六、管理SELinux安全性
1、更改SELinux执行模式
1.1 SELinux如何保护资源
(1)SELinux的核心安全机制
SELinux(Security-Enhanced Linux,安全性增强Linux)是由美国国家安全局(NSA)开发的强制访问控制(MAC)系统,集成于Linux 2.6及以上内核,安全级别达到信息安全评估标准的B1级(军事安全性能)。其核心保护逻辑如下:
- 精准访问控制:相比传统Linux的用户/组/其他(DAC)权限模型,SELinux通过预设策略实现更细粒度的资源管控,可精确限制“进程-文件/端口”的访问关系。
- 基于策略的标签系统:SELinux通过“目标策略(targeted policy)”定义规则,为每个程序、文件、网络端口分配预定义的安全标签(label),仅允许符合标签规则的访问。
- 防御权限扩散:即使某服务(如Apache)因漏洞被攻陷,入侵者仅能获取该服务的有限权限,无法突破SELinux限制访问其他系统资源(如数据库文件、系统配置目录),避免攻击范围扩散。
(2)SELinux与传统DAC权限的区别
| 对比维度 | 传统DAC(自主访问控制) | SELinux(强制访问控制) |
|---|---|---|
| 权限控制主体 | 资源所有者(可自主修改权限) | 系统管理员(基于预设策略,不可随意修改) |
| 判断依据 | 用户UID/组GID | 进程与资源的安全上下文(context) |
| 安全边界 | 依赖用户配置,易因误操作导致漏洞 | 策略强制管控,高权限进程也受限制 |
| 攻击防御能力 | 若root进程被劫持,攻击者可控制整个系统 | 即使root进程被劫持,仍受SELinux策略限制 |
1.2 为什么使用SELinux
(1)核心价值
- 防御未知漏洞:即使应用程序存在未被发现的安全漏洞,SELinux的强制访问控制可限制漏洞利用范围,避免整个系统被入侵。
- 额外安全层:在传统DAC权限基础上增加一层防护,即使DAC权限配置错误(如文件设为777),SELinux仍可通过策略阻止未授权访问。
- 隔离系统资源:通过标签和策略隔离不同服务的资源(如Web服务文件、数据库文件),某一服务被攻陷不影响其他服务。
(2)SELinux的三种运行模式
SELinux支持三种模式,对应不同的安全管控强度,需根据场景选择:
| 模式 | 核心特性 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcing(强制模式) | 严格执行SELinux策略,任何违反策略的访问都会被拒绝,并记录到审计日志 | 生产环境(需最高安全性) |
| Permissive(宽容模式) | 不拒绝任何访问,但会将违反策略的行为记录到日志,不影响服务运行 | 测试/故障排查(定位策略冲突) |
| Disabled(关闭模式) | 完全关闭SELinux,不加载任何策略,不进行安全管控 | 仅用于特殊测试(生产环境严禁使用) |
(3)RHEL 9的模式配置变化
自红帽企业Linux 9起,不再支持通过/etc/selinux/config文件设置SELINUX=disabled,完全禁用SELinux需通过 内核参数 实现:
- 禁用命令:grubby --update-kernel ALL --args selinux=0(需重启生效)
- 恢复启用:grubby --update-kernel ALL --remove-args selinux(需重启生效)
1.3 SELinux安全基本概念
(1)核心术语:安全上下文(SELinux Context)
SELinux为每个进程、文件、目录、端口分配唯一的“安全标签”,称为安全上下文,是策略判断访问权限的核心依据。其格式为user:role:type:sensitivity,目标策略(RHEL默认)主要基于type字段(类型上下文)制定规则,type通常以_t结尾。
| 字段 | 含义示例 |
|---|---|
| user(用户) | system_u(系统用户)、unconfined_u(无限制用户) |
| role(角色) | system_r(系统角色)、object_r(对象角色,用于文件/目录) |
| type(类型) | httpd_t(Apache进程类型)、httpd_sys_content_t(Apache可访问文件类型) |
| sensitivity(敏感度) | s0(默认敏感度,MLS策略中使用,目标策略下通常为s0) |

(2)典型服务的安全上下文示例
| 服务/资源 | 类型上下文(type) | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Apache进程 | httpd_t | Apache服务进程的类型标签 |
| Apache网站根目录 | httpd_sys_content_t | Apache可读取的静态文件类型标签 |
| MariaDB进程 | mysqld_t | MariaDB ** 数据库进程的类型**标签 |
| MariaDB数据目录 | mysqld_db_t | MariaDB可访问的数据文件类型标签 |
| 临时目录(/tmp) | tmp_t | 临时文件的类型标签,默认限制Apache访问 |
| HTTP端口(80/443) | http_port_t | HTTP服务可使用的端口类型标签 |
MariaDB 服务器的 type context 为 mysqld_t,默认情况下,在 /data/mysql 中的文件具有 mysqld_db_t type context,该 type context 允许 MariaDB 访问这些文件,但禁止其他服务(如 Apache 服务)的访问:
