乘法API
一维tensor相乘:torch.dot
这个只支持一维相同维度的向量相乘,不支持2维以上。
torch.dot(torch.tensor([2, 3]), torch.tensor([2, 1]))
Note: np.dot就有点类似下面的matmul,和torch.dot完全不一样。
[TORCH.DOT]
二维tensor相乘:torch.mm
a是 [m, k],b是[k, n],结果是 [m, n]
c = torch.mm(a, b)
三维tensor相乘torch.bmm
c = torch.bmm(a, b)
只能用于三维tensor相乘,这个函数不支持广播,也就是第一维必须相同,另外两维符合矩阵相乘法则。
示例:实现A=ab,B=abc到ac,即a1b*abc=a1c
torch.bmm(A.unsqueeze(1),B).squeeze(1)
等价于torch.einsum("ab,abc->ac", A, B)
任意多维tensor相乘:torch.matmul
等价于@运算符。
支持广播;当两个都是一维时,表示点积
c = torch.matmul(a, b)
广播的意思同numpy,如ab维度为[1,2,1152,1,8][10,1,1152,8,16],则matmul结果c的维度为[10,2,1152,1,16],即只有最后两维会执行一一的矩阵运算,其它都是取有维度的那个(注意必须是两个维度一样大,或者其中一个是1,否则没法一一矩阵运算了,实际就是把1维变成了另一个维度大小且元素和1维一样)。
另外,如下例,[2,3,1]和[2,1,3]的结果维度是[2,3,3]。
利用这个可以实现规避batch维度功能,如想实现[揭秘 Deep & Cross : 如何自动构造高阶交叉特征 - 知乎]中x0*x0^t*w0,假如inputs = batch*feature_dim = 2*3,w0 = 3*1这里不需要batch维度,则x_l = x_0 = inputs.unsqueeze(2)变成x_0 = 2*3*1,x_l^t = x0^t = 2*1*3,则xl_w = torch.matmul(x_l.transpose(1, 2), self.weight[i].unsqueeze(0))就是2*1*3 matmul 1*3*1,0维不管,结果是2*1*1,然后dot_ = torch.matmul(x_0, xl_w)就是2*3*1 matmul 2*1*1,结果是2*3*1,正确。
按元素相乘/element-wise乘法:torch.mul /*
两个相同尺寸的张量,对应元素相乘,就是哈达玛积,也叫element wise乘法。
1 element wise乘法是支持广播的,如维度为[10,2,1152,1,16]和[10,2,1,1,16]的张量相乘结果是取大的[10,2,1152,1,16]。
2 tensor ** 2 表示的含义是 tensor * tensor,也是element wise乘法。
示例:
两种等价方式
c = torch.mul(a, b)
c = a * b
Note: 可以发现的torch.div()其实就是/, 类似的:torch.add就是+,torch.sub()就是-,不过符号的运算更简单常用。
通用的张量相乘方法:torch.tensordot
tensordot是一种非常简单灵活的乘法计算函数。可以这样理解:输入数组a, b,通过参数axes指定要计算的维度(这里axes 是一个元组,里面必须有两个tuple元素 ,第一个元素是a要用于计算的 axis,第二个元素是b要用于计算的 axis)被参数axis指定的维度会执行sum-reduction,简单来说就是相乘之后求和这样被指定的axes将不会出现在输出中;而输入数组的其他维度将会变成输出数组的维度,对应的顺序和输入的顺序相同。
c = torch.tensordot(a, b, dims)
## 输入A和B,维度如size参数所示
A = np.random.randint(2, size=(2, 6, 5))
B = np.random.randint(2, size=(3, 2, 4))
## 指定axes=((0), (1)),也就是说,
## 按A的axis=0的列和B的axis=1列取元素,对应元素相乘求和
## 于是两个维度从输出中消失
np.tensordot(A, B, axes=((0),(1))).shape
np.tensordot(A, B, axes=((0),(1))).shape
Output: (6, 5, 3, 4)
A : (2, 6, 5) -> reduction of axis=0
B : (3, 2, 4) -> reduction of axis=1
Output : `(2, 6, 5)`, `(3, 2, 4)` ===(2 gone)==> `(6,5)` + `(3,4)` => `(6,5,3,4)`
[TORCH.TENSORDOT]
爱因斯坦求和约定einsum
求和简记法,能够以一种统一的方式表示各种各样的张量运算(内积、外积、转置、点乘、矩阵的迹、其他自定义运算),为不同运算的实现提供了一个统一模型。
示例
# trace
>>> torch.einsum('ii', torch.randn(4, 4))
tensor(-1.2104)
# diagonal
>>> torch.einsum('ii->i', torch.randn(4, 4))
tensor([-0.1034, 0.7952, -0.2433, 0.4545])
# outer product
>>> x = torch.randn(5)
>>> y = torch.randn(4)
>>> torch.einsum('i,j->ij', x, y)
tensor([[ 0.1156, -0.2897, -0.3918, 0.4963],
[-0.3744, 0.9381, 1.2685, -1.6070],
[ 0.7208, -1.8058, -2.4419, 3.0936],
