Mybatis学习02:使用xml进行Mybatis开发
使用xml配置sql语句
CRUD的sql语句
查询操作
在持久层xml配置文件中使用<select>标签配置查询操作的sql语句.
在java/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.java中声明查询方法如下:
// 根据id查询用户信息
User findById(Integer userId);
在resources/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.xml中配置对应的sql语句如下:
<!-- 根据id查询用户信息 -->
<select id="findById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="cn.maoritian.domain.User">
select * from user where id = #{userId};
</select>
其中sql语句的占位符可以使用#{}或${}表示,其区别如下:
-
#{}最后会编译成PreparedStatement对象的?占位符,花括号内为接收的方法参数,支持ONGL语句,即可以通过对象.属性调用pojo对象的对象.get属性()方法.通过
#{}解析的占位符在进行变量替换时,会带上单引号',可以有效防止sql注入,应优先使用这种方式. -
${}表示拼接sql串,将占位符表示的内容直接拼接进sql语句.有可能发生sql注入漏洞.单这种表示方式也有其使用场景,因为
#{}方式进行变量替换时,会带上单引号',因此表示sql语句中非参数部分,如表名和数据库列名时,只能使用${}.此时通过白名单的形式过滤花括号中的内容.
select * from ${tableName} where username = #{username} order by ${columnName}
-- sql注入隐患: 若tablename为" users; delete users; --"时,上面sql语句将会被解析为
select * from users; delete users; -- where username = #{username} order by ${columnName}
增加操作
在持久层xml配置文件中使用<insert>标签配置查询操作的sql语句.
在java/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.java中声明增加方法如下:
// 保存用户
void saveUser(User user);
在resources/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.xml中配置对应的sql语句如下:
<!-- 保存用户 -->
<insert id="saveUser" parameterType="cn.maoritian.domain.User">
<!-- 配置插入操作后,获取插入数据的id -->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" keyColumn="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id();
</selectKey>
insert into users(username,address,sex,birthday)values(#{username},#{address},#{sex},#{birthday});
</insert>
因为传入的是pojo对象,因此#{}占位符自动解析为其属性.
其中<selectKey>标签内调用sql语句select last_insert_id()可以返回上次操作的主键,并将其封装回原pojo对象.
@Test
public void testSave() {
User user = new User(0, "姓名", "地区", "男", new Date());
System.out.println("保存操作之前:" + user);
userDao.saveUser(user); // 执行保存方法
System.out.println("保存操作之后:" + user);
}
可以看到,执行saveUser()方法之后,数据库中对应记录的主键被存进user对象的id字段.
更新操作
在持久层xml配置文件中使用<update>标签配置更新操作的sql语句.
在java/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.java中声明查询方法如下:
// 更新用户
void updateUser(User user);
在resources/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.xml中配置对应的sql语句如下:
<!-- 更新用户 -->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="cn.maoritian.domain.User">
update users set username=#{username},address=#{address},sex=#{sex},birthday=#{birthday} where id=#{id};
</update>
删除操作
在持久层xml配置文件中使用<delete>标签配置删除操作的sql语句.
在java/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.java中声明查询方法如下:
// 删除用户
void deleteUser(Integer userId);
在resources/cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.xml中配置对应的sql语句如下:
<!-- 删除用户-->
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from users where id = #{userId};
</delete>
输入输出参数的映射
输入参数的映射
在配置CRUD语句时,我们在parameterType属性中定义其参数类型名称
-
对于基本类型,我们可以可以直接写类型名称,也可以使用
包名.类名的方式,例如:对于字符串类型的参数,我们既可以写
string,也可以写java.lang.String. -
对于我们自己定义的实体类,必须写其全类名.
在Mybatis中,对于常见的类型,已经为我们配好了别名如下:
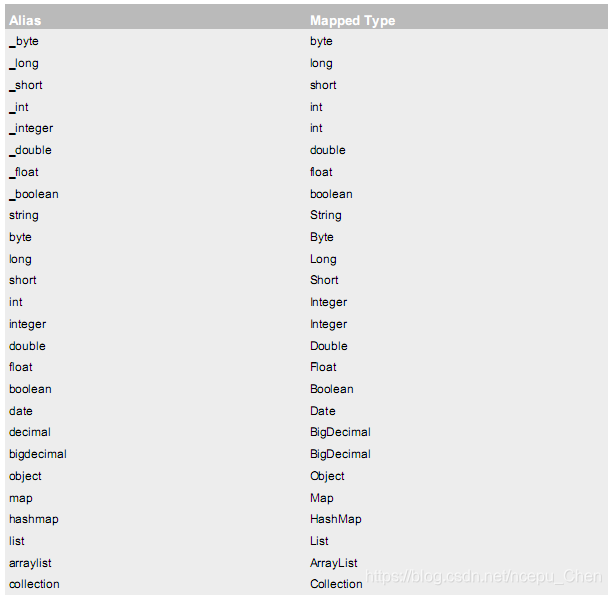
输出参数的映射
原来我们执行查询时,在sql语句上使用resultType=全类名或其别名,将数据库中的记录封装到pojo类中,但这种方式要求pojo类中的属性名与数据库表中的字段名完全相同.我们可以在dao接口实现类的xml配置文件中使用<resultMap>标签配置pojo类属性名到数据库字段名的映射,语法如下:
<!-- 配置 pojo类属性名 到 数据库字段名 的映射 -->
<resultMap type="cn.maoritian.domian.User" id="userMap">
<!-- 主键字段的对应 -->
<id column="id" property="userId"/>
<!-- 非主键字段的对应 -->
<result column="username" property="userName"/>
<result column="sex" property="userSex"/>
<result column="address" property="userAddress"/>
<result column="birthday" property="userBirthday"/>
</resultMap>
各标签的属性:
type为pojo类的全类名,id为该映射的唯一标志,通过sql语句的resultMap属性引用该idcolumn属性指定数据库表的字段名,property属性指定pojo类的属性名
<select id="findById" resultMap="userMap">
select * from users where id = #{userId};
</select>
动态sql语句
if标签-执行判断
<if>标签可以进行简单的逻辑判断,示例如下:
-
DAO层接口方法如下
List<User> findByCondition(User user); -
在mapper中定义其实现如下
<select id="findByCondition" resultMap="cn.maoritian.domain.User" parameterType="cn.maoritian.domain.User"> select * from users where 1=1 <if test="userName != null"> and username like #{userName} </if> <if test="userSex != null"> and sex = #{userSex} </if> </select> -
测试方法如下
