1、桑基图—echarts
桑基图是一种用于表示流动或关系的可视化图表,特别适合展示数据的流向和相对大小。
桑基图通过箭头的宽度表示流量的大小,通常用于展示各个节点之间的流动关系。节点表示数据的来源和去向,箭头表示流动的量。
1.1 数据结构
ECharts 桑基图需要两部分数据:data 和 links。
data:节点数据,包含节点名称。
links:连接数据,定义流动的来源、目标和流量值。
下方图是我们的目标结果:

<template>
<div class="data-work">
<div ref="chartRef" style="max-width: 1850px; height: 400px"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref, nextTick, onMounted } from 'vue';
import * as echarts from 'echarts';
const chartRef = ref();
const chart = ref();
const options = ref({
animation: true,
animationThreshold: 2000,
animationDuration: 1000,
animationEasing: 'cubicOut',
animationDelay: 0,
animationDurationUpdate: 300,
animationEasingUpdate: 'cubicOut',
animationDelayUpdate: 0,
hoverLayerThreshold: 3000,
series: {
type: 'sankey',
layout: 'none',
// focusNodeAdjacency: 'outEdges',
// silent: true, //取消hover效果
data: [],
links: [],
itemStyle: {
borderColor: 'transparent', // 设置边框颜色为透明
borderWidth: 0, // 或者直接设置宽度为0
// color: '#409eff', // 你可以设置节点的填充颜色
},
left: '0',
top: '24px',
right: '300px',
bottom: '8px',
nodeWidth: 30,
nodeGap: 16,
nodeAlign: 'left', // 桑基图中节点的对齐方式,默认是双端对齐
layoutIterations: 0, // 如果希望图中节点的顺序是按照原始 data 中的顺序排列的,可设该值为 0。否则是按照大小排列
orient: 'horizontal',
draggable: true,
levels: [
{
depth: 0,
itemStyle: {
color: '#8B7EFF', //图形的颜色
},
lineStyle: {
show: true,
width: 2,
opacity: 0.1,
curveness: 0.5,
type: 'solid',
color: 'source',
},
},
{
depth: 1,
itemStyle: {
color: '#8B7EFF',
},
lineStyle: {
show: true,
width: 1,
opacity: 0.1,
curveness: 0.5,
type: 'solid',
color: 'source',
},
},
{
depth: 2,
itemStyle: {
color: '#8B7EFF',
},
lineStyle: {
show: true,
width: 1,
opacity: 0.1,
curveness: 0.5,
type: 'solid',
color: 'source',
},
},
{
depth: 3,
itemStyle: {
color: '#8B7EFF',
},
lineStyle: {
