Abstract
Over the past decade, multivariate time series classification has
received great attention. We propose transforming the existing
univariate time series classification models, the Long Short Term
Memory Fully Convolutional Network (LSTM-FCN) and Attention LSTM-FCN (ALSTM-FCN), into a multivariate time series classification model by
augmenting the fully convolutional block with a squeeze-and-excitation
block to further improve accuracy. Our proposed models outperform most
state-of-the-art models while requiring minimum preprocessing. The
proposed models work efficiently on various complex multivariate time
series classification tasks such as activity recognition or action
recognition. Furthermore, the proposed models are highly efficient at
test time and small enough to deploy on memory constrained systems.
在过去的几十年里,多变量时间序列分类问题引起了广泛的关注。我们提出转换现存的单变量时间序列分类模型:长短期记忆全卷积神经网络和注意力LSTM-FCN,转换为多变量时间序列分类模型通过应用挤压-激励块到FCN中去提升准确性。我们提出的模型表现优于最先进的模型,同时需要最少的预处理。这提出的模型在各种复杂的多变量时间上有效工作实现分类任务,如活动识别或操作认可。此外,所提出的模型在测试时十分高效,并且足够小,可以在内存受限的系统上部署。
1.Introduction
Time series data is used in various fields of studies, ranging from
weather readings to psychological signals [1, 2, 3, 4]. A time series
is a sequence of data points in a time domain, typically in a uniform
interval [5]. There is a significant increase of time series data
being collected by sensors [6]. A time series dataset can be
univariate, where a sequence of measurements from the same variable
are collected, or multivariate, where a sequence of measurements from
multiple variables or sensors are collected [7]. Over the past decade,
multivariate time series classification has received significant
interest. Multivariate time series classifications are applied in
healthcare [8], phoneme classification [9], activity recognition,
object recognition, and action recognition [10, 11, 12, 13]. In this
paper, we propose two deep learning models that outperform existing
algorithms.
时间序列被很多研究领域所使用,从天气读数与心理信号。时间序列是时域中的一系列数据点,通常采用统一间隔。
Several time series classification algorithms have been developed
over the years. Distance based methods along with k-nearest neighbors
have proven to be successful in classifying multivariate time series [14]. Plenty of research indicates Dynamic Time Warping (DTW)
as the best distance-based measure to use along k-NN [15].
一些时间序列分类算法在这些年中被开发了出来。基于距离的k近邻算法已经在分类多变量时间序列中取得了成功,大量研究表明动态时间规划 (DTW)是沿 k-NN 使用的最佳基于距离的方法 [15]。
In addition to distance-based metrics, other algorithms are used.
Typically, featurebased classification algorithms rely heavily on the
features being extracted from the time series data [16]. However,
feature extraction is arduous because intrinsic features of time
series data are challenging to capture. For this reason,
distance-based approaches are more successful in classifying
multivariate time series data [17]. Hidden State Conditional Random
Field (HCRF) and Hidden Unit Logistic Model (HULM) are two successful
feature-based algorithms which have led to state-of-the-art results on
various benchmark datasets, ranging from online character recognition
to activity recognition [18]. HCRF is a computationally expensive
algorithm that detects latent structures of the input time series data
using a chain of k-nominal latent variables. The number of parameters
in the model increases linearly with the total number of latent states
required [19]. Further, datasets that require a large number of latent
states tend to overfit the data. To overcome this, HULM proposes using
H binary stochastic hidden units to model 2H latent structures of the
data with only O(H) parameters. Results indicate HULM outperforming
HCRF on most datasets [18]
Traditional models, such as the naive logistic model (NL) and Fisher
kernel learning (FKL) [20], show strong performance on a wide variety
of time series classification problems. The NL logistic model is a
linear logistic model that makes a prediction by summing the inner
products between the model weights and feature vectors over time,
which is followed by a softmax function [18]. The FKL model is
effective on time series classification problems when based on Hidden
Markov Models (HMM). Subsequently, the features or representation from
the FKL model is used to train a linear SVM to make a final
prediction. [20, 21]
传统的模型,比如NL模型在诸多时间序列的分类问题上展现出了很好的性能。NL逻辑模型是一个线性逻辑模型,其通过对内部求和进行预测随时间推移在模型权重和特征向量之间乘积,其后紧跟为softmax函数。
Another common approach for multivariate time series classification is
by applying dimensional reduction techniques or by concatenating all
dimensions of a multivariate time series into a univariate time
series. Symbolic Representation for Multivariate Time Series (SMTS)
[22] applies a random forest on the multivariate time series to
partition it into leaf nodes, each represented by a word to form a
codebook. Every word is used with another random forest to classify
the multivariate time series. Learned Pattern Similarity (LPS) [23] is
a similar model that extracts segments from the multivariate time
series. These segments are used to train regression trees to find
dependencies between them. Each node is represented by a word.
