index, test_index in tscv.split(X):
X_train, X_test = X.iloc[train_index], X.iloc[test_index]
y_train, y_test = y.iloc[train_index], y.iloc[test_index]
# 标准化 - 仅使用训练数据
scaler = RobustScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 训练模型
model.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
# 评估模型
train_score = model.score(X_train_scaled, y_train)
test_score = model.score(X_test_scaled, y_test)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test_scaled)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
fold_scores.append(test_score)
fold_mae.append(mae)
# 计算平均性能
avg_score = np.mean(fold_scores)
avg_mae = np.mean(fold_mae)
results['model'].append(model_name)
results['train_score'].append(train_score)
results['test_score'].append(avg_score)
results['mae'].append(avg_mae)
# 选择最佳模型
if avg_score > best_score:
best_score = avg_score
best_model = model
# 使用最近3年数据重新训练最佳模型
recent_data = X[X.index.year >= datetime.now().year - 3]
if not recent_data.empty:
y_recent = y.loc[recent_data.index]
scaler = RobustScaler()
X_recent_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(recent_data)
best_model.fit(X_recent_scaled, y_recent)
return best_model, pd.DataFrame(results)
6.分析结果可视化
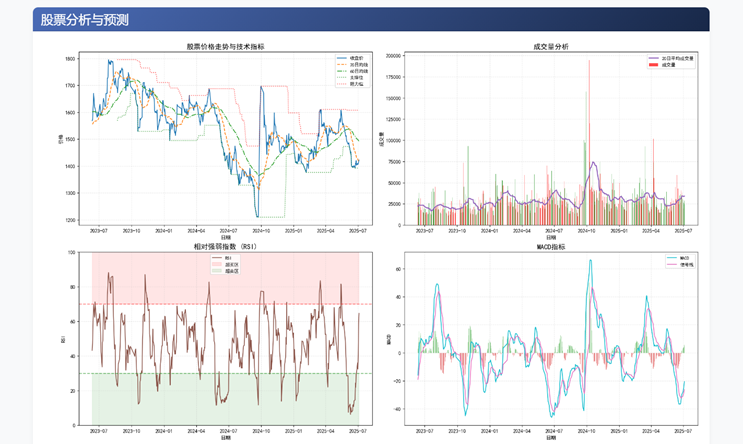
使用Matplotlib将模型的分析结果数据绘制为图表的形式方便用户进行数据分析。
def create_visualizations(df, model_performance, feature_importance):
"""生成股票分析可视化图表(优化版)"""
# 第一部分:技术指标图表
fig1 = plt.figure(figsize=(18, 22), constrained_layout=True)
gs = fig1.add_gridspec(4, 2)
# 1. 价格走势图(添加支撑/阻力线)
ax1 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])
ax1.plot(df.index, df['close'], label='收盘价', linewidth=1.5, color='#1f77b4')
ax1.plot(df.index, df['ma20'], label='20日均线', linestyle='--', color='#ff7f0e')
ax1.plot(df.index, df['ma60'], label='60日均线', linestyle='-.', color='#2ca02c')
# 添加支撑阻力线(示例逻辑,可根据实际需求调整)
support = df['close'].rolling(50).min().dropna()
resistance = df['close'].rolling(50).max().dropna()
ax1.plot(support.index, support, 'g:', alpha=0.7, label='支撑位')
ax1.plot(resistance.index, resistance, 'r:', alpha=0.7, label='阻力位')
ax1.set_title('股票价格走势与技术指标', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax1.set_xlabel('日期')
ax1.set_ylabel('价格')
ax1.legend(loc='best', fontsize=9)
ax1.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 2. 成交量分析(添加颜色编码)
ax2 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
# 根据涨跌着色
colors = np.where(df['close'].diff() >= 0, 'g', 'r')
ax2.bar(df.index, df['volume'], color=colors, alpha=0.7, label='成交量')
ax2.plot(df.index, df['volume_ma20'], color='#9467bd', linewidth=2, label='20日平均成交量')
ax2.set_title('成交量分析', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax2.set_xlabel('日期')
ax2.set_ylabel('成交量')
ax2.legend(loc='best', fontsize=9)
ax2.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 3. RSI指标(添加超买超卖区域)
ax3 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[1, 0])
ax3.plot(df.index, df['rsi'], label='RSI', color='#8c564b', linewidth=1.5)