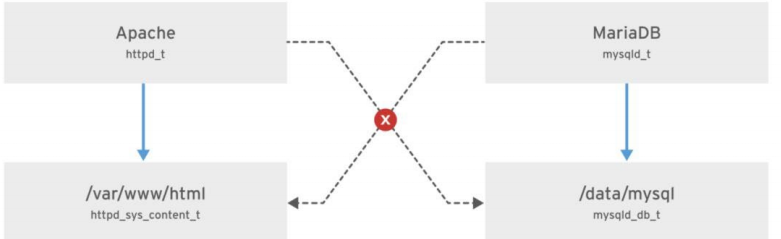
详细解释:
mysqld_t:这是 MariaDB 服务进程的 type context,表示 MariaDB 服务器进程(通常是 mysqld)的安全上下文。mysqld_t 是 SELinux 用来标识 MariaDB 服务进程的标签,它定义了该进程对系统其他资源的访问权限。
mysqld_db_t:这是分配给 MariaDB 数据库文件 的 type context。在默认配置下,MariaDB 数据目录(如 /data/mysql)中的文件会被标记为 mysqld_db_t 类型。mysqld_db_t 表示这些文件是 MariaDB 使用的数据库文件,它允许 MariaDB 访问这些文件,并执行相应的数据库操作。
如何工作:
MariaDB 服务(mysqld) 运行时,操作系统会检查进程的 type context(在这种情况下是 mysqld_t)以及它想要访问的文件的 type context(例如 mysqld_db_t)。
默认访问控制:根据 SELinux 的安全策略,进程和文件的访问权限是通过它们的 type context 来控制的。在这个例子中,mysqld_t 被允许访问 mysqld_db_t 类型的文件(即数据库文件),但是 mysqld_t 进程不被允许访问其他服务的文件,比如 Apache 相关文件。
MariaDB(mysqld_t)可以读取和修改 /data/mysql 中的文件(mysqld_db_t),因为它们属于允许访问的类型。
其他服务,比如 Apache(通常是 httpd_t),没有权限访问 /data/mysql 中的数据库文件,因为这些文件的 type context 被设置为 mysqld_db_t,而 httpd_t(Apache)没有这个权限。
安全性提升:
隔离性:通过这种方式,MariaDB 的文件和 Apache 等其他服务的文件被严格区分,确保不同服务之间不会随意互相访问。
访问控制:SELinux 会根据进程和文件的 type context 来决定是否允许操作,从而提高了系统的安全性。
防止越权访问:即使攻击者利用 Apache 服务入侵系统,也无法访问数据库文件,因为它们有严格的 type context 限制。
(3)查看安全上下文的命令
多个常用命令支持-Z选项查看SELinux上下文:
1. 查看进程的安全上下文(以Apache为例)
[root@host ~]# systemctl start httpd
[root@host ~]# ps -ZC httpd # -Z显示上下文,-C指定进程名
LABEL PID TTY TIME CMD
system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 1608 ? 00:00:05 httpd
system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 1609 ? 00:00:00 httpd
2. 查看文件的安全上下文(以Apache网站文件为例)
[root@host ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
3. 查看目录的安全上下文(以用户家目录为例)
[root@host ~]# ls -Zd /home/student
drwx------. student student unconfined_u:object_r:user_home_dir_t:s0 /home/student
1.4 更改当前SELinux模式(临时生效)
通过getenforce和setenforce命令可查看和临时切换SELinux模式(重启后失效),仅支持在Enforcing和Permissive之间切换(Disabled模式需重启)。
/ˈɡɛt ɪnˈfɔrs/ /ˈsɛt ɪnˈfɔrs/
| 命令格式 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
getenforce | 查看当前SELinux模式(输出:Enforcing/Permissive/Disabled) |
setenforce 1 或 setenforce Enforcing | 切换到强制模式(仅当当前模式为Permissive时有效) |
setenforce 0 或 setenforce Permissive | 切换到宽容模式(仅当当前模式为Enforcing时有效) |
示例操作
1. 查看当前模式
[user@host ~]$ getenforce
Enforcing
2. 切换到宽容模式
[root@host ~]# setenforce 0
[root@host ~]# getenforce
Permissive
3. 切换回强制模式
[root@host ~]# setenforce 1
[root@host ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
1.5 设置默认SELinux模式(永久生效)
通过修改/etc/selinux/config配置文件,可永久设置SELinux模式(需重启生效),文件核心内容如下:
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. (RHEL 9已不支持此方式禁用)
SELINUX=enforcing # 默认强制模式
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected (默认目标策略)
