M - Closest Common Ancestors
Crawling in process...
Crawling failed
Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:10000KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u
Appoint description:
Description
Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree description, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
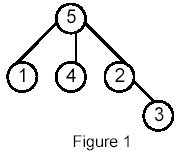
For example, for the following tree:

Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1 5:5
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
思路:就是道简单题,统计最近公共祖先,不算重就行。
注意点:根是无入度点,相同的边可能查询多次,答案要累加。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;++i)
#define clr(f,z) memset(f,z,sizeof(f))
using namespace std;
const int mm=902;
class Edge
{
public:int v,next;bool has;
}e[mm*mm];
int qh[mm],head[mm],edge,rt[mm],id[mm];
bool vis[mm];
int anc[mm],n,m,root;
void data()
{
clr(qh,-1);clr(head,-1);edge=0;
}
void add(int u,int v,int*h)
{ e[edge].has=0;
e[edge].v=v;e[edge].next=h[u];h[u]=edge++;
}
int find(int x)
{
if(x^rt[x])
{
rt[x]=find(rt[x]);
}
return rt[x];
}
void dfs(int u)
{ int v;
rt[u]=u;vis[u]=1;
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].next)
{
v=e[i].v;
if(!vis[v])
{
dfs(v);rt[v]=u;
}
}
for(int i=qh[u];~i;i=e[i].next)
{
v=e[i].v;
if(vis[v]&&e[i].has==0)
{ //printf("%d %d %d\n",u,v,find(v));
++anc[find(v)];e[i].has=e[i^1].has=1;
}
}
}
void find_bcc()
{
clr(vis,0);clr(anc,0);
dfs(root);
}
int main()
{ int u,v;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{ data();
clr(id,0);
FOR(i,1,n)
{
scanf("%d:(%d)",&u,&m);
FOR(j,1,m)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
id[v]++;
add(u,v,head);add(v,u,head);
}
}
FOR(i,1,n)
if(id[i]==0)root=i;
scanf("%d",&m);
FOR(i,1,m)
{ while(1)
{
char z=getchar();
if(z=='(')break;
}
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
add(u,v,qh);add(v,u,qh);
while(1)
{
char z=getchar();
if(z==')')break;
}
}
find_bcc();
FOR(i,1,n)
if(anc[i])
printf("%d:%d\n",i,anc[i]);
}
}





 本文介绍了一个简单的最近公共祖先(LCA)算法实现,用于解决给定树中节点对的最近公共祖先问题。输入包括树的描述及节点对列表,输出为每一对节点的最近公共祖先及其出现次数。
本文介绍了一个简单的最近公共祖先(LCA)算法实现,用于解决给定树中节点对的最近公共祖先问题。输入包括树的描述及节点对列表,输出为每一对节点的最近公共祖先及其出现次数。
















 353
353

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