ax3.axhline(70, color='red', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
ax3.axhline(30, color='green', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
ax3.fill_between(df.index, 70, 100, color='red', alpha=0.1, label='超买区')
ax3.fill_between(df.index, 0, 30, color='green', alpha=0.1, label='超卖区')
ax3.set_title('相对强弱指数 (RSI)', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax3.set_xlabel('日期')
ax3.set_ylabel('RSI')
ax3.set_ylim(0, 100)
ax3.legend(loc='best', fontsize=9)
ax3.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 4. MACD指标(优化柱状图显示)
ax4 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[1, 1])
ax4.plot(df.index, df['macd'], label='MACD', color='#17becf', linewidth=1.5)
ax4.plot(df.index, df['signal'], label='信号线', color='#e377c2', linewidth=1.5)
# 使用更高效的bar绘制方法
diff = df['macd'] - df['signal']
ax4.bar(df.index, diff, color=np.where(diff > 0, '#2ca02c', '#d62728'), alpha=0.5, width=1)
ax4.set_title('MACD指标', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax4.set_xlabel('日期')
ax4.set_ylabel('MACD')
ax4.legend(loc='best', fontsize=9)
ax4.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 5. 波动率分析(添加布林带)
ax5 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[2, 0])
ax5.plot(df.index, df['volatility_20d'] * 100, label='20日波动率', color='#bcbd22', linewidth=1.5)
ax5.set_title('波动率分析', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax5.set_xlabel('日期')
ax5.set_ylabel('波动率 (%)')
ax5.legend(loc='best', fontsize=9)
ax5.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 6. 模型性能比较(添加具体数值标签)
ax6 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[2, 1])
bars = ax6.bar(model_performance['model'], model_performance['test_score'],
color=['#1f77b4', '#ff7f0e', '#2ca02c'])
ax6.set_title('模型性能比较 (测试集$R^2$得分)', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax6.set_ylabel('$R^2$得分')
ax6.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 在柱状图上添加数值标签
for bar in bars:
height = bar.get_height()
ax6.annotate(f'{height:.3f}',
xy=(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width() / 2, height),
xytext=(0, 3), # 3 points vertical offset
textcoords="offset points",
ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
# 7. 特征重要性(优化显示)
ax7 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[3, 0])
top_features = feature_importance.head(10).sort_values(by='importance', ascending=True)
colors = plt.cm.viridis(np.linspace(0, 1, len(top_features)))
ax7.barh(top_features['feature'], top_features['importance'], color=colors)
ax7.set_title('Top 10特征重要性', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax7.set_xlabel('重要性')
ax7.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 8. 预测与实际对比(添加回归线和R²)
ax8 = fig1.add_subplot(gs[3, 1])
ax8.scatter(df['future_return'], df['prediction'], alpha=0.5, color='#d62728', s=20)
# 添加回归线
slope, intercept = np.polyfit(df['future_return'], df['prediction'], 1)
regression_line = slope * df['future_return'] + intercept
ax8.plot(df['future_return'], regression_line, 'b-', linewidth=2, label=f'回归线 (斜率={slope:.2f})')