@Test public void testFindByCondiion() throws Exception { // 通过赋值给对象属性确定查询条件 User user = new User(); user.setUserName("%王%"); // 查询名字时使用模糊查询 user.setUserSex("女"); // 执行查询方法 List<User> users = userDao.findByCondition(user); for (User u : users) { System.out.println(u); } }
where标签-为sql语句加上where限定符
上边例子中的sql语句加上了一个限定条件where 1=1,以防止我们传入的user对象为空,这种实现方式并不优雅.我们可以使用<where>标签,它可以根据我们传入的pojo对象判断是否加上where语句,示例如下:
<select id="findByCondition" resultMap="cn.maoritian.domain.User" parameterType="cn.maoritian.domain.User">
select * from users
<where>
<if test="userName != null">
and username like #{userName}
</if>
<if test="userSex != null">
and sex = #{userSex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
foreach标签-遍历集合
当我们想要执行范围查询时(如select * from users where id in (1,2,3,4,5);),要用到<foreach>标签.
-
DAO层接口方法如下:
List<User> findInIds(List<Integer> ids); -
在mapper中定义其实现如下:
<select id="findUserInIds" resultMap="cn.maoritian.domain.User" parameterType="list"> select * from users <where> <if test="ids!=null and ids.size()>0"> <foreach collection="ids" open="and id in (" close=")" item="uid" separator=","> #{uid} </foreach> </if> </where> </select><foreach>标签的属性如下:collection: 代表被遍历的对象,支持ONGL语言(如paramObject.idList)item: 代表每次循环拿到的对象
<foreach>标签更具体的使用方法参考这篇文章使用foreach实现mybatis查询
sql标签-抽取重复语句
每个方法的sql语句中,有大量重复的部分,可以使用<sql>标签声明sql语句,使用<include>标签引用其中内容.
<sql id="defaultUser">
select * from users
</sql>
<select id="findByCondition" resultMap="cn.maoritian.domain.User" parameterType="cn.maoritian.domain.User">
<include refid="defaultUser"/>
<where>
<if test="userName != null">
and username like #{userName}
</if>
<if test="userSex != null">
and sex = #{userSex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
Mybatis配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
一个完整的Mybatis配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml的结构和顺序如下:
-properties(属性)
--property
-settings(全局配置参数)
--setting
-typeAliases(类型别名)
--typeAliase
--package
-typeHandlers(类型处理器)
-objectFactory(对象工厂)
-plugins(插件)
-environments(环境集合属性对象)
--environment(环境子属性对象)
---transactionManager(事务管理)
---dataSource(数据源)
-mappers(映射器)
--mapper
--package
Properties标签-配置JDBC连接参数
在<properties>标签内可以配置JDBC参数,具体来说有两种方式配置
-
使用
<property>标签直接配置<properties> <property name="jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名"></property> <property name="jdbc.username" value="用户名"></property> <property name="jdbc.password" value="密码"></property> </properties> <!-- 其他内容 --> <environments default="mysql"> <environment id="mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <!--配置连接池--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> -
使用
<properties>标签的resource属性或URL属性<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties" /> <!-- 其他内容 --> <environments default="mysql"> <environment id="mysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager> <!--配置连接池--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>其中
jdbcConfig.properties文件resources目录下,其内容如下:jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名 jdbc.username=用户名 jdbc.password=密码
typeAliases标签-为bean类起别名
<typeAliases>可以为bean类起别名. 通过type,parameterType,resultType等属性引用该实体类.
<typeAliases>标签内指定的别名不区分大小写
有两种方式配置别名
-
使用
<typeAlias>标签为单个bean类起别名:<typeAliases> <typeAlias type="cn.maoritian.domain.User" alias="user"></typeAlias> </typeAliases> -
通过
<package>标签为整个包内的bean类起别名,其别名即为该类的直接类名,不区分大小写<typeAliases> <package name="cn.maoritian.domain"></package> </typeAliases>
配置别名之后,就可以在指定dao层方法sql语句时通过type,parameterType,resultType属性引用该实体类.
mappers映射器-指定dao层方法的具体实现
可以通过两种方式配置<mappers>
-
通过
<mapper>标签为每一个dao层类配置具体实现<mappers> <mapper resource="cn/maoritian/dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper> <mapper resource="cn/maoritian/dao/IAccountDao.xml"></mapper> <mapper resource="cn/maoritian/dao/IProductDao.xml"></mapper> </mappers> -
通过
<package>标签配置dao层类所在的包,相当于为其中每一个dao层类都配置了具体实现<typeAliases> <package name="cn.maoritian.domain"></package> </typeAliases>





 本文详细介绍MyBatis中XML配置文件的使用方法,包括CRUD操作、输入输出参数映射、动态SQL语句及MyBatis配置文件的结构解析。
本文详细介绍MyBatis中XML配置文件的使用方法,包括CRUD操作、输入输出参数映射、动态SQL语句及MyBatis配置文件的结构解析。
















 5436
5436

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