show: true,
width: 1,
opacity: 0.1,
curveness: 0.5,
type: 'solid',
color: 'source',
},
},
],
label: {
show: true,
position: 'right',
margin: 8,
fontSize: 12,
formatter: (params: any) => {
return `${params.name} ${params.data.value} (${params.data.rate})`;
},
},
lineStyle: {
show: true,
width: 1,
opacity: 0.2,
curveness: 0.5,
type: 'solid',
color: 'source',
},
},
aria: {
enabled: false,
},
color: ['#5470c6', '#91cc75', '#fac858', '#ee6666', '#73c0de', '#3ba272', '#fc8452', '#9a60b4', '#ea7ccc'],
tooltip: {
show: true,
trigger: 'item',
triggerOn: 'mousemove|click',
axisPointer: {
type: 'line',
},
showContent: true,
alwaysShowContent: false,
showDelay: 0,
hideDelay: 100,
enterable: false,
confine: false,
appendToBody: false,
transitionDuration: 0.4,
textStyle: {
fontSize: 14,
// color: '#fff',
},
borderWidth: 0,
padding: 16,
order: 'seriesAsc',
backgroundColor: 'rgba(0,0,0,0.8)',
formatter: (params) => {
if (params.data.source) { //自定义tooltip 模板字符串
const html = `<div style="height:auto;">
<div style="display:flex;align-items:center;justify-content:space-between;font-size:12px;line-height:1;">
<span style="display:inline-block;width:8px;height:8px;background:#8b7efe;margin-right:5px;"></span>
<span style="display:inline-block;margin-right:25px;">${params.data.source}—>${params.data.target}</span>
<span>${(params.data.value, 1)}(${params.data.rate})</span>
</div>
</div>`;
return html;
}
const html = `<div style="height:auto;">
<div style="display:flex;align-items:center;justify-content:space-between;font-size:12px;line-height:1;">
<span style="display:inline-block;width:8px;height:8px;background:#8b7efe;margin-right:5px;"></span>
<span style="display:inline-block;margin-right:25px;">${params.name}</span>