# 添加45度参考线
ax8.plot([df['future_return'].min(), df['future_return'].max()],
[df['future_return'].min(), df['future_return'].max()],
'r--', linewidth=1.5, label='理想线')
# 计算R²
r2 = r2_score(df['future_return'], df['prediction'])
ax8.annotate(f'$R^2$ = {r2:.3f}', xy=(0.05, 0.9), xycoords='axes fraction', fontsize=12)
ax8.set_xlabel('实际收益率')
ax8.set_ylabel('预测收益率')
ax8.set_title('预测 vs 实际', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax8.legend(loc='best', fontsize=9)
ax8.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 保存为Base64编码
buffer1 = BytesIO()
fig1.savefig(buffer1, format='png', dpi=120, bbox_inches='tight')
buffer1.seek(0)
img_base64 = base64.b64encode(buffer1.read()).decode()
plt.close(fig1) # 明确关闭图形释放内存
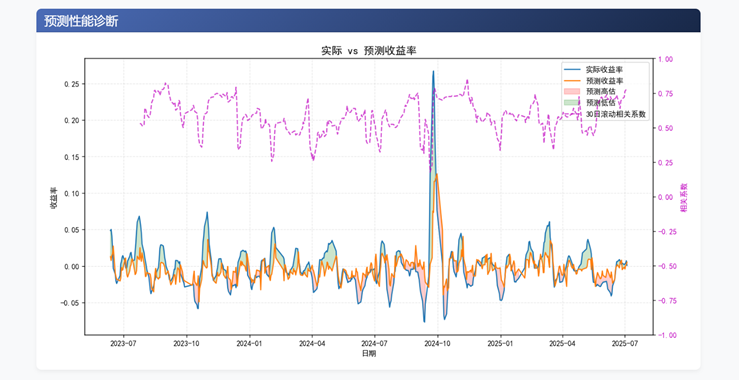
# 第二部分:诊断图 - 实际vs预测的时间序列对比
fig2, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6), tight_layout=True)
# 绘制实际和预测值
ax.plot(df.index, df['future_return'], label='实际收益率', color='#1f77b4', linewidth=1.5)
ax.plot(df.index, df['prediction'], label='预测收益率', color='#ff7f0e', linewidth=1.5)
# 添加残差区域
ax.fill_between(df.index, df['future_return'], df['prediction'],
where=(df['prediction'] > df['future_return']),
color='red', alpha=0.2, label='预测高估')
ax.fill_between(df.index, df['future_return'], df['prediction'],
where=(df['prediction'] <= df['future_return']),
color='green', alpha=0.2, label='预测低估')
# 添加滚动相关系数
rolling_corr = df['future_return'].rolling(30).corr(df['prediction'])
ax2 = ax.twinx()
ax2.plot(df.index, rolling_corr, 'm--', alpha=0.7, label='30日滚动相关系数')
ax2.set_ylabel('相关系数', color='m')
ax2.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor='m')
ax2.set_ylim(-1, 1)
ax.set_title('实际 vs 预测收益率', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel('日期')
ax.set_ylabel('收益率')
# 合并图例
lines, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
lines2, labels2 = ax2.get_legend_handles_labels()
ax.legend(lines + lines2, labels + labels2, loc='best')
ax.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.3)
# 保存为Base64编码
buffer2 = BytesIO()
fig2.savefig(buffer2, format='png', dpi=120, bbox_inches='tight')
buffer2.seek(0)
diag_img = base64.b64encode(buffer2.read()).decode()
plt.close(fig2) # 明确关闭图形释放内存
return img_base64, diag_img
7.web交互
为了给用户提供一个良好的交互体验,我们可以借助Flask框架快速构建一个后端服务器,用来监听用户请求,并调用业务代码完成股票数据的查询、处理、模型性训练以及数据分析的完整流程,最终将分析结果返回到前端HTML页面中,实现前后端数据的交互。
from flask import Flask, render_template, request
import traceback
from datetime import datetime
from data_fetcher import get_stock_data
from data_processor import process_data
from feature_selector import select_features
from model_trainer import train_and_evaluate_models, get_feature_importance
from visualizer import create_visualizations
from sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScaler
# 实例化一个Flask框架应用
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def stock_analysis():
print("表单提交内容:", request.form)
if request.method == 'POST':
