DextrAH-G 教师网络
Network(
(value_mean_std): RunningMeanStd()
(running_mean_std): RunningMeanStd()
(a2c_network): Network(
(actor_cnn): Sequential()
(critic_cnn): Sequential()
(actor_mlp): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=512, bias=True)
(1): ELU(alpha=1.0)
(2): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(3): ELU(alpha=1.0)
)
(critic_mlp): Sequential()
(rnn): LSTMWithDones(
(rnn): LSTM(319, 1024)
)
(layer_norm): LayerNorm((1024,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
(value): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=1, bias=True)
(value_act): Identity()
(mu): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=11, bias=True)
(mu_act): Identity()
(sigma_act): Identity()
)
)
网络结构解释
这是一个典型的 Actor-Critic 架构,专为连续动作空间的强化学习任务设计,具有以下特点:
🔍 核心组件分析
1. 标准化层(Normalization)
- value_mean_std和 running_mean_std:用于对输入状态和值函数进行动态标准化,提高训练稳定性
2. 特征提取网络(A2C Network)
- CNN部分:actor_cnn和 critic_cnn都是空的,说明不使用图像输入
- MLP部分:- actor_mlp:两层全连接 (1024→512→512) + ELU激活,用于提取策略特征
- critic_mlp:空的,可能与actor共享特征或使用其他方式
3. 时序处理(RNN)
- LSTM(319, 1024):处理319维输入,输出1024维隐藏状态
- 适用于部分可观测环境或需要记忆的任务
4. 输出层
- Critic:Linear(512→1)→ 输出状态价值 V(s)
- Actor:Linear(512→11)→ 输出11维连续动作的均值 μ
- 使用高斯策略:动作 ~ N(μ, σ),其中σ可能是固定值或可学习参数
🎯 任务类型
- 连续控制任务:11维动作空间(机器人关节控制)
- 向量输入:非图像输入状态向量
- 时序依赖:使用LSTM处理部分可观测或序列依赖任务
网络结构图
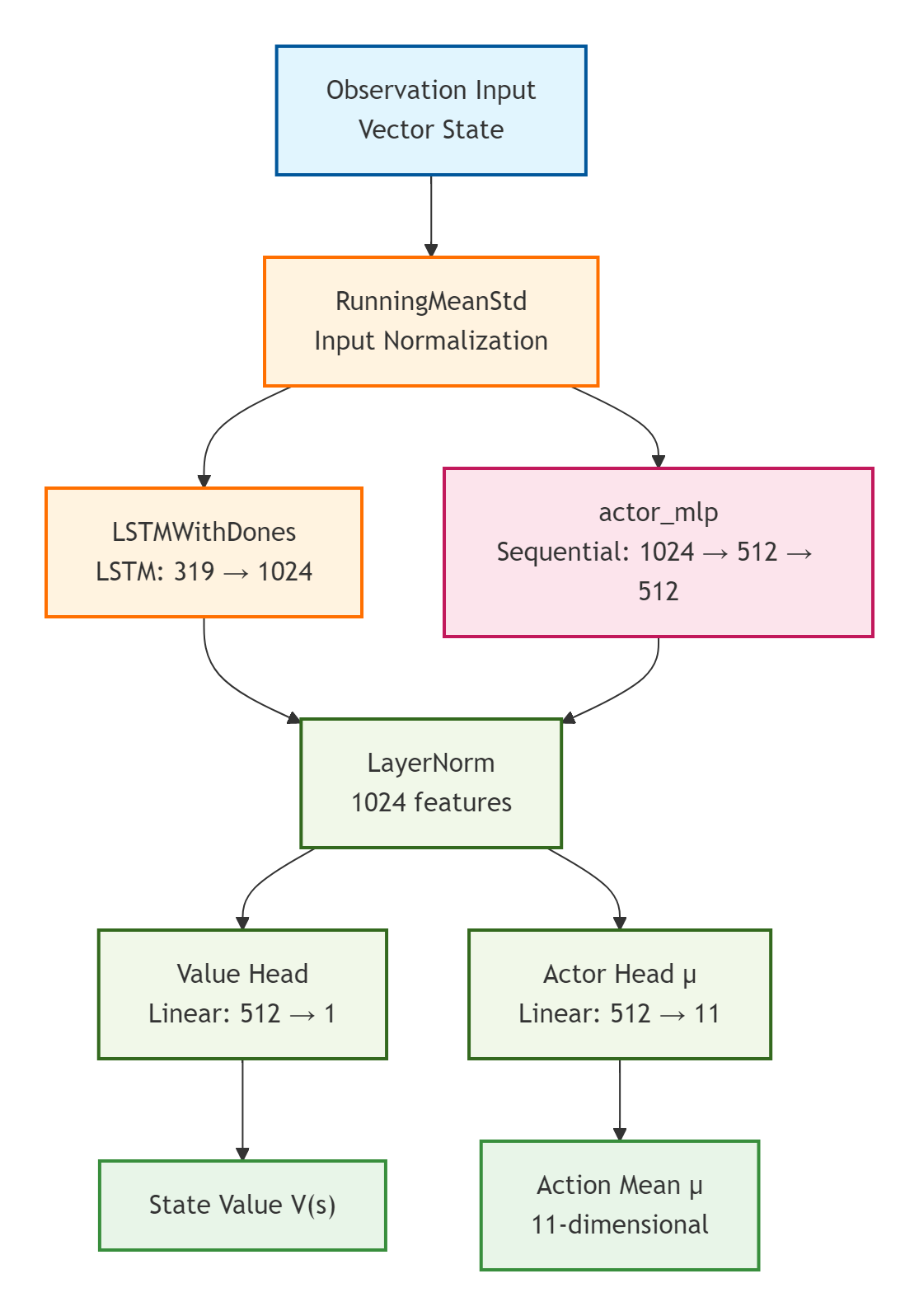
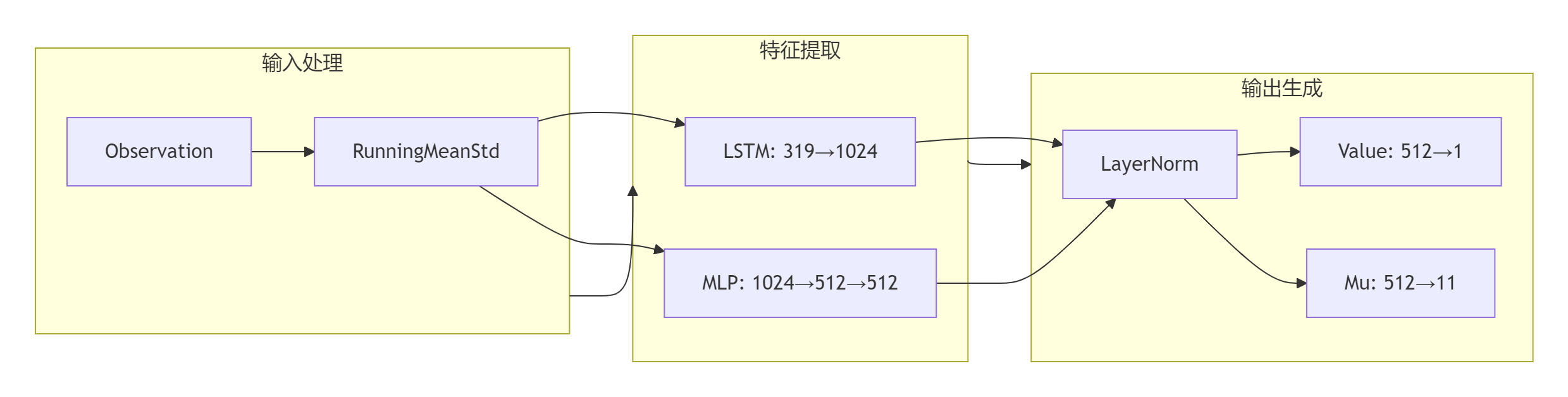
数据流说明
创建教师模型的demo
创建这个特定网络结构的完整代码。
这个网络是一个带有 LSTM 的 Actor-Critic 架构,适用于连续控制任务。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
from typing import Dict, Tuple, Optional
class RunningMeanStd(nn.Module):
"""Running mean and standard deviation normalization"""
def __init__(self, shape: tuple = (1,), epsilon: float = 1e-4):
super().__init__()
self.register_buffer('mean', torch.zeros(shape))
self.register_buffer('var', torch.ones(shape))
self.register_buffer('count', torch.tensor(epsilon))
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Normalize input using running statistics"""
if self.training:
# Update statistics during training
batch_mean = x.mean(dim=0)
batch_var = x.var(dim=0, unbiased=False)
batch_count = x.size(0)
# Update running statistics
delta = batch_mean - self.mean
total_count = self.count + batch_count
self.mean = self.mean + delta * batch_count / total_count
self.var = (self.var * self.count + batch_var * batch_count +
delta ** 2 * self.count * batch_count / total_count) / total_count
self.count = total_count
# Normalize input
return (x - self.mean) / torch.sqrt(self.var + 1e-8)
class LSTMWithDones(nn.Module):
"""LSTM with proper hidden state reset on episode termination"""
def __init__(self, input_size: int, hidden_size: int):
super().__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, batch_first=True)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, dones: torch.Tensor,
