题目链接:
题目描述:
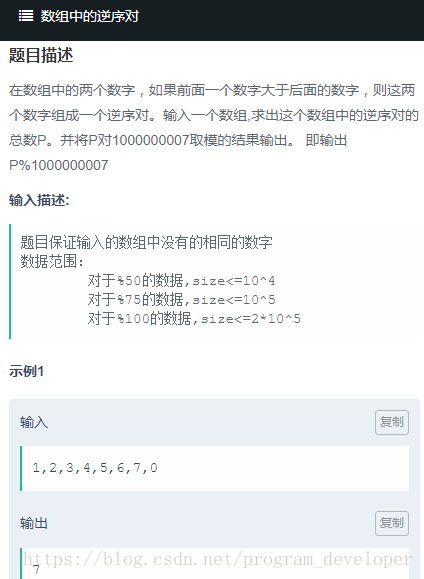
解题思路:
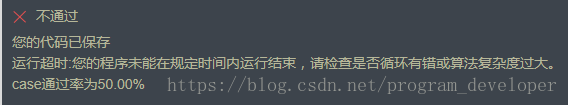
(1)两层循环遍历,时间复杂度为O()。
顺序扫描整个数组,每扫描到一个数字的时候,逐个比较该数字和它后面的数字的大小。如果后面的数字比它小,则这两个数字就组成一个逆序对。假设数组中含有n个数字,由于每个数字都要和O(n)个数字作比较,因此这个算法的时间复杂度是O()。
代码实现:
public class Solution {
public int InversePairs(int [] array) {
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=i; j<array.length; j++) {
if(array[i] > array[j])
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}结果:不能被AC。
(2)归并排序的思想实现:
已经AC的代码:
public class ArrayInversePairs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[] arr = {7, 5, 6, 4};
System.out.println(InversePairs(arr));
}
public static int InversePairs(int[] array) {
if(array == null || array.length <= 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] tmpArr = new int[array.length];
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
tmpArr[i] = array[i];
}
int count = InversePairsCore(array, tmpArr, 0, array.length - 1);
return count;
}
public static int InversePairsCore(int[] arr, int[] tmpArr, int low, int high) {
if(low == high) {
tmpArr[low] = arr[low];
return 0;
}
int len = (high - low) / 2;
int left = InversePairsCore(tmpArr, arr, low, low + len) % 1000000007;
int right = InversePairsCore(tmpArr, arr, low + len + 1, high) % 1000000007;
//p1初始化为前半段最后一个数字的下标
int p1 = low + len;
//p2 初始化为后半段最后一个数字的下标
int p2 = high;
// 开始拷贝的位置
int p3 = high;
// 逆序数
int count = 0;
while(p1 >= low && p2 >= low + len + 1) {
if(arr[p1] > arr[p2]) {
//对应的逆序数
count += p2 - low - len;
tmpArr[p3] = arr[p1];
p3--;
p1--;
if(count >= 1000000007)
count %= 1000000007;
} else {
tmpArr[p3] = arr[p2];
p3--;
p2--;
}
}
while(p1 >= low) {
tmpArr[p3] = arr[p1];
p3--;
p1--;
}
while(p2 >= low + len + 1) {
tmpArr[p3] = arr[p2];
p3--;
p2--;
}
return (count + left + right) % 1000000007;
}
}(3)用Python实现归并排序的思想
归并排序能够有效的减少最坏时间复杂度,但是它有额外的开销,以空间换时间。归并排序,就是把原数据分成两个数组,每次取两个数组中的最小值放入一个新的数组中,直到其中一个数组全部取完。归并排序思想没法用python做,用python始终是超时的。
class Solution:
def InversePairs(self, data):
if data is None or len(data) <= 0:
return 0
copy = [i for i in data]
count = self.InversePairsCore(data, copy, 0, len(data) - 1)
return count % 1000000007
def InversePairsCore(self, data, copy, start, end):
if start == end:
copy[start] = data[start]
return 0
length = (end - start) // 2
left = self.InversePairsCore(copy, data, start, start + length)
right = self.InversePairsCore(copy, data, start + length + 1, end)
# p1 初始化为前半段最后一个数字的下标
p1 = start + length
# p2 初始化为后半段最后一个数字的下标
p2 = end
# 开始拷贝的位置
p3 = end
# 逆序数
count = 0
# 对两个数组进行对比取值的过程
while p1 >= start and p2 >= start + length + 1:
if data[p1] > data[p2]:
copy[p3] = data[p1]
p3 -= 1
p1 -= 1
# 对应的逆序数
count += p2 - start - length
else:
copy[p3] = data[p2]
p3 -= 1
p2 -= 1
# 剩下的一个数组未取完的操作
while p1 >= start:
copy[p3] = data[p1]
p3 -= 1
p1 -= 1
while p2 >= start + length + 1:
copy[p3] = data[p2]
p3 -= 1
p2 -= 1
return count + left + right
if __name__ == "__main__":
# input_data = [7, 5, 6, 4]
input_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0]
sol = Solution()
print(sol.InversePairs(input_data))






 本文探讨了逆序对的两种求解方法:暴力解法和归并排序思想的运用。首先介绍了简单但效率低下的两层循环遍历法,然后深入解析了归并排序如何有效降低时间复杂度。通过Java和Python代码实例,展示了如何利用归并排序核心思想解决逆序对问题。
本文探讨了逆序对的两种求解方法:暴力解法和归并排序思想的运用。首先介绍了简单但效率低下的两层循环遍历法,然后深入解析了归并排序如何有效降低时间复杂度。通过Java和Python代码实例,展示了如何利用归并排序核心思想解决逆序对问题。
















 609
609

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