stock_code = request.form.get('stock_code', '600519')
start_date = request.form.get('start_date', '20200101')
prediction_window = int(request.form.get('prediction_window', '5'))
else:
stock_code = "600519"
start_date = "20200101"
prediction_window = 5
print(start_date,'开始时间')
# 默认结束日期为今天
end_date = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d")
if start_date >= end_date:
return render_template("error.html", message="起始日期不能大于等于结束日期")
try:
# 获取并处理数据
df = get_stock_data(stock_code, start_date=start_date,end_date=end_date)
if df.empty:
return render_template('error.html', message="无法获取股票数据,请检查股票代码是否正确")
# 构建特征
processed_df = process_data(df, prediction_window)
# 特征选择
features = select_features(processed_df)
X = processed_df[features]
y = processed_df['future_return']
# 训练模型并评估
model, model_performance = train_and_evaluate_models(X, y)
# 在完整数据集上生成预测
scaler = RobustScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
processed_df['prediction'] = model.predict(X_scaled)
# 获取特征重要性
feature_imp = get_feature_importance(model, features)
# 关键指标计算
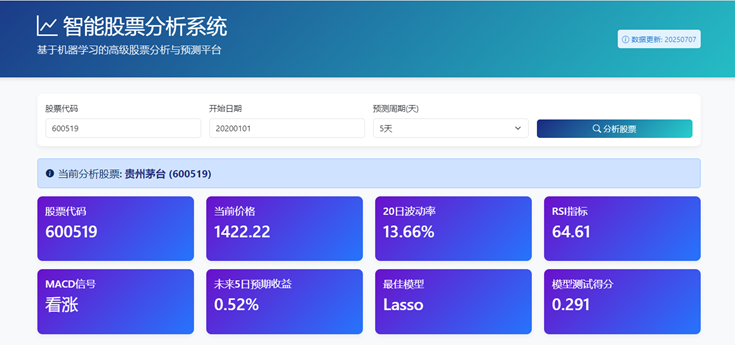
latest = processed_df.iloc[-1]
metrics = {
"股票代码": stock_code,
"当前价格": f"{latest['close']:.2f}",
"20日波动率": f"{latest['volatility_20d'] * 100:.2f}%",
"RSI指标": f"{latest['rsi']:.2f}",
"MACD信号": "看涨" if latest['macd'] > latest['signal'] else "看跌",
f"未来{prediction_window}日预期收益": f"{latest['prediction'] * 100:.2f}%",
"最佳模型": model_performance.loc[model_performance['test_score'].idxmax(), 'model'],
"模型测试得分": f"{model_performance['test_score'].max():.3f}"
}
# 模型性能表格
model_table = model_performance.to_dict('records')
# 特征重要性表格
feature_table = feature_imp.head(10).to_dict('records')
# 生成可视化图表
plot_img, diag_img = create_visualizations(processed_df.tail(500), model_performance, feature_imp)
# 获取股票名称
try:
import akshare as ak
stock_info = ak.stock_individual_info_em(symbol=stock_code)
stock_name = stock_info.loc[stock_info['item'] == '股票简称', 'value'].values[0]
print(stock_name)
except:
stock_name = "未知股票"
# 返回股票分析HTML页面,并将数据嵌入页面中
return render_template('dashboard.html',
plot=plot_img,# 股票分析与预测股票图片
diag_plot=diag_img,# 股票预测性能诊断图片
metrics=metrics,# 股票分析指标
model_table=model_table,# 模型性能表格
feature_table=feature_table,# 特征重要性表格
stock_name=stock_name,# 股票名称
prediction_window=prediction_window,# 预测窗口
start_date=start_date,# 开始日期
current_date=end_date,# 当前日期
stock_code=stock_code)# 股票代码
except Exception as e:
error_trace = traceback.format_exc()
return render_template('error.html', message=str(e), trace=error_trace)
# 错误处理页面
@app.errorhandler(404)
def page_not_found(e):
return render_template('error.html', message="页面未找到"), 404
@app.errorhandler(500)
def internal_server_error(e):
error_trace = traceback.format_exc()
return render_template('error.html', message="服务器内部错误", trace=error_trace), 500
# 程序主入口,运行Flask框架
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
项目运行效果图:




















 5186
5186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








