2018.4.27 尝试用 Java 实现二叉树
import java.util.Queue ;
import java.util.Scanner ;
import java.util.LinkedList ;
// 定义一个外部的类
class Node {
private int data ;
public Node [] ch = new Node[2] ;
// ch[0] 左孩子, ch[1] 右孩子
public Node () {
data = 0 ;
ch[0] = ch[1] = null ;
}
// 构造函数重载
public Node ( final int data , Node l , Node r ) {
this.data = data ;
this.ch[0] = l ;
this.ch[1] = r ;
}
// 主键值比根更小, 搜索左子树 ; 更大, 搜索右子树
public int cmp ( final int data ) {
return data < this.data ? 0 : data == this.data ? -1 : 1 ;
}
// 返回主键值
public int get_data () {
return data ;
}
}
// 定义文件类名
public class Binary_Tree_2 {
// main 函数入口
public static void main ( String[] args ) {
Binary_Tree_2 One = new Binary_Tree_2 () ;
System.out.print ( "\n前序遍历 : " ) ;
One.pre_Visit ( One.Root ) ;
System.out.print ( "\n\n中序遍历 : " ) ;
One.mid_Visit ( One.Root ) ;
System.out.print ( "\n\n后序遍历 : " ) ;
One.post_Visit ( One.Root ) ;
System.out.print ( "\n\n层次遍历 : \n\n" ) ;
One.level_visit () ; // 无法从静态上下文中引用非静态
System.out.print ( "二叉树的高度是 : " + One.get_height ( One.Root ) + "\n\n" ) ;
}
// 定义一个二叉树的根
private Node Root = null ;
// 二叉树的构造函数, 初始化, 我插入了一个序列
public Binary_Tree_2 () {
int [] arr = new int [] { 12 , 5 , 3 , 20 , 9 , 7 , 11 , 4 , 2 , 1 } ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; ++i )
Root = insert ( Root , arr[i] ) ;
}
// 递归插入, 不允许插入已经存在的值
public Node insert ( Node root , final int x ) {
if ( root == null ) {
root = new Node ( x , null , null ) ; return root ;
}
int d = root.cmp ( x ) ;
if ( d != -1 )
root.ch[d] = insert ( root.ch[d] , x ) ;
return root ;
}
// 前序遍历
public void pre_Visit ( Node root ) {
if ( root == null ) return ;
System.out.print ( root.get_data () + " " ) ;
if ( root.ch[0] != null ) pre_Visit ( root.ch[0] ) ;
if ( root.ch[1] != null ) pre_Visit ( root.ch[1] ) ;
}
// 中序遍历
public void mid_Visit ( Node root ) {
if ( root == null ) return ;
if ( root.ch[0] != null ) mid_Visit ( root.ch[0] ) ;
System.out.print ( root.get_data () + " " ) ;
if ( root.ch[1] != null ) mid_Visit ( root.ch[1] ) ;
}
// 后序遍历
public void post_Visit ( Node root ) {
if ( root == null ) return ;
if ( root.ch[0] != null ) post_Visit ( root.ch[0] ) ;
if ( root.ch[1] != null ) post_Visit ( root.ch[1] ) ;
System.out.print ( root.get_data () + " " ) ;
}
// 用 Queue 来实现队列
public void level_visit () {
if ( Root == null ) return ;
Queue < Node > Q = new LinkedList < Node > () ;
Q.offer ( Root ) ;
while ( Q.size () != 0 ) {
Node cur = Q.poll () ;
System.out.print ( cur.get_data () ) ;
if ( cur.ch[0] != null ) {
System.out.print ( "\tlchild : " + cur.ch[0].get_data () ) ;
Q.offer ( cur.ch[0] ) ;
} else {
System.out.print ( "\tlchild : null" ) ;
}
if ( cur.ch[1] != null ) {
System.out.print ( "\t\trchild : " + cur.ch[1].get_data () ) ;
Q.offer ( cur.ch[1] ) ;
} else {
System.out.print ( "\t\trchild : null" ) ;
}
System.out.print ( "\n\n" ) ;
}
}
// 递归求树的高度
public int get_height ( Node root ) {
if ( root == null ) return 0 ;
return Math.max ( get_height ( root.ch[0] ) , get_height ( root.ch[1] ) ) + 1 ;
}
}程序结果:
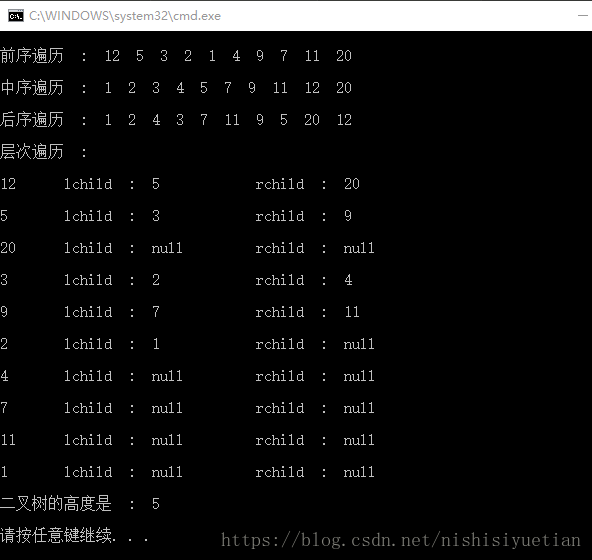
本人刚学 Java, 如果在类的封装,函数使用,等等上有什么弊病,请路过的朋友多提些意见








 本文介绍了一种使用Java实现二叉树的方法,并演示了前序、中序、后序及层次遍历的过程。此外,还展示了如何计算二叉树的高度。
本文介绍了一种使用Java实现二叉树的方法,并演示了前序、中序、后序及层次遍历的过程。此外,还展示了如何计算二叉树的高度。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