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy (仅保护选定进程)
# mls - Multi Level Security protection (多级安全策略)
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
配置步骤
- 编辑配置文件:
[root@host ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config 或 [root@host ~]# vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux - 修改
SELINUX=字段为目标模式(如SELINUX=permissive)。 - 保存文件并重启系统(仅模式切换涉及
Disabled或从Disabled切换时需重启):[root@host ~]# reboot - 验证配置:重启后执行
getenforce,确认模式已更新。
2、控制SELinux文件上下文
2.1 初始SELinux上下文(默认标签规则)
(1)上下文的继承与默认规则
- 继承规则:新创建的文件/目录默认从父目录继承SELinux上下文(
mv命令移动文件时保留原上下文,cp -a复制时继承目标目录上下文)。 - 默认规则来源:SELinux在
/etc/selinux/targeted/contexts/files/目录中维护“文件标签策略数据库”,根据文件路径匹配预设规则分配默认标签(如/var/www/html下的文件默认标签为httpd_sys_content_t)。
(2)查看文件/目录的上下文
1. 查看单个文件的上下文
[root@host ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/index.html
2. 查看目录的上下文(-d选项指定目录)
[root@host ~]# ls -Zd /var/www/html
drwxr-xr-x. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html
2.2 更改SELinux文件上下文(临时与永久)
SELinux提供三种命令修改文件上下文,核心区别在于是否将规则持久化到策略数据库:
/ˈtʃeɪ kən/ /ˈsiː ˌmænɪdʒ fɪˈkɒntɛkst/ /rɪˈstɔːrkən/
| 命令 | 作用 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
chcon | 临时修改文件上下文 | 不持久化,执行restorecon后会还原 | 临时测试(如验证标签是否适配服务) |
semanage fcontext | 定义文件的永久默认上下文规则(写入策略数据库) | 持久化,新文件自动继承,restorecon可应用 | 长期使用的自定义目录/文件 |
restorecon | 应用semange fcontext定义的默认规则,修复文件的上下文 | 基于策略数据库修复,覆盖临时修改 | 批量应用规则、修复异常上下文 |
示例1:使用chcon临时修改
1. 创建测试目录,查看默认上下文(默认为default_t)
[root@host ~]# mkdir /virtual
[root@host ~]# ls -Zd /virtual
drwxr-xr-x. root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /virtual
2. 临时修改为Apache可访问的类型(httpd_sys_content_t)
[root@host ~]# chcon -t httpd_sys_content_t /virtual
[root@host ~]# ls -Zd /virtual
drwxr-xr-x. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /virtual
3. 执行restorecon修复(还原为默认上下文)
[root@host ~]# restorecon -v /virtual # -v显示详细过程
Relabeled /virtual from unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0
[root@host ~]# ls -Zd /virtual
drwxr-xr-x. root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /virtual
示例2:使用semange fcontext+restorecon永久修改
1. 创建自定义Web目录,查看默认上下文
[root@host ~]# mkdir /myweb
[root@host ~]# touch /myweb/index.html
[root@host ~]# ls -Z /myweb/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 /myweb/index.html
2. 定义永久规则:/myweb目录及子目录文件默认类型为httpd_sys_content_t
正则表达式(/.*)?表示递归匹配所有子目录和文件
[root@host ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t '/myweb(/.*)?'