hidden_state: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Tuple]:
"""
Args:
x: input tensor of shape (batch, seq_len, input_size)
dones: episode termination flags of shape (batch, seq_len)
hidden_state: previous hidden and cell states
"""
batch_size, seq_len = x.shape[0], x.shape[1]
if hidden_state is None:
# Initialize hidden state
h = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, self.hidden_size, device=x.device)
c = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, self.hidden_size, device=x.device)
hidden_state = (h, c)
# Process sequence through LSTM
lstm_out, (h_n, c_n) = self.lstm(x, hidden_state)
# Reset hidden states where episodes are done
dones = dones.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) # shape: (batch, seq_len, 1, 1)
h_n = h_n * (1 - dones[:, -1:]).transpose(0, 1)
c_n = c_n * (1 - dones[:, -1:]).transpose(0, 1)
return lstm_out, (h_n, c_n)
class A2CNetwork(nn.Module):
"""Core Actor-Critic network with LSTM"""
def __init__(self, obs_size: int, action_size: int = 11,
lstm_hidden_size: int = 1024, mlp_hidden_size: int = 512):
super().__init__()
self.obs_size = obs_size
self.action_size = action_size
self.lstm_hidden_size = lstm_hidden_size
self.mlp_hidden_size = mlp_hidden_size
# Empty CNN components (not used in this configuration)
self.actor_cnn = nn.Sequential()
self.critic_cnn = nn.Sequential()
# Actor MLP
self.actor_mlp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(lstm_hidden_size, mlp_hidden_size),
nn.ELU(),
nn.Linear(mlp_hidden_size, mlp_hidden_size),
nn.ELU()
)
# Critic MLP (empty in your structure)
self.critic_mlp = nn.Sequential()
# LSTM for temporal processing
self.rnn = LSTMWithDones(obs_size, lstm_hidden_size)
# Layer normalization
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(lstm_hidden_size)
# Value head
self.value = nn.Linear(mlp_hidden_size, 1)
self.value_act = nn.Identity()
# Policy head (mu for continuous actions)
self.mu = nn.Linear(mlp_hidden_size, action_size)
self.mu_act = nn.Identity()
# Sigma activation (sigma might be learned separately)
self.sigma_act = nn.Identity()
# Learnable log_std parameter for Gaussian policy
self.log_std = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, action_size))
def forward(self, obs: torch.Tensor, dones: torch.Tensor = None,
hidden_state: Optional[Tuple] = None) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""
Forward pass through the network
Args:
obs: observations of shape (batch, seq_len, obs_size) or (batch, obs_size)
dones: episode termination flags
hidden_state: previous LSTM hidden state
Returns:
Dictionary containing value, action mean, and other outputs
"""
# Handle single step vs sequence input
if len(obs.shape) == 2:
obs = obs.unsqueeze(1) # (batch, 1, obs_size)
if dones is not None:
dones = dones.unsqueeze(1)
batch_size, seq_len = obs.shape[0], obs.shape[1]
# Initialize dones if not provided
if dones is None:
dones = torch.zeros(batch_size, seq_len, device=obs.device)
# Process through LSTM
lstm_out, new_hidden = self.rnn(obs, dones, hidden_state)
# Apply layer normalization
normalized_out = self.layer_norm(lstm_out)
# Process through actor MLP
actor_features = self.actor_mlp(normalized_out)
# Get value and action outputs
value = self.value_act(self.value(actor_features))
mu = self.mu_act(self.mu(actor_features))
# Sigma is typically a learned parameter for Gaussian policy
sigma = torch.exp(self.log_std).expand_as(mu)
return {
'value': value, # State value V(s)
'mu': mu, # Action mean
'sigma': sigma, # Action standard deviation
'hidden_state': new_hidden # New LSTM hidden state
}
def get_action(self, obs: torch.Tensor, hidden_state: Optional[Tuple] = None,
deterministic: bool = False) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""Sample action from policy distribution"""
with torch.no_grad():
output = self.forward(obs.unsqueeze(0), hidden_state=hidden_state)
if deterministic:
action = output['mu']
else:
# Sample from Gaussian distribution
dist = torch.distributions.Normal(output['mu'], output['sigma'])
action = dist.sample()
return {
'action': action.squeeze(0),
'value': output['value'].squeeze(0),
'hidden_state': output['hidden_state'],
'log_prob': dist.log_prob(action).sum(-1) if not deterministic else None
}
class Network(nn.Module):
"""Main network wrapper with normalization"""
def __init__(self, obs_size: int, action_size: int = 11):
super().__init__()
self.value_mean_std = RunningMeanStd(shape=(1,))
self.running_mean_std = RunningMeanStd(shape=(obs_size,))
self.a2c_network = A2CNetwork(obs_size, action_size)
def forward(self, obs: torch.Tensor, dones: torch.Tensor = None,
hidden_state: Optional[Tuple] = None) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
"""Forward pass with input normalization"""
# Normalize observations
normalized_obs = self.running_mean_std(obs)
# Pass through A2C network
return self.a2c_network(normalized_obs, dones, hidden_state)
def get_value_normalized(self, values: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Normalize value outputs"""
return self.value_mean_std(values)
使用示例
def create_and_test_network():
"""创建并测试网络"""
# 网络参数
OBS_SIZE = 319 # LSTM输入维度
ACTION_SIZE = 11 # 连续动作空间维度
BATCH_SIZE = 32
SEQ_LEN = 10
# 创建网络实例
network = Network(obs_size=OBS_SIZE, action_size=ACTION_SIZE)
print("网络结构:")
print(network)
print(f"\n参数数量: {sum(p.numel() for p in network.parameters()):,}")
# 测试前向传播
dummy_obs = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, SEQ_LEN, OBS_SIZE)
