63. Unique Paths II
Description:
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as
1and0respectively in the grid.Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input: [ [0,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,0] ] Output: 2 Explanation: There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above. There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner: 1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down 2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
解题思路:
(1)动态规划
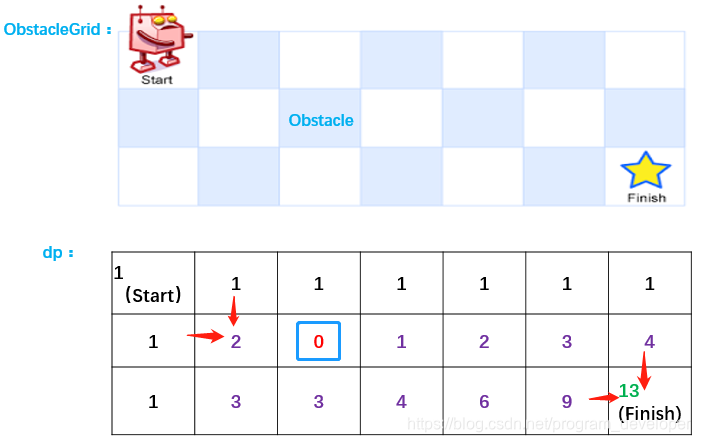
动态规划三要素:
1. 最优子结构:我们发现除去第一行第一列,其他dp二维数组中的数据都是由它上面格子和左边格子数据之和。如果有障碍物,那么dp表格对应的位置为0。
2. 边界条件:
- 如果obstacleGrid表格中第一行、第一列都没有障碍物,那么dp表格中第一行、第一列都为1。
- 如果start位置(即obstacleGrid[0][0]==1)有障碍物,那么不管obstacleGrid表格后边是什么,路径和都为0。
- 如果obstacleGrid表格中第一行第
列有障碍物,那么dp表格中第一行第
列后边都为0。
- 如果obstacleGrid表格中第一列第
行有障碍物,那么dp表格中第一列第
行后边都为0。
3. 状态转移方程:dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
已经AC的代码:
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
"""
:type obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
if not obstacleGrid:
return 0
row = len(obstacleGrid)
col = len(obstacleGrid[0])
if obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1:
return 0
dp = [[1 for i in range(col)] for i in range(row)]
for i in range(col):
if obstacleGrid[0][i] == 1:
for j in range(i,col):
dp[0][j] = 0
break
for i in range(row):
if obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1:
for j in range(i,row):
dp[j][0] = 0
break
for i in range(1,row):
for j in range(1,col):
if(obstacleGrid[i][j]) == 1:
dp[i][j] = 0
else:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
return dp[-1][-1]
solution = Solution()
obstacleGrid = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,0]]
print(solution.uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid))上面代码逻辑清晰,但是不够简洁。重新整理上边分析的解题思路,可以写出如下简化代码:
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid):
"""
:type obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
row = len(obstacleGrid)
col = len(obstacleGrid[0])
dp = [[1] * col for _ in range(row)]
for i in range(0, row):
for j in range(0, col):
if obstacleGrid[i][j]:
dp[i][j] = 0
elif i == 0:
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1]
elif j == 0:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
else:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1]
return dp[-1][-1]
solution = Solution()
obstacleGrid = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,0]]
print(solution.uniquePathsWithObstacles(obstacleGrid))






 本文介绍了一种使用动态规划方法解决机器人在包含障碍物的网格中寻找从起点到终点路径的问题。通过分析网格的第一行和第一列,并利用状态转移方程,求得机器人到达每个网格节点的路径数,最终返回到达终点的路径总数。
本文介绍了一种使用动态规划方法解决机器人在包含障碍物的网格中寻找从起点到终点路径的问题。通过分析网格的第一行和第一列,并利用状态转移方程,求得机器人到达每个网格节点的路径数,最终返回到达终点的路径总数。

















 1141
1141

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