3. 应用规则(-R递归处理目录,-F强制覆盖,-vv显示详细日志)
[root@host ~]# restorecon -RFvv /myweb
restorecon reset /myweb context unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0->system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
restorecon reset /myweb/index.html context unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0->system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
4. 验证结果(上下文已永久更新)
[root@host ~]# ls -Zd /myweb
drwxr-xr-x. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /myweb
[root@host ~]# ls -Z /myweb/index.html
-rw-r--r--. root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /myweb/index.html
(/. * )?:这是一个正则表达式,表示匹配 /myweb 下的所有子目录和文件。/.* 表示匹配以 / 开头,后面跟任意字符的路径(即 /myweb 目录下的所有文件和子目录)。? 表示这个部分是可选的,因此也可以只匹配 /myweb 目录本身。
定义SELinux默认文件上下文策略:
(1)semanage fcontext命令选项
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
-a, --add | 添加新的文件上下文规则 |
-d, --delete | 删除已有的文件上下文规则 |
-l, --list | 列出所有已定义的文件上下文规则(可搭配 grep 筛选特定路径) |
-t, --type | 指定目标上下文类型(如httpd_sys_content_t、mysqld_db_t) |
(2)常用操作示例
1. 列出所有与Apache相关的上下文规则
[root@host ~]# semanage fcontext -l | grep httpd
/var/www(/.*)? all files system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
/var/www/cgi-bin(/.*)? all files system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_script_exec_t:s0
...output omitted...
2. 修复Apache网站目录的上下文(递归处理子文件)
[root@host ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/file1 # 异常上下文(user_tmp_t)
unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 /var/www/html/file1
[root@host ~]# restorecon -Rv /var/www/html # 递归修复
Relabeled /var/www/html/file1 from unconfined_u:object_r:user_tmp_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0
[root@host ~]# ls -Z /var/www/html/file1 # 已恢复正常
unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 /var/www/html/file1
3. 删除自定义的上下文规则(如删除/myweb的规则)
[root@host ~]# semanage fcontext -d -t httpd_sys_content_t '/myweb(/.*)?'
3、用bool调整SELinux策略
3.1 使用SELinux布尔值(Boolean)
(1)布尔值的核心作用
SELinux布尔值是策略的“开关参数”,可在不修改核心策略文件的情况下,动态启用/禁用特定访问规则(如允许Apache访问用户家目录、允许FTP服务写入文件),无需重启服务或系统。
(2)相关软件包与命令
- 依赖包:selinux-policy-doc(提供布尔值的详细说明,可通过dnf install selinux-policy-doc安装)。
- 管理命令:
| 命令格式 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
getsebool -a | 列出所有SELinux布尔值及其当前状态(on/off) |
getsebool 布尔值名称 | 查看指定布尔值的状态(如getsebool httpd_enable_homedirs) |
setsebool 布尔值名称 on/off | 临时修改布尔值状态(重启后失效) |
setsebool -P 布尔值名称 on/off | 永久修改布尔值状态(-P表示persistent,写入策略数据库) |
semanage boolean -l | 列出布尔值的详细信息(包括默认状态、描述) |
semanage boolean -l -C | 列出当前状态与默认状态不同的布尔值(即已自定义修改的布尔值) |
(3)权限控制
- 普通用户:仅可执行
getsebool查看布尔值状态。 - root用户:可执行
setsebool(临时/永久修改)、semanage boolean(查看详细信息)。
示例操作
1. 查看所有布尔值(筛选Apache相关)
[user@host ~]$ getsebool -a | grep httpd
httpd_anon_write --> off
httpd_builtin_scripting --> on
httpd_enable_homedirs --> off # 允许Apache访问用户家目录的开关(默认关闭)
httpd_execmem --> off
...output omitted...
2. 查看指定布尔值的详细信息
[root@host ~]# semanage boolean -l | grep httpd_enable_homedirs
httpd_enable_homedirs (off, off) Allow httpd to enable homedirs
说明:(当前状态, 默认状态),描述为“允许Apache启用用户家目录访问”
3. 临时启用该布尔值(重启后失效)
[root@host ~]# setsebool httpd_enable_homedirs on
[root@host ~]# getsebool httpd_enable_homedirs
httpd_enable_homedirs --> on
4. 永久启用该布尔值(-P选项)
[root@host ~]# setsebool -P httpd_enable_homedirs on
[root@host ~]# semanage boolean -l | grep httpd_enable_homedirs
httpd_enable_homedirs (on, off) Allow httpd to enable homedirs
当前状态已变为on
5. 列出所有已自定义的布尔值
[root@host ~]# semanage boolean -l -C
SELinux boolean State Default Description
httpd_enable_homedirs (on, off) Allow httpd to enable homedirs