[ 0.1713, -0.4291, -0.5802, 0.7350],
[ 0.5704, -1.4290, -1.9323, 2.4480]])
其它:torch.einsum('bld,brd->blr', x, y)
# batch matrix multiplication
>>> As = torch.randn(3,2,5)
>>> Bs = torch.randn(3,5,4)
>>> torch.einsum('bij,bjk->bik', As, Bs)
tensor([[[-1.0564, -1.5904, 3.2023, 3.1271],
[-1.6706, -0.8097, -0.8025, -2.1183]],
[[ 4.2239, 0.3107, -0.5756, -0.2354],
[-1.4558, -0.3460, 1.5087, -0.8530]],
[[ 2.8153, 1.8787, -4.3839, -1.2112],
[ 0.3728, -2.1131, 0.0921, 0.8305]]])
# batch permute
>>> A = torch.randn(2, 3, 4, 5)
>>> torch.einsum('...ij->...ji', A).shape
torch.Size([2, 3, 5, 4])
# equivalent to torch.nn.functional.bilinear
>>> A = torch.randn(3,5,4)
>>> l = torch.randn(2,5)
>>> r = torch.randn(2,4)
>>> torch.einsum('bn,anm,bm->ba', l, A, r)
tensor([[-0.3430, -5.2405, 0.4494],
[ 0.3311, 5.5201, -3.0356]])
[einsum满足你一切需要:深度学习中的爱因斯坦求和约定]
xDeepFM中每层向量计算:即h个d维向量 点乘 m个d维向量,形成h*m个d维向量。
x = torch.einsum('bhd,bmd->bhmd', hidden_nn_layers[-1], hidden_nn_layers[0])
通过attention求attention后的向量,即加权和
current_context_vec = torch.einsum("ab,abc->ac", attention_score, encoder_output)
等价于torch.bmm(attention_score.unsqueeze(1), encoder_output).squeeze(1)
相当于(batch,seq_len) * (batch,seq_len,emb) = (batch,1,seq_len) * (batch,seq_len,emb) = (batch,emb)
[torch.einsum(equation, *operands) → Tensor]
tensor.scatter_add(dim, index, src) → Tensor
Out-of-place version of torch.Tensor.scatter_add_(),作用是一样的,但是 scatter_add() 不会直接修改原来的 Tensor,而 scatter_add_() 会修改原先的 Tensor。
将src中的数据,按照index中的索引位置,添加至self_tensor中,如:
For a 3-D tensor, self is updated as:
self[index[i][j][k]][j][k] += src[i][j][k] # if dim == 0
self[i][index[i][j][k]][k] += src[i][j][k] # if dim == 1
self[i][j][index[i][j][k]] += src[i][j][k] # if dim == 2
就是dim决定了哪个维度的索引是由index提供的,其他所有位置是self_tensor和src一一对应!
示例1:
src = torch.ones((2, 5))
index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 0, 0]])
torch.zeros(3, 5, dtype=src.dtype).scatter_add_(0, index, src)
index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 0, 0], [0, 1, 2, 2, 2]])
torch.zeros(3, 5, dtype=src.dtype).scatter_add_(0, index, src)
示例2:pgn网络中生成和复制的分布合并
final_dist = vocab_dist_p.scatter_add(dim = -1,index=encoder_with_oov,src = context_dist_p)
这里encoder_with_oov和context_dist_p的维度是(batch_size, max_seq_len),vocab_dist_p维度是(batch_size, vocab_size)。数据内容大概是这种tensor([[ 73, 90, 6, ..., 0, 0, 0], [ 30, 34, 6, ..., 0, 0, 0], ..., [ 19, 32, 6, ..., 0, 0, 0]])
逻辑操作
torch.logical_and
torch.logical_or(input, other, *, out=None)
torch.logical_not
torch.lt(input, other, *, out=None)
torch.where(condition, input, other, *, out=None)
Return a tensor of elements selected from either input or other, depending on condition.
