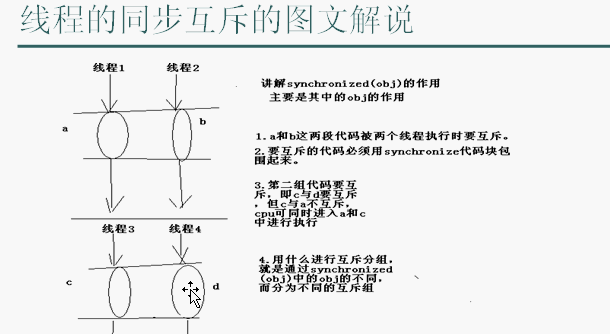
1、使用synchronized代码块
2、使用synchronized方法
3、分析静态方法锁使用的同步监视器对象是什么?
4、wait与notify实现线程间的通信
例一:使用内部类和两个线程交替不停的打印lisi和zhangsan两个名字
public class ThreadSynchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ThreadSynchronized().init();
}
public void init(){
/*在静态方法中不能new内部类的实例对象,
因为内部类的最重要的一个特点就是它可以直接访问它外部类的成员变量。成员变量是对象身上的。对象创建完成了,才会为成员变量分配空间。能调用成员变量,意味着一定有了实例对象.
main方法是静态的,它执行的时候可以不用创建那个对象。这就矛盾了。
*/
final Outputer outputer=new Outputer();//创建内部类
new Thread(new Runnable() {//创建一个线程
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
outputer.output("lisi");
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {//创建一个线程
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
outputer.output("zhangsan");
}
}
}).start();
}
//内部类
class Outputer{
public void output(String name){
int len=name.length();
synchronized (name)
{
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
运行结果为:
lisi
zhangsan
zhangsan
lisi
lisi
zhangsan
lisi
使用synchronized代码块
public class ThreadSynchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ThreadSynchronized().init();
}
public void init(){
/*在静态方法中不能new内部类的实例对象,
因为内部类的最重要的一个特点就是它可以直接访问它外部类的成员变量。成员变量是对象身上的。对象创建完成了,才会为成员变量分配空间。能调用成员变量,意味着一定有了实例对象.
main方法是静态的,它执行的时候可以不用创建那个对象。这就矛盾了。
*/
final Outputer outputer=new Outputer();//创建内部类
new Thread(new Runnable() {//创建一个线程
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
outputer.output("lisi");
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {//创建一个线程
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
outputer.output("zhangsan");
}
}
}).start();
}
//内部类
class Outputer{
public void output(String name){
int len=name.length();
synchronized (this)
{
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadSynchronized {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ThreadSynchronized().init();
}
public void init(){
/*在静态方法中不能new内部类的实例对象,
因为内部类的最重要的一个特点就是它可以直接访问它外部类的成员变量。成员变量是对象身上的。对象创建完成了,才会为成员变量分配空间。能调用成员变量,意味着一定有了实例对象.
main方法是静态的,它执行的时候可以不用创建那个对象。这就矛盾了。
*/
final Outputer outputer=new Outputer();//创建内部类
new Thread(new Runnable() {//创建一个线程
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
outputer.output("lisi");
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {//创建一个线程
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
outputer.output("zhangsan");
}
}
}).start();
}
//内部类
class Outputer{
public synchronized void output(String name){
int len=name.length();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
System.out.print(name.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
例子:子线程循环10次和主线程循环10次,两者实现同步