4、分析和解决SELinux问题
4.1 监控SELinux冲突(日志与工具)
(1)常见SELinux问题原因
- 文件/目录的SELinux上下文类型错误(如Apache文件的类型不是
httpd_sys_content_t)。 - 相关SELinux布尔值未启用(如未开启
httpd_enable_homedirs导致Apache无法访问家目录)。 - 端口的类型标签错误(如自定义端口未设置为
http_port_t,导致服务无法监听)。
(2)日志文件与分析工具
- 核心日志文件:
/var/log/audit/audit.log:记录SELinux的审计消息(包括AVC拒绝信息,即访问被阻止的详细日志)。/var/log/messages:记录setroubleshoot工具解析后的SELinux冲突消息(需安装setroubleshoot-server包)。
- 关键工具:
setroubleshoot-server:实时监控audit.log,将SELinux冲突转换为易懂的中文消息,并提供解决方案(安装命令:dnf install setroubleshoot-server)。sealert:分析SELinux日志,生成详细的冲突报告和修复建议。ausearch:搜索audit.log中的特定类型消息(如AVC拒绝、用户登录)。
(3)示例:分析并解决Apache访问文件被阻止的问题
-
查看冲突日志:
1. 查看/var/log/messages中的SELinux消息(筛选setroubleshoot) [root@host ~]# tail /var/log/messages Feb 20 19:55:42 servera setroubleshoot: SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/httpd from getattr access on the file /var/www/html/file3. For complete SELinux messages, run sealert -l 613ca624-248d-48a2-a7d9-d28f5bbe2763 说明:冲突UUID为613ca624-248d-48a2-a7d9-d28f5bbe2763 2. 查看audit.log中的原始AVC消息(使用ausearch搜索AVC类型) [root@host ~]# ausearch -m AVC -ts recent # -m AVC指定消息类型,-ts recent表示最近事件 time->Tue Apr 9 13:13:07 2019 type=AVC msg=audit(1554808387.778:4002): avc: denied { name_bind } for pid=9340 comm="httpd" src=82 scontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:object_r:reserved_port_t:s0 tclass=tcp_socket permissive=0 -
使用
sealert生成解决方案:[root@host ~]# sealert -l 613ca624-248d-48a2-a7d9-d28f5bbe2763 # 传入冲突UUID SELinux is preventing /usr/sbin/httpd from getattr access on the file /var/www/html/file3. ***** Plugin catchall (100. confidence) suggests ************************** If you believe that httpd should be allowed getattr access on the file3 file by default. Then you should report this as a bug. You can generate a local policy module to allow this access. Do allow this access for now by executing: # grep httpd /var/log/audit/audit.log | audit2allow -M mypol # semodule -i mypol.pp Additional Information: Source Context system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 Target Context unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 Target Objects /var/www/html/file3 [ file ] Source httpd Source Path /usr/sbin/httpd ...output omitted...- 日志分析:
/var/www/html/file3的上下文类型为admin_home_t(管理员家目录类型),而Apache进程(httpd_t)仅允许访问httpd_sys_content_t类型的文件,导致访问被阻止。
- 日志分析:
-
解决问题:
修复文件上下文(改为Apache可访问的类型) [root@host ~]# restorecon -v /var/www/html/file3 Relabeled /var/www/html/file3 from unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 to unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 验证:Apache可正常访问该文件
一般就是上下文不对,先查看哪不对,查看错误消息然后更改SELinux文件上下文,对应2. 控制SELinux文件上下文 的命令
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t ‘/lab-content(/.*)?’
这条命令会将 /lab-content 目录及其所有子文件的 SELinux 类型设置为 httpd_sys_content_t,使得 Apache 进程能够读取该目录中的文件。
restorecon -Rv /lab-content
使用 restorecon 命令来应用新的 SELinux 上下文:-R 表示递归应用到子目录和文件。-v 显示详细信息。
4.2 使用Web Console进行SELinux故障排除
红帽Web Console(图形化管理界面)提供可视化的SELinux故障排查工具,步骤如下:
- 登录Web Console:使用root或具有sudo权限的用户登录,访问地址为
https://服务器IP:9090。 - 进入SELinux管理界面:在左侧导航栏选择“SELinux”,界面显示两部分内容:
- SELinux policy:当前SELinux模式(Enforcing/Permissive)。
- SELinux access control errors:列出所有未解决的SELinux冲突事件。
- 查看冲突详情:
- 单击冲突事件前的“>”,展开显示事件的关键信息(如源进程、目标文件、上下文类型)。
- 单击“Solution details”,查看系统推荐的解决方案(如修复上下文、启用布尔值)。
- 应用解决方案:单击“Apply the solution”,系统自动执行修复操作(如运行
restorecon、setsebool)。 - 验证结果:修复后,冲突事件会从“SELinux access control errors”列表中移除,显示“No SELinux alerts”表示当前无SELinux问题。





















 387
387

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