<span>${params.data.value}(${params.data.rate})</span>
</div>
</div>`;
return html;
},
},
});
// 重新设置options
const setOption = (chartDataInfo) => {
if (chart.value) {
chart.value.dispose();
}
if (!chartRef.value) {
return;
}
const { flow_data, node_data } = chartDataInfo;
if (!flow_data?.length) {
const optionEmpty = {
title: {
text: '暂无数据',
left: 'center',
top: 'center',
textStyle: {
fontSize: 20,
color: '#999',
},
},
tooltip: {
show: false, // 隐藏 tooltip
},
series: [], // 不显示任何系列
};
chart.value = echarts.init(chartRef.value, 'white', { renderer: 'canvas' });
chart.value.setOption(optionEmpty);
return;
}
options.value.series.links = flow_data;
options.value.series.data = node_data;
nextTick(() => {
chart.value = echarts.init(chartRef.value, 'white', { renderer: 'canvas' });
chart.value.setOption(options.value);
});
};
onMounted(() => {
const chartDataInfo = {
flow_data: [],
node_data: [],
};
setOption(chartDataInfo);
});
</script>
数据结构示例:
links:
flow_data: [
{
source: 'SG-A', //边的源节点名称
target: '汇总', //边的目标节点名称
value: 10, //边的数值,决定边的宽度。
rate: '10%', //这个是自定义要展示的字段
},
{
source: 'SG-B',
target: '汇总',
value: 50,
rate: '50%',
},
{
source: 'SG-C',
target: '汇总',
value: 40,
rate: '60%',
},
{
source: '汇总',
target: '抖音',
value: 50,
rate: '50%',
},
{
source: '汇总',
target: 'B站',
value: 20,
rate: '20%',
},
{
source: '汇总',
target: '小红书',
value: 8,
rate: '8%',
},
{
source: '汇总',
target: '快手',
value: 10,
rate: '10%',
},
{
source: '汇总',
target: '微博',
value: 8,
rate: '8%',
},
{
source: '汇总',
target: '虎牙',
value: 4,
rate: '4%',
},
{
source: '抖音',
target: '抖音-a',
value: 10,
rate: '10%',
},
{
source: '抖音',
target: '抖音-b',
value: 30,
rate: '30%',
},
{
source: '抖音',
target: '抖音-c',
value: 10,
rate: '10%',
},
{
source: 'B站',
target: 'B站-a',
value: 5,
rate: '5%',
},
{