public class ThreadCommunication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Business business=new Business();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
business.sub(i);
}
}
}).start();
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
business.main(i);
}
}
}
class Business{
public synchronized void sub(int i){
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
System.out.println("sub thread sequence of"+j+",loop of"+i);
}
}
public synchronized void main(int i){
for(int j=0;j<100;j++){
System.out.println("main thread sequence of"+j+",loop of"+i);
}
}
} 例子:子线程循环10次和主线程循环10次,两者交替运行50次的例子
public class ThreadCommunication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Business business=new Business();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
business.sub(i);
}
}
}).start();
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
business.main(i);
}
}
}
class Business{
private boolean bSholdSub=true;
public synchronized void sub(int i){
if(!bSholdSub){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
System.out.println("sub thread sequence of"+j+",loop of"+i);
}
bSholdSub=false;
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void main(int i){
if(bSholdSub){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
for(int j=0;j<10;j++){
System.out.println("main thread sequence of"+j+",loop of"+i);
}
bSholdSub=true;
this.notify();
}
}运行结果为:
sub thread sequence of0,loop of0
sub thread sequence of1,loop of0
sub thread sequence of2,loop of0
sub thread sequence of3,loop of0
sub thread sequence of4,loop of0
sub thread sequence of5,loop of0
sub thread sequence of6,loop of0
sub thread sequence of7,loop of0
sub thread sequence of8,loop of0
sub thread sequence of9,loop of0
main thread sequence of0,loop of0
main thread sequence of1,loop of0
main thread sequence of2,loop of0
main thread sequence of3,loop of0
main thread sequence of4,loop of0
main thread sequence of5,loop of0
main thread sequence of6,loop of0
main thread sequence of7,loop of0
main thread sequence of8,loop of0main thread sequence of9,loop of0
sub thread sequence of0,loop of0
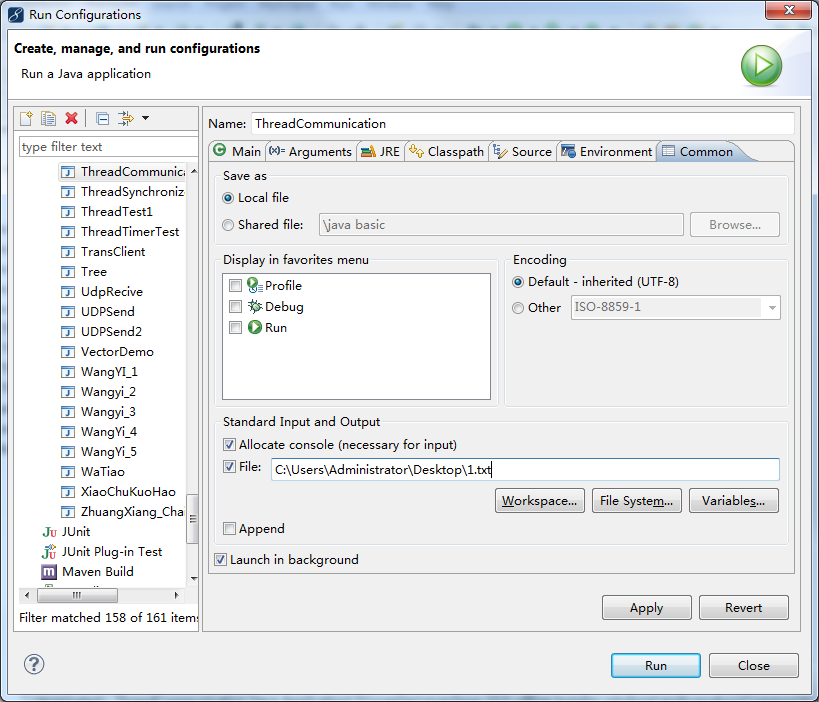
为了观察程序的运行结果,可以在myeclipse中设置运行对话框,让结果重定向到一个文本文件,然后去查看该文本文件中的特殊行号是否正好对应了线程的切换点。
RUN AS-->Run Configurations-->右边Common-->File前面打钩,--》输入路径,比如输入C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\1.txt,最后点击run,就可在选择路径下看到运行程序的结果。
经验:要用到共同数据(包括同步锁)的若干个方法应该归在同一个类上,这个设计正好体现了高内聚和程序的健壮性。





 本文介绍了Java中线程同步的三种方式:使用synchronized代码块、synchronized方法及线程间如何通过wait与notify进行通信。通过示例代码详细展示了不同同步方式的具体应用,并演示了如何使两个线程交替执行。
本文介绍了Java中线程同步的三种方式:使用synchronized代码块、synchronized方法及线程间如何通过wait与notify进行通信。通过示例代码详细展示了不同同步方式的具体应用,并演示了如何使两个线程交替执行。
















 343
343

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








