1、已知一张user用户表,每个用户都有一个最新的版本号:
(1)查询所有版本号使用的人数,并倒叙排序
select count(version) from user group by version desc;
(2)统计每个版本号用户总数大于1000的版本号以及总数
select version ,count(version) from user group by version having count(version)>1000;
(3)统计符合这样的版本号有多少个
select count(*) from (selct version ,count(version) from user group by version having count(version)>1000;)
2、有以下两张表
| 表名:department | |
| id | name |
| 200 | 技术 |
| 201 | 人力资源 |
| 202 | 销售 |
| 203 | 运营 |
| 表名:employeel | ||||
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id |
| 1 | egon | man | 18 | 200 |
| 2 | alex | man | 48 | 201 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | woman | 38 | 201 |
| 4 | yuanhao | woman | 28 | 202 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | man | 18 | 200 |
| 6 | jiangli | man | 18 | 204 |
建表以及新增数据sql
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL
)
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`department` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('200', '技术');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`department` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('201', '人力资源');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`department` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('202', '销售');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`department` (`id`, `name`) VALUES ('203', '运营');
CREATE TABLE `employee1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` enum('male','female') COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT 'male',
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`dep_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`employee1` (`id`, `name`, `sex`, `age`, `dep_id`) VALUES ('1', 'egon', 'male', '18', '200');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`employee1` (`id`, `name`, `sex`, `age`, `dep_id`) VALUES ('2', 'alex', 'female', '48', '201');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`employee1` (`id`, `name`, `sex`, `age`, `dep_id`) VALUES ('3', 'wupeiqi', 'male', '38', '201');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`employee1` (`id`, `name`, `sex`, `age`, `dep_id`) VALUES ('4', 'yuanhao', 'female', '28', '202');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`employee1` (`id`, `name`, `sex`, `age`, `dep_id`) VALUES ('5', 'liwenzhou', 'male', '18', '200');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`employee1` (`id`, `name`, `sex`, `age`, `dep_id`) VALUES ('6', 'jingliyang', 'female', '18', '204');
(1)查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门
SELECT name from department where id in(SELECT dep_id from employee1 GROUP BY dep_id HAVING AVG(age)>25) ;
(2)查看技术部员工的姓名
SELECT name from employee1 where dep_id =(SELECT id from department where name = '技术');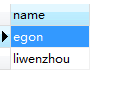
(3)查看小于两人的部门
SELECT name from department where id in(SELECT dep_id from employee1 GROUP BY dep_id HAVING COUNT(dep_id)<2);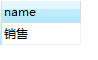
3、有以下三张表
表:student
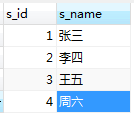
表:class
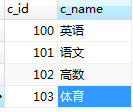
表:choosen_class
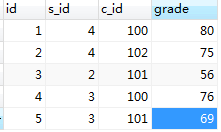
创建表以及插入数据的sql:
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`s_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`s_name` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL
)
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`student` (`s_id`, `s_name`) VALUES ('1', '张三');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`student` (`s_id`, `s_name`) VALUES ('2', '李四');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`student` (`s_id`, `s_name`) VALUES ('3', '王五');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`student` (`s_id`, `s_name`) VALUES ('4', '周六');
CREATE TABLE `class` (
`c_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`c_name` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL
)
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`class` (`c_id`, `c_name`) VALUES ('100', '英语');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`class` (`c_id`, `c_name`) VALUES ('101', '语文');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`class` (`c_id`, `c_name`) VALUES ('102', '高数');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`class` (`c_id`, `c_name`) VALUES ('103', '体育');
CREATE TABLE `choosen_class` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`s_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`c_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`grade` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
)
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`choosen_class` (`id`, `s_id`, `c_id`, `grade`) VALUES ('1', '4', '100', '80');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`choosen_class` (`id`, `s_id`, `c_id`, `grade`) VALUES ('2', '4', '102', '75');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`choosen_class` (`id`, `s_id`, `c_id`, `grade`) VALUES ('3', '2', '101', '56');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`choosen_class` (`id`, `s_id`, `c_id`, `grade`) VALUES ('4', '3', '100', '76');
INSERT INTO `Apollo115`.`choosen_class` (`id`, `s_id`, `c_id`, `grade`) VALUES ('5', '3', '101', '69');
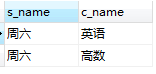
(1)查询选修课程名称为‘语文’的学生姓名以及选修课程
SELECT student.s_name,class.c_name from student,class,choosen_class where student.s_id not in(SELECT choosen_class.s_id from choosen_class where
choosen_class.c_id = (SELECT c_id from class where c_name = '语文')) and student.s_id = choosen_class.s_id and choosen_class.c_id = class.c_id;
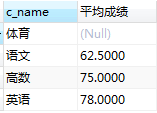
(2)查出每门的课程名称和平均成绩,并按照升序排序
SELECT class.c_name,avg(choosen_class.grade) as '平均成绩' from class LEFT JOIN choosen_class on class.c_id = choosen_class.c_id GROUP BY (choosen_class.c_id)
ORDER BY avg(choosen_class.grade)
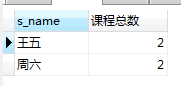
(3)查询选了2门课程以上的学生姓名以及学生选修的课程总数
SELECT student.s_name,COUNT(choosen_class.s_id) as '课程总数' from student,choosen_class where student.s_id in (SELECT choosen_class.s_id from choosen_class GROUP BY
choosen_class.s_id HAVING COUNT(choosen_class.s_id)>=2) and student.s_id = choosen_class.s_id GROUP BY choosen_class.s_id





 本文通过一系列复杂的SQL查询题目,涵盖了用户表版本号统计、部门及员工信息查询,以及学生选课情况分析,旨在考察和提升SQL查询和数据分析能力。包括:版本号用户数倒序排序、人数超过1000的版本号统计、部门平均年龄筛选、特定部门员工姓名查询、不足两人部门的查找、选修特定课程的学生排除、课程平均成绩排序以及选修两门以上课程的学生统计。
本文通过一系列复杂的SQL查询题目,涵盖了用户表版本号统计、部门及员工信息查询,以及学生选课情况分析,旨在考察和提升SQL查询和数据分析能力。包括:版本号用户数倒序排序、人数超过1000的版本号统计、部门平均年龄筛选、特定部门员工姓名查询、不足两人部门的查找、选修特定课程的学生排除、课程平均成绩排序以及选修两门以上课程的学生统计。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