聚合操作
TORCH.MAX
形式: torch.max(input) → Tensor
返回输入tensor中所有元素的最大值:
a = torch.randn(1, 3)
>>0.4729 -0.2266 -0.2085
torch.max(a) #也可以写成a.max()
>>0.4729形式: torch.max(input, dim, keepdim=False, out=None) -> (Tensor, LongTensor)
参数:keepdim=True时,原size是(2,3),返回时就不是(2,)或者(3,)而是(2,1)或者(1,3)。
dim参数:按维度dim 返回最大值,并且返回索引(dim未指定时,不返回索引)。
torch.max(a,0)返回每一列中最大值的那个元素,且返回索引(返回最大元素在这一列的行索引)。返回的最大值和索引各是一个tensor,一起构成元组(Tensor, LongTensor)。
torch.max()[0], 只返回最大值的每个数。即一般用法tensor1.mean(dim=0).values。
troch.max()[1], 只返回最大值的每个索引。
a = torch.randn(4, 4)
tensor([[-1.2360, -0.2942, -0.1222, 0.8475],
[ 1.1949, -1.1127, -2.2379, -0.6702],
[ 1.5717, -0.9207, 0.1297, -1.8768],
[-0.6172, 1.0036, -0.6060, -0.2432]])
>>> torch.max(a, 1)
torch.return_types.max(values=tensor([0.8475, 1.1949, 1.5717, 1.0036]), indices=tensor([3, 0, 0, 1]))
Note: 在有的地方我们会看到torch.max(a, 1).data.numpy()的写法,这是因为在早期的pytorch的版本中,variable变量和tenosr是不一样的数据格式,variable可以进行反向传播,tensor不可以,需要将variable转变成tensor再转变成numpy。现在的版本已经将variable和tenosr合并,所以只用torch.max(a,1).numpy()就可以了。
TORCH.MEAN
torch.mean(input) → Tensor
Returns the mean value of all elements in the input tensor.
torch.mean(input, dim, keepdim=False, *, out=None) → Tensor
Returns the mean value of each row of the input tensor in the given dimension dim. If dim is a list of dimensions, reduce over all of them.
和max区别在于返回的值只有一个tensor,没有最大值多余的位置索引tensor。
用法tensor1.mean(dim=0)。
torch.softmax归一化
torch.softmax(input, dim, *, dtype=None)
一个函数。Alias for torch.nn.functional.softmax(input, dim=None, _stacklevel=3, dtype=None)
torch.nn.Softmax(dim=None)
等价的一个Module。
区别:Some thoughts on functional vs. Module:
If you write for re-use, the functional / Module split of PyTorch has turned out
to be a good idea.
Use functional for stuff without state (unless you have a quick and dirty Sequential).
Never re-use modules (define one torch.nn.ReLU and use it 5 times). It’s a trap! When doing analysis or quantization (when ReLU becomes stateful due to quantization params), this will break.应该是说量化时会break,onnx不行。
[What's difference of nn.Softmax(), nn.softmax(), nn.functional.softmax()?]
