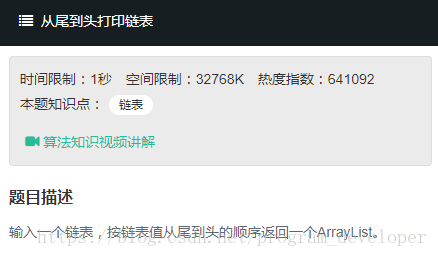
"微信公众号"

题目链接:
题目:
解题思路:
(1)用递归方法遍历链表输出
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class SingleLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def add(self, data):
node = ListNode(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = node
self.tail = node
else:
self.tail.next =node
self.tail = node
def iter(self):
if not self.head:
return
cur = self.head
yield cur.val
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
yield cur.val
class Solution:
# 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3]
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
if listNode is None:
return []
return self.printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next) + [listNode.val]
if __name__=="__main__":
link_list = SingleLinkedList()
for i in range(5):
link_list.add(i)
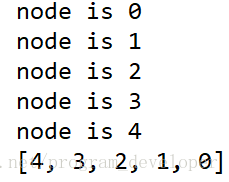
for node in link_list.iter():
print("node is {0}".format(node))
solution = Solution()
# Python递归实现。
print(solution.printListFromTailToHead(link_list.head))
运行结果:
(2)顺序遍历链表,反转遍历的结果
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
if not listNode:
return []
res = []
index = listNode
while index:
res.append(index.val)
index = index.next
return res[::-1](3)辅助栈法
解题思路:
链表特点: 只能从前至后访问每个节点。
题目要求: 倒序输出节点值。
这种 先入后出 的需求可以借助 栈 来实现。
算法流程:
入栈: 遍历链表,将各节点值 push 入栈。(Python 使用 append() 方法,Java借助 LinkedList 的addLast()方法)。
出栈: 将各节点值 pop 出栈,存储于数组并返回。(Python 直接返回 stack 的倒序列表,Java 新建一个数组,通过 popLast() 方法将各元素存入数组,实现倒序输出)。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N): 入栈和出栈共使用 O(N) 时间。
空间复杂度 O(N): 辅助栈 stack 和数组 res 共使用 O(N) 的额外空间。
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
stack = []
while listNode:
stack.append(listNode.val)
listNode = listNode.next
return stack[::-1](4)链表原地反转
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
if not listNode:
return []
p1 = listNode
p2 = listNode.next
p3 = listNode.next.next
while p2:
p3 = p2.next
p2.next = p1
p1 = p2
p2 = p3
listNode.next = None
listNode = p1
res = []
while listNode:
res.append(listNode.val)
listNode = listNode.next
return resReference:






 这篇博客介绍了如何解决《剑指offer》中的一道面试题——从尾到头打印链表。提供了四种解题方法,包括递归遍历、顺序遍历反转结果、辅助栈法以及链表原地反转。详细阐述了每种方法的思路,并分析了时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
这篇博客介绍了如何解决《剑指offer》中的一道面试题——从尾到头打印链表。提供了四种解题方法,包括递归遍历、顺序遍历反转结果、辅助栈法以及链表原地反转。详细阐述了每种方法的思路,并分析了时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
















 1292
1292

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