Finally, these words are used with a similarity measure to classify
the unknown multivariate time series. Ultra Fast Shapelets (UFS) [24]
obtains random shapelets from the multivariate time series and applies
a linear SVM or a Random Forest classifier. Subsequently, UFS was
enhanced by computing derivatives as features (dUFS) [24]. The
Auto-Regressive (AR) kernel [25] applies an AR kernel-based distance
measure to classify the multivariate time series. Auto-Regressive
forests for multivariate time series modeling (mv-ARF) [26] uses a
tree ensemble, where the trees are trained with different time lags.
Most recently, WEASEL+MUSE [27] builds a multivariate feature vector
using a classical bag of patterns approach on each variable with
various sliding window sizes to capture discrete features, words, and
pairs of words. Subsequently, feature selection is used to remove
non-discriminative features using a Chi-squared test. The final
classification is obtained using a logistic classifier on the final
feature vector.
Deep learning has also yielded promising results for multivariate time
series classification. In 2014, Yi et al. propose using Multi-Channel
Deep Convolutional Neural Network (MCDCNN) for multivariate time
series classification. MC-DCNN takes input from each variable to
detect latent features. The latent features from each channel are fed
into an MLP to perform classification [17]. This paper proposes two
deep learning models for multivariate time series classification.
These proposed models require minimal preprocessing and are tested on
35 datasets, obtaining strong performances in most of them.
Performance is the classification accuracy of a model on a particular
dataset. The rest of the paper is ordered as follows. Background works
are discussed in Section 2. We present the architecture of the two
proposed models in Section 3. In Section 4, we discuss the dataset,
evaluate the models on them, present our results and analyze our
findings. In Section 5, we draw our conclusion.
2.Background Works
2.1Recurrent Neural Networks
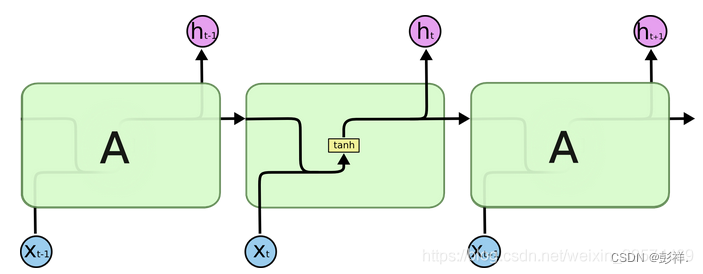
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) are a form of neural networks that
display temporal behavior through the direct connections betw





 本文提出了一种新的多变量时间序列分类模型,该模型通过在全卷积块中加入挤压-激励块,改进了现有的单变量时间序列分类模型。新模型在多个数据集上表现优秀,且对数据预处理要求较低。
本文提出了一种新的多变量时间序列分类模型,该模型通过在全卷积块中加入挤压-激励块,改进了现有的单变量时间序列分类模型。新模型在多个数据集上表现优秀,且对数据预处理要求较低。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1024
1024

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