source: 'B站',
target: 'B站-b',
value: 10,
rate: '10%',
},
{
source: 'B站',
target: 'B站-c',
value: 5,
rate: '5%',
},
],
data:
node_data: [
{
name: '汇总',
rate: '100%',
value: '100',
},
{
name: 'SG-A',
rate: '10%',
value: '10',
},
{
name: 'SG-B',
rate: '50%',
value: '50',
},
{
name: 'SG-C',
rate: '40%',
value: '40',
},
{
name: '抖音',
rate: '50%',
value: '50',
},
{
name: 'B站',
rate: '20%',
value: '20',
},
{
name: '小红书',
rate: '8%',
value: '8',
},
{
name: '快手',
rate: '10%',
value: '10',
},
{
name: '微博',
rate: '8%',
value: '8',
},
{
name: '虎牙',
rate: '4%',
value: '4',
},
{
name: '抖音-a',
rate: '10%',
value: '10',
},
{
name: '抖音-b',
rate: '30%',
value: '30',
},
{
name: '抖音-c',
rate: '10%',
value: '10',
},
{
name: 'B站-a',
rate: '5%',
value: '5',
},
{
name: 'B站-b',
rate: '10%',
value: '10',
},
{
name: 'B站-c',
rate: '5%',
value: '5',
},
],
1、请求数据后首次加载图表渲染失败:
原因:dom节点没加载出来
解决方案: nextTick()
2、图表从上到下排列顺序与数据返回顺序不一致
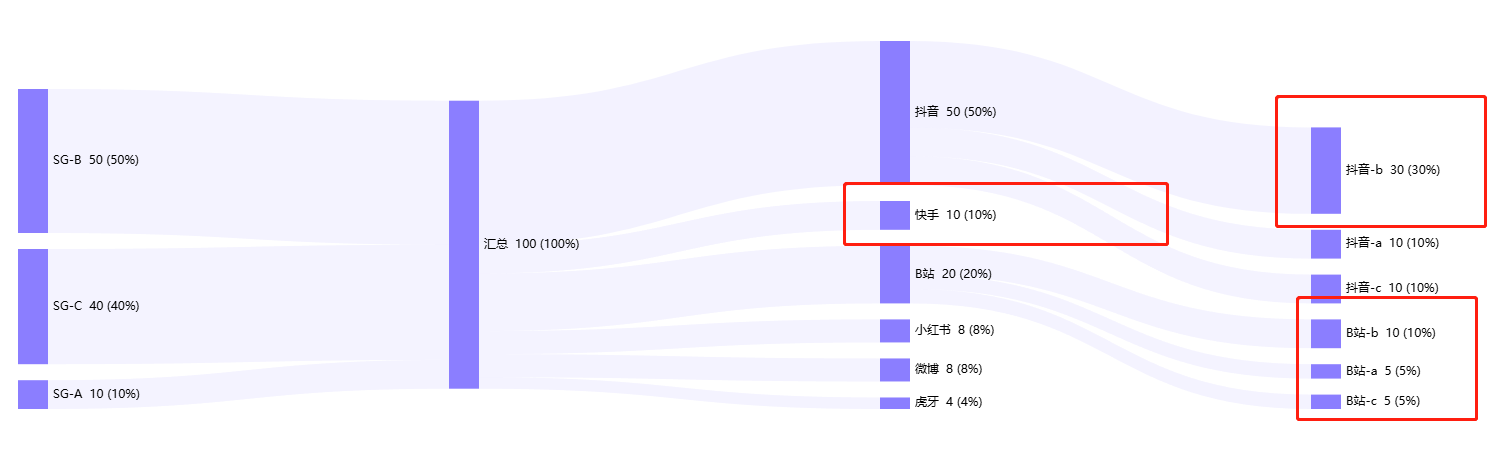
原因:默认按数据大小排列
解决方案:layoutIterations: 0
3、图表第4列没有数据时,默认第三列节点在第四列
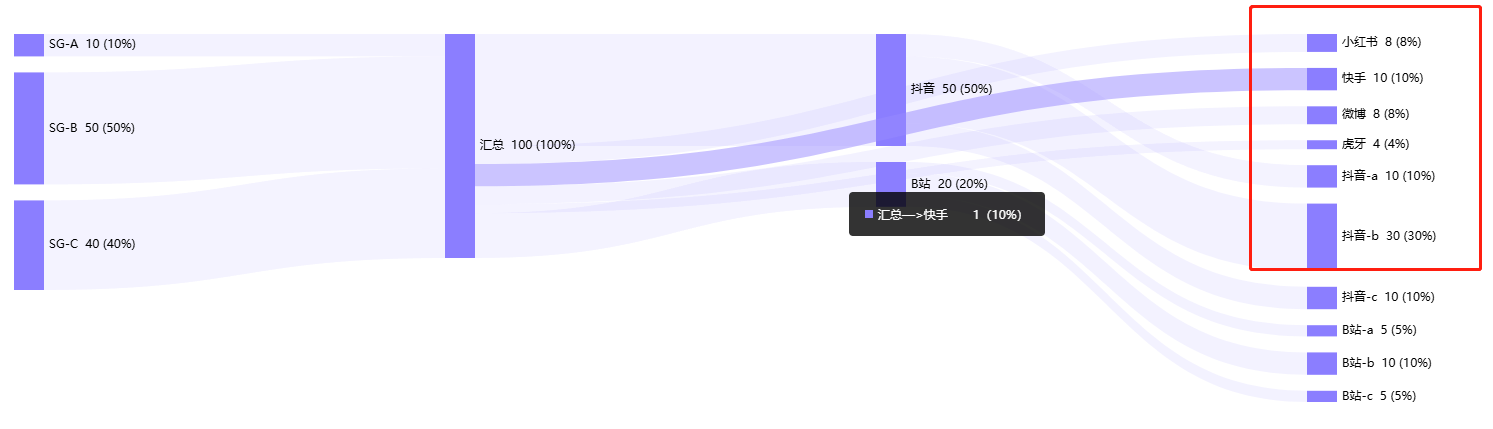
解决方案:nodeAlign:left ,该属性是节点的对齐方式
4、设置节点矩形的样式有两种方式:
统一设置:
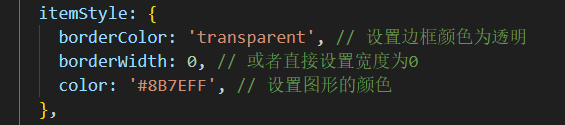
单独设置每一列的:
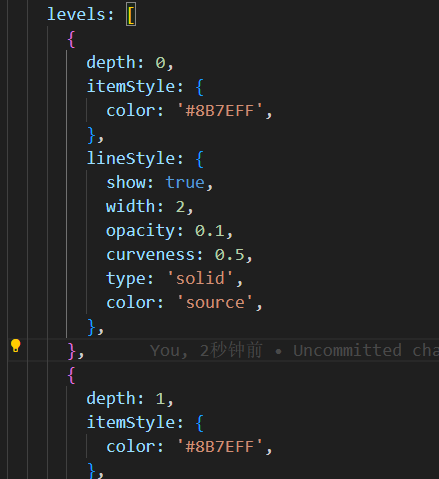
5、tooltip、文案展示等自定义样式可通过模板字符串实现,但是不支持图标、图片
6、注意:返回数据节点不能有重复,否则渲染失败;
2、柱状图–自定义tooltip样式以及字段展示—-G2
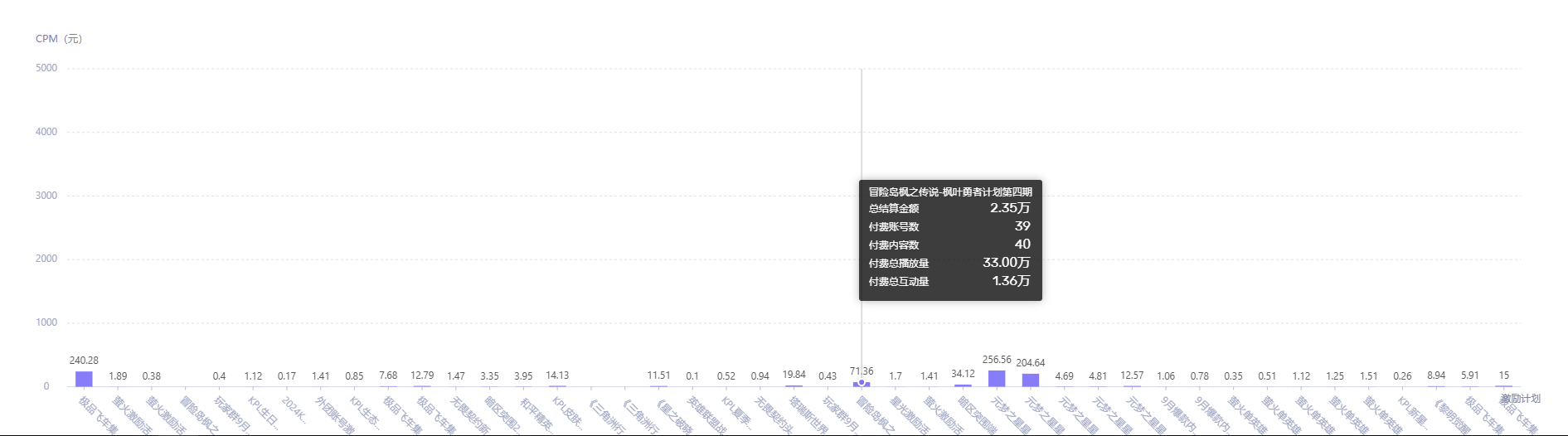
通常tooltip展示的都是key和value值,即横坐标与纵坐标对应的值,如果需要额外展示其他字段,则需要自定义写
数据结构:
在原有数据结构中,加入一个数组,如下proList数组,tooltip的数据展示则可以遍历该数组(如果多嵌套一层对象的话,tooltip那边拿不到值,比如{proObj:{name:‘其他1’}})拿不到proObj.name,只能直接拿到第一层)
data=[
{
key:'label名称',
value: 1000,
proList:[
{
name:'其他1',
value: 20
},
{
name:'其他2',
value: 30
},
{
name:'其他3',
value: 40
},
{
name:'其他4',
value: 50
},
]
}
]
用模板字符串定义html,插入到图表中,下面码代码用来遍历数组
const itemTpl =
'<li data-index={index}>' +