dummy_dones = torch.zeros(BATCH_SIZE, SEQ_LEN)
print(f"\n输入形状: {dummy_obs.shape}")
# 前向传播
output = network(dummy_obs, dummy_dones)
print(f"价值输出形状: {output['value'].shape}")
print(f"动作均值形状: {output['mu'].shape}")
print(f"动作标准差形状: {output['sigma'].shape}")
# 测试动作采样
single_obs = torch.randn(OBS_SIZE)
action_output = network.a2c_network.get_action(single_obs)
print(f"\n单步动作采样:")
print(f"动作形状: {action_output['action'].shape}")
print(f"价值形状: {action_output['value'].shape}")
return network
def training_example():
"""训练示例"""
# 创建网络和优化器
network = Network(obs_size=319, action_size=11)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(network.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# 模拟训练循环
for episode in range(100):
# 生成模拟数据
obs_sequence = torch.randn(16, 20, 319) # (batch, seq_len, obs_size)
dones = torch.zeros(16, 20)
targets = torch.randn(16, 20, 1) # 价值目标
# 前向传播
outputs = network(obs_sequence, dones)
# 计算损失(示例)
value_loss = F.mse_loss(outputs['value'], targets)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
value_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if episode % 10 == 0:
print(f"Episode {episode}, Value Loss: {value_loss.item():.4f}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建并测试网络
model = create_and_test_network()
# 运行训练示例
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("开始训练示例...")
training_example()
网络统计
def print_network_details(network):
"""打印网络详细参数信息"""
total_params = 0
print("\n网络各层参数详情:")
print("-" * 60)
for name, module in network.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, (nn.Linear, nn.LSTM, nn.LayerNorm)):
num_params = sum(p.numel() for p in module.parameters())
total_params += num_params
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
print(f"{name:30} | Linear({module.in_features}→{module.out_features}) | {num_params:>8,} params")
elif isinstance(module, nn.LSTM):
print(f"{name:30} | LSTM({module.input_size}→{module.hidden_size}) | {num_params:>8,} params")
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
print(f"{name:30} | LayerNorm({module.normalized_shape}) | {num_params:>8,} params")
print("-" * 60)
print(f"{'总参数数量':30} | {total_params:>8,} params")
# 运行详细分析
network = Network(obs_size=319, action_size=11)
print_network_details(network)
配置类(可选)
class NetworkConfig:
"""网络配置类"""
def __init__(self):
self.obs_size = 319
self.action_size = 11
self.lstm_hidden_size = 1024
self.mlp_hidden_size = 512
self.use_lstm = True
self.use_layer_norm = True
def create_network(self):
"""根据配置创建网络"""
return Network(
obs_size=self.obs_size,
action_size=self.action_size
)
# 使用配置创建网络
config = NetworkConfig()
network = config.create_network()





















 1731
1731

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








