关于本项目应做的准备及介绍,见上一篇博客,上一篇讲的是get方法
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/ppsiri/article/details/93471790
本文主要讲一下POST方法与后台Tomcat交互。
由于http包含header和数据包两个部分,因此我们可以用两种方式同时传输,即,我在header里设置username和pwd的属性,再在数据包中也包含这两部分数据,实际使用中我建议使用第二种。现在我们来试一下。
public void sendLogReq(){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
try {
jsonObject.put("username", email);
jsonObject.put("password", password );
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String svrUrl="http://192.168.43.184:8080/blog/TestServlet";
String result = getDataFromServer(svrUrl, jsonObject.toString(), email, password);
}
}).start();
}
public String getDataFromServer(String svrUrl, String ParamStr, String a, String b) {
try {
// 转成指定格式
Log.d("AAAAA",""+ParamStr);
byte[] requestData = ParamStr.getBytes("UTF-8");
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
DataOutputStream outStream = null;
String MULTIPART_FORM_DATA = "multipart/form-data";
// 构造一个post请求的http头
URL url = new URL(svrUrl); // 服务器地址
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setDoInput(true); // 允许输入
conn.setDoOutput(true); // 允许输出
conn.setUseCaches(false); // 不使用caches
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setRequestProperty("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", MULTIPART_FORM_DATA);
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", Long.toString(requestData.length));
conn.setRequestProperty("username", a + "");
conn.setRequestProperty("password", b + "");
// 请求参数内容, 获取输出到网络的连接流对象
outStream = new DataOutputStream(conn.getOutputStream());
outStream.write(requestData, 0, requestData.length);
//将json转换成的数据写到输出流。
outStream.flush();
outStream.close();
ByteArrayOutputStream outStream2 = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int cah = conn.getResponseCode();
if (cah != 200) {
Log.v("data", "服务器响应错误代码:" + cah);
return "0";
}else if(cah == 200){
Log.v("data", "服务器响应成功:" + cah);
}
//下面是读取来自服务器的输入流数据
InputStream inputStream = conn.getInputStream();
int len = 0;
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
while ((len = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) {
outStream2.write(data, 0, len);
}
outStream2.close();
inputStream.close();
String responseStr = new String(outStream2.toByteArray());
Log.v("data", "data = " + responseStr);
return responseStr;
} catch (Exception e) {
return "";
}
}下面是服务器的部分
服务器的部分需要导入json 的jar包,请大家自行搜索下载,位置为
服务器端对应代码,doPost方法为对request的header进行的解析,而下面的getData方法是对请求流的数据的解析,因为我们在android端附着了一个jsonObject的字符串。
/**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("---------00000000----");
String result;
String name = request.getHeader("username").toString();
String pwd = request.getHeader("password").toString();
System.out.println("/" + name + "/" + pwd);
result=" I get your name is "+name+" and "+"pwd is "+pwd;
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
response.getWriter().append(result + "");
getData(request);//对数据包的解析
}
public String getData(HttpServletRequest req){
String result = null;
try {
//包装request的输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader((ServletInputStream) req.getInputStream(), "utf-8"));
//缓冲字符
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("");
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
sb.append(line);
}
br.close();//关闭缓冲流
result=sb.toString();//转换成字符
System.out.println("result = " + result);
JSONObject resultObject = JSONObject.fromObject(result);//将数据转换成jsonObject
System.out.println("from json "+ resultObject.get("username")+"////"+resultObject.get("password"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}下面我们运行一下试试。
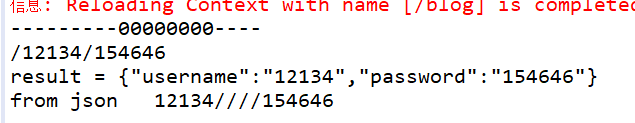
而服务器给我们返回的数据是这样的
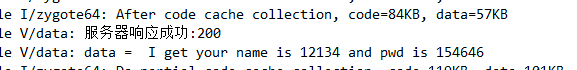
可以看到我们成功通过两种方式读取到了数据。
以上就是我们通过post与后台进行的交互。






 本文是关于Android使用POST方法与后台Tomcat服务器交互的教程。内容包括如何在HTTP请求头中设置参数,并在数据包中传递JSON对象。示例代码展示了如何在服务器端解析header和请求流中的数据,成功实现了数据的双向传输。
本文是关于Android使用POST方法与后台Tomcat服务器交互的教程。内容包括如何在HTTP请求头中设置参数,并在数据包中传递JSON对象。示例代码展示了如何在服务器端解析header和请求流中的数据,成功实现了数据的双向传输。
















 3583
3583