'<span style="background-color:{color};width:8px;height:8px;border-radius:50%;display:inline-block;margin-right:8px;"></span>' +
'{name}: <span class="g2-tooltip-value" style="display:inline-block;"><span class="g2-tooltip-num">{numValue}</span>{chineseValue}</span></li>';
chart.value.tooltip({
// 处理数据
customItems: (items) => {
console.log(items);
items.forEach((v) => {
const str = v.value.match(/[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+/g);
v.chineseValue = str ? str[0] : ''; // 中文
v.numValue = v.chineseValue ? v.value.replace(v.chineseValue, '') : v.value;
let elementStr = '';
v.data.proList.forEach((ele) => {
elementStr += `<div style="padding:0 0 10px;">${
ele.name
} <span class="g2-tooltip-value" style="display:inline-block;"><span class="g2-tooltip-num">${formatBigNumberToZhY(
ele.value,
2,
)}</span></span></div>`;
});
v.elementStr = elementStr;
});
return items;
},
showCrosshairs: true, // 辅助线
shared: true,
containerTpl:
'<div class="g2-tooltip">' +
'<div class="g2-tooltip-title" style="margin:10px 0;"></div>' +
'<ul class="g2-tooltip-list"></ul></div>',
itemTpl,
});
数据过多时,柱状图部分label缺失
原因:每条数据的柱状图展示间距不够
解决方案:categorySize的值设置大点
chart.value.option(‘scrollbar’, {
type: ‘horizontal’,
categorySize: 40,
});
3、条形图—G2
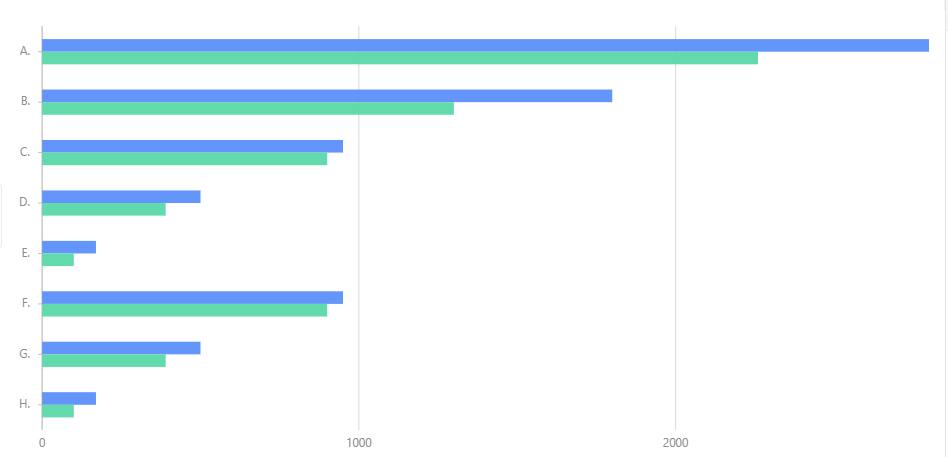
数据:
const data = [
{ label: 'A.', type: 'series1', value: 2800 },
{ label: 'A.', type: 'series2', value: 2260 },
{ label: 'B.', type: 'series1', value: 1800 },
{ label: 'B.', type: 'series2', value: 1300 },
{ label: 'C.', type: 'series1', value: 950 },
{ label: 'C.', type: 'series2', value: 900 },
{ label: 'D.', type: 'series1', value: 500 },
{ label: 'D.', type: 'series2', value: 390 },
{ label: 'E.', type: 'series1', value: 170 },
