变量命名:见名知意
由字母、数字、下划线组成
不能以数字开头
不能和关键字重名
驼峰命名法:
1.大驼峰:FirstName
2.小驼峰:firstName
输入输出练习
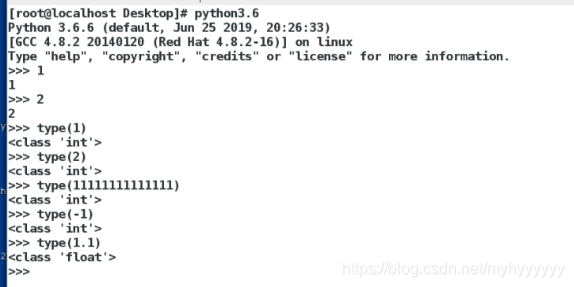
In [1]: 1 ##无定义,输入等于输出
Out[1]: 1
In [2]: 2
Out[2]: 2
In [3]: type(1) ##定义输出1的类型
Out[3]: int ##整数型
In [4]: type(2)
Out[4]: int
In [5]: type(111111111111111111111111111111111111)
Out[5]: int
In [6]: type(-1)
Out[6]: int
In [7]: type(1.1) ## 定义输出1.1的类型
Out[7]: float ##浮点数
In [8]: type(1.111111111111111111111111)
Out[8]: float
#python2.x
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
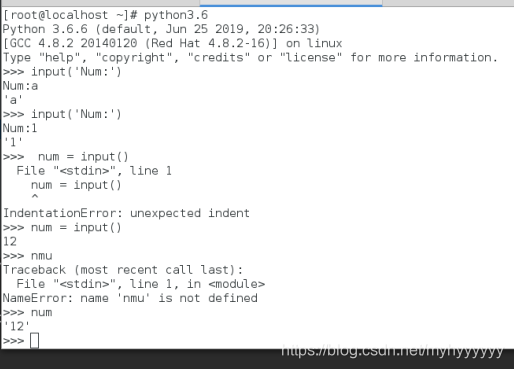
>>> input('Num:')
Num:a
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'a' is not defined
>>> input('Num:')
Num:2
2
>>> raw_input('Num:')
Num:a
'a'
>>> raw_input('Num:')
Num:1
'1'
>>>

#python3.x
>>> input('Num:)
File "<stdin>", line 1
input('Num:)
^
SyntaxError: EOL while scanning string literal
>>> input('Num:')
Num:a
'a'
>>> input('Num:')
Num:2
'2'
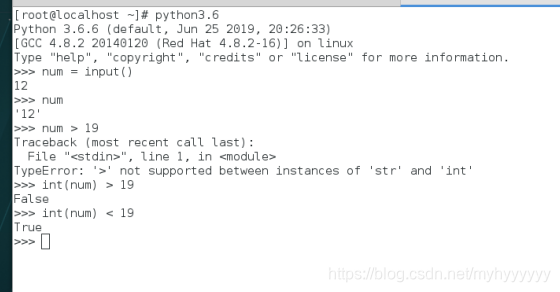
>>> num = input()
12
>>> num
'12'
>>> num > 19
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'int'
>>> int(num) > 19
False
>>> int(num) < 19
True
>>>
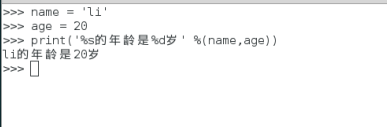
>>> name = 'li'
>>> age = '20'
>>> print('%s的年龄是%d岁' %(name,age))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str
