点击查看剑指Offer全解【Java & Golang】实现
题目描述
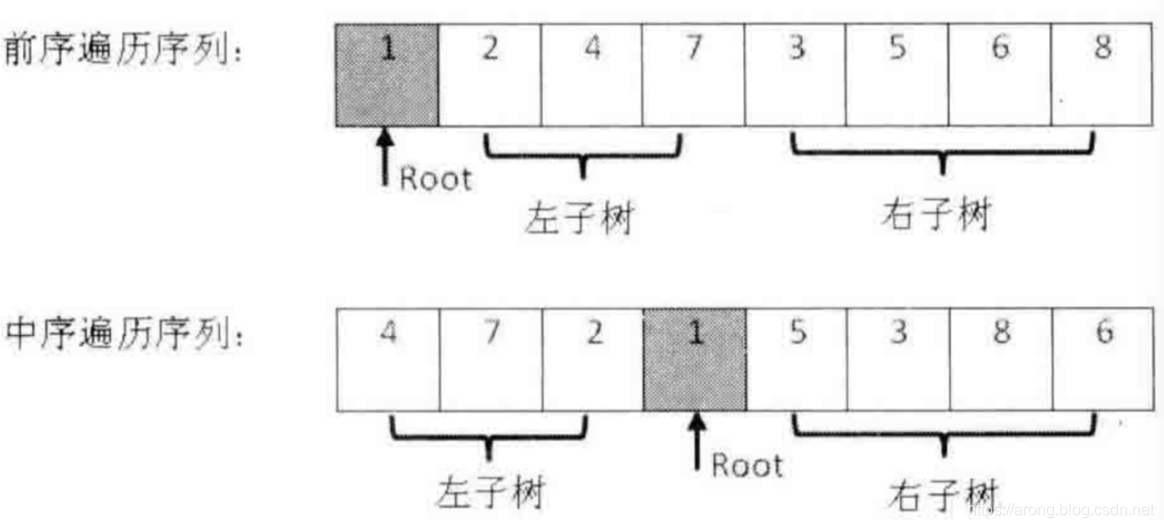
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
思路
前序遍历:跟节点 + 左子树前序遍历 + 右子树前序遍历
中序遍历:左子树中序遍历 + 跟节点 + 右字数中序遍历
后序遍历:左子树后序遍历 + 右子树后序遍历 + 跟节点
根据上面的规律:
前序遍历找到根结点root
找到root在中序遍历的位置 -> 左子树的长度和右子树的长度 ->
截取左子树的中序遍历、右子树的中序遍历 ->
截取左子树的前序遍历、右子树的前序遍历 ->
递归重建二叉树
Java第一种做法【传递数组索引定位,高效,但比较复杂】
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
return helper(pre, in, 0, pre.length - 1, 0, in.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode helper(int[] pre, int[] in, int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight) {
//
if (preLeft > preRight || inLeft > inRight) {
return null;
}
// 由前序遍历序列获取根节点
int rootValue = pre[preLeft];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
// 在中序遍历序列中,搜索出根节点的位置
int index = findRootIndex(rootValue, in);
// 通过根节点位置,在中序遍历序列中可划分出左子树和右子树的中序遍历序列
// 在前序遍历中,可划分出左子树和右子树的前序遍历序列,继续递归地构建树
// preLeft + index - inLeft:通过preLeft + 左子树节点数(index - inLeft)确定左子树前序遍历的右边界
// preLeft + index - inLeft + 1:通过左子树前序遍历序列的右边界+1确定右子树前序遍历序列的左边界
root.left = helper(pre, in, preLeft + 1, preLeft + index - inLeft, inLeft, index - 1);
root.right = helper(pre, in, preLeft + index - inLeft + 1, preRight, index + 1, inRight);
return root;
}
private int findRootIndex(int target, int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Java第二种做法 【使用Arrays工具类复制数组,比较占用空间,但简洁】
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
// 当前序遍历序列或后序遍历序列为空时,说明该节点为空节点
if (pre.length == 0 || in.length == 0) {
return null;
}
// 由前序遍历序列获取根节点
int rootValue = pre[0];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
// 在中序遍历序列中,搜索出根节点的位置
int index = findRootIndex(rootValue, in);
// 通过根节点位置,在中序遍历序列中可划分出左子树和右子树的中序遍历序列
// 在前序遍历中,可划分出左子树和右子树的前序遍历序列,继续递归地构建树
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(
Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, index + 1),
Arrays.copyOfRange(in, 0, index)
);
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(
Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, index + 1, pre.length),
Arrays.copyOfRange(in, index + 1, in.length)
);
return root;
}
private int findRootIndex(int target, int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
Golang第一种做法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func buildTree(pre []int, in []int) *TreeNode {
return helper(pre, in, 0, len(pre) - 1, 0, len(in) - 1)
}
func helper(pre []int, in []int, preLeft int, preRight int, inLeft int, inRight int) *TreeNode{
if preLeft > preRight || inLeft > inRight {
return nil
}
var rootValue int = pre[preLeft]
var root *TreeNode = &TreeNode{rootValue, nil, nil}
var index = findRootIndex(rootValue, in)
root.Left = helper(pre, in, preLeft + 1, preLeft + index - inLeft, inLeft, index - 1)
root.Right = helper(pre, in, preLeft + index - inLeft + 1, preRight, index + 1, inRight)
return root
}
func findRootIndex(target int, array []int) int{
for i := 0; i < len(array); i++ {
if array[i] == target {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
Golang第二种做法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func buildTree(pre []int, in []int) *TreeNode {
if len(pre) == 0 || len(in) == 0 {
return nil
}
var rootValue int = pre[0]
var root *TreeNode = &TreeNode{rootValue, nil, nil}
var index = findRootIndex(rootValue, in)
root.Left = buildTree(pre[1:index + 1], in[0:index])
root.Right = buildTree(pre[index + 1:], in[index + 1:])
return root
}
func findRootIndex(target int, array []int) int{
for i := 0; i < len(array); i++ {
if array[i] == target {
return i
}
}
return -1
}





 本文介绍了一种利用前序和中序遍历结果重建二叉树的算法,提供了Java和Golang两种语言的实现方式,详细解析了算法的思路与步骤。
本文介绍了一种利用前序和中序遍历结果重建二叉树的算法,提供了Java和Golang两种语言的实现方式,详细解析了算法的思路与步骤。

















 244
244

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