对于n维张量,如果dim=k,那就是对k维度进行softmax(这时其它维度取固定值时,维度k上的值加起来为1。)。比k更高维度的d(d<k)是不需要考虑的,直接去掉分析。
示例1:
t = torch.zeros([5,2,3])
t1 = torch.softmax(t, dim = 0)
t1:
tensor([[[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000],
[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000]],
[[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000],
[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000]],
[[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000],
[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000]],
[[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000],
[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000]],
[[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000],
[0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000]]])
t1[:,0,0]
tensor([0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000, 0.2000])
sum(t1[:,0,0])
tensor(1.)
图的表示为(只对立方体中的k维度进行):
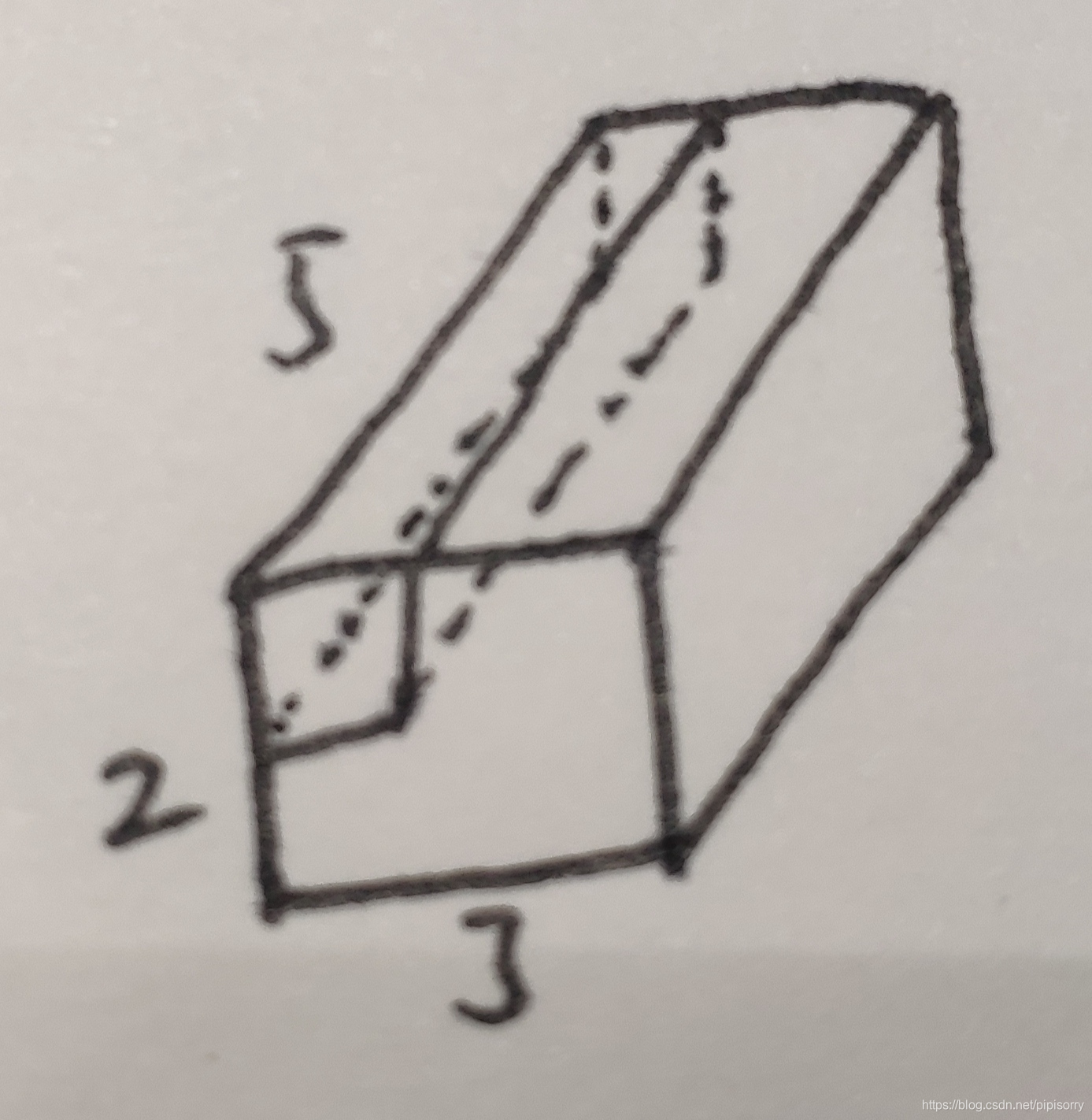
示例2:如果有更高维度不用管
t = torch.zeros([4,5,2,3])
t1 = torch.softmax(t, dim = 1)
sum(t1[0,:,0,0])
tensor(1.)
示例3:
对2个维度同时进行softmax(即其它维度固定时,这2个维度的值加起来为1)。
t = torch.zeros([4,5,2,3])
# t1 = torch.softmax(t, dim = (1,2)), dim只能是数字,下面就是要模拟这个操作。
t1 = t.view(t.size(0), -1, t.size()[-1])
t2 = torch.softmax(t1, dim = 1).view(t.size())
t2[0,:,:,0].sum()
Out[14]: tensor(1.0000)
# sum(t2[0,:,:,0])
# Out[13]: tensor([0.5000, 0.5000])
[torch.nn.Softmax(dim=None)]
from: -柚子皮-





 本文详细介绍了PyTorch中的多种张量乘法操作,包括torch.dot的一维向量乘法,torch.mm和torch.bmm的二维和三维张量乘法,以及torch.matmul的任意多维张量乘法。此外,还讨论了element-wise乘法、tensordot的灵活性以及einsum的通用性。文章进一步解释了torch.scatter_add的功能,用于在特定索引处累加张量数据。最后,概述了逻辑操作、最大值聚合函数torch.max以及均值计算torch.mean,以及softmax的使用。这些内容涵盖了张量操作的基础和高级用法,对于理解和应用PyTorch至关重要。
本文详细介绍了PyTorch中的多种张量乘法操作,包括torch.dot的一维向量乘法,torch.mm和torch.bmm的二维和三维张量乘法,以及torch.matmul的任意多维张量乘法。此外,还讨论了element-wise乘法、tensordot的灵活性以及einsum的通用性。文章进一步解释了torch.scatter_add的功能,用于在特定索引处累加张量数据。最后,概述了逻辑操作、最大值聚合函数torch.max以及均值计算torch.mean,以及softmax的使用。这些内容涵盖了张量操作的基础和高级用法,对于理解和应用PyTorch至关重要。

















 935
935