{ label: 'E.', type: 'series2', value: 100 },
{ label: 'F.', type: 'series1', value: 950 },
{ label: 'F.', type: 'series2', value: 900 },
{ label: 'G.', type: 'series1', value: 500 },
{ label: 'G.', type: 'series2', value: 390 },
{ label: 'H.', type: 'series1', value: 170 },
{ label: 'H.', type: 'series2', value: 100 },
];
不需要滚动条的情况下,可以通过以下方法实现:
const chart = new Chart({
container: 'container',
autoFit: true,
height: 500,
});
chart.data(data);
chart
.coordinate()
.transpose()
.scale(1, -1);
chart.axis('value', {
position: 'right',
});
chart.axis('label', {
label: {
offset: 12,
},
});
chart
.interval()
.position('label*value')
.color('type')
.adjust([
{
type: 'dodge',
marginRatio: 0,
},
]);
chart.interaction('active-region');
chart.render();
chart.coordinate() .transpose().scale(1, -1);
transpose是将X、Y轴互换,scale(1, -1) 是保持 X 轴的规模不变,而将 Y 轴的方向反转(即 Y 轴的值从上到下递减,而不是从下到上递增)
下方图是不设置scale(1, -1)
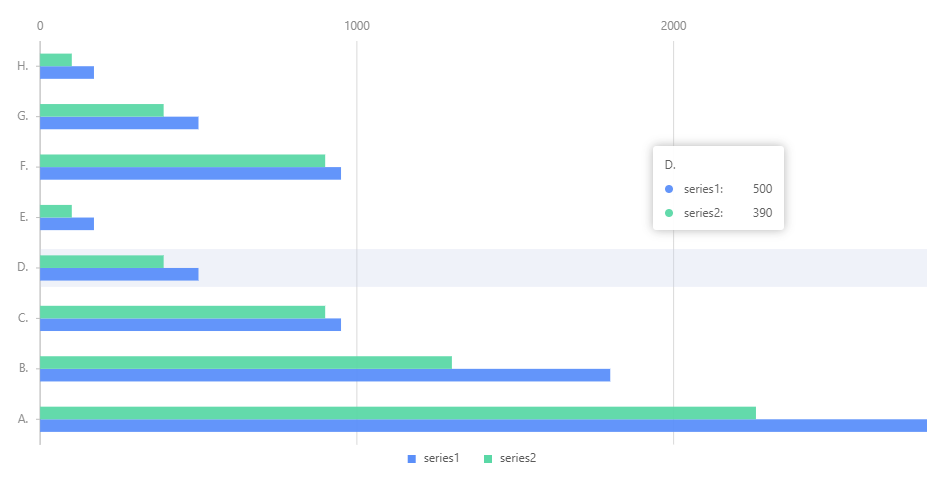
但是这种写法如果使用滚动条,就会有问题
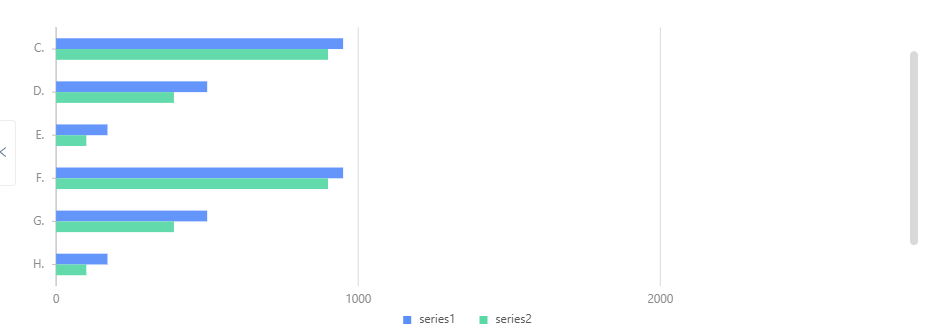

所以这里换一种写法:
1、引入g2的内置方法
import { DataView } from ‘@antv/data-set’;
2、使用里面的方法进行数据倒序排列
const dv = new DataView().source(data);
dv.transform({
type: ‘reverse’,
});
console.log(dv.rows)
此时的数据就是完全倒序排列,如下:
[
{
“label”: “H.”,
“type”: “series2”,
“value”: 100
},
{
“label”: “H.”,
“type”: “series1”,
“value”: 170
},
…
{
“label”: “A.”,
“type”: “series2”,
“value”: 2260
},
{
“label”: “A.”,
“type”: “series1”,
“value”: 2800
}
]
chart.data(dv.rows);
chart.coordinate().transpose();
chart.option(‘scrollbar’, {
type: ‘vertical’,
categorySize: 40,
animate: false,
});
这里就不需要使用scale(1,-1);
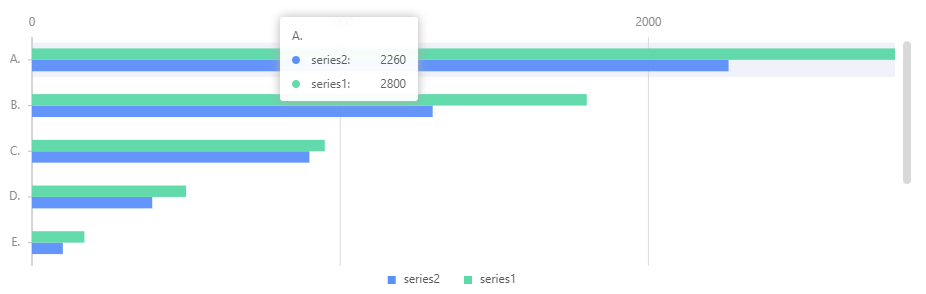
这里我们发现tooltip的展示数据并不是我们想要的顺序,则进行如下处理:
将tooltip也进行倒序排列:




















 1807
1807

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