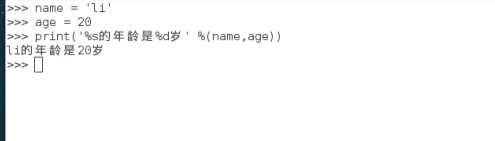
>>> name = 'li'
>>> age = 20
>>> print('%s的年龄是%d岁' %(name,age))
li的年龄是20岁
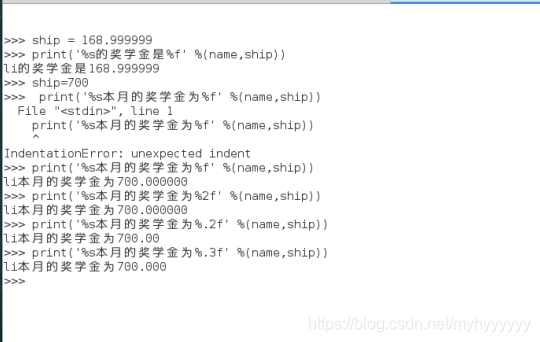
>>> ship = 168.999999
>>> print('%s的奖学金是%f' %(name,ship))
li的奖学金是168.999999
>>> ship=700
>>> print('%s本月的奖学金为%f' %(name,ship))
File "<stdin>", line 1
print('%s本月的奖学金为%f' %(name,ship))
^
IndentationError: unexpected indent
>>> print('%s本月的奖学金为%f' %(name,ship))
li本月的奖学金为700.000000
>>> print('%s本月的奖学金为%2f' %(name,ship))
li本月的奖学金为700.000000
>>> print('%s本月的奖学金为%.2f' %(name,ship))
li本月的奖学金为700.00
>>> print('%s本月的奖学金为%.3f' %(name,ship))
li本月的奖学金为700.000
>>>
>>> studentid=1
>>> studentid=9
File "<stdin>", line 1
studentid=9
^
IndentationError: unexpected indent
>>> studentid=9
>>> print('%s的学号为130%d' %(name,studentid))
li的学号为1309
>>> print('%s的学号为130%.3d' %(name,studentid))
li的学号为130009
>>> scale = 0.2
>>> print('比例是 %.2f' %scale)
比例是 0.20
>>> print('比例是 %.2f' %(scale * 100))
比例是 20.00
>>> print('比例是 %.2f%%' %(scale * 100))
比例是 20.00%
>>>

#
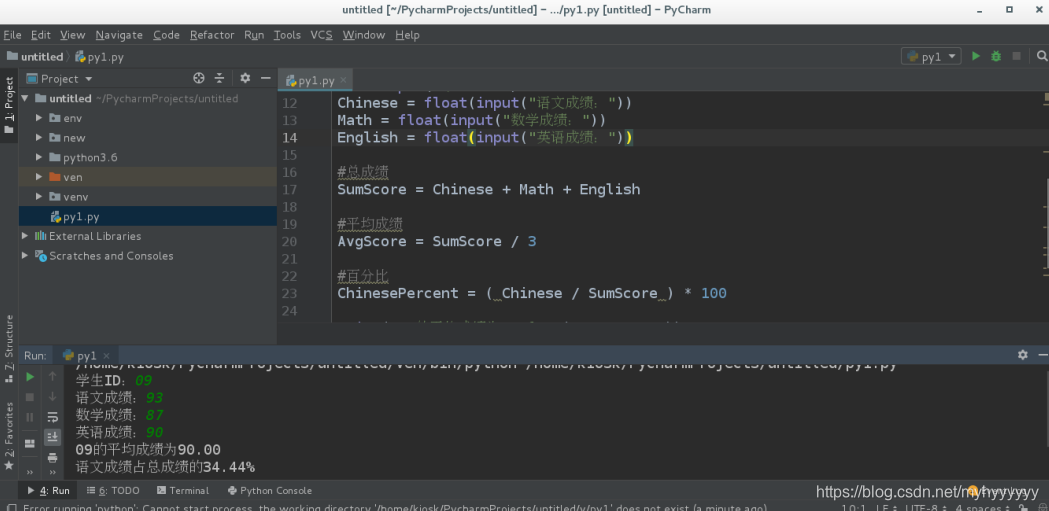
#- 输入学生学号;
#- 依次输入学生的三门科目成绩;
#- 计算该学生的平均成绩, 并打印;
#- 平均成绩保留两位小数点;
#- 计算该学生语文成绩占总成绩的百分之多少?并打印。
ID = input("学生ID:")
Chinese = float(input("语文成绩:"))
Math = float(input("数学成绩:"))
English = float(input("英语成绩:"))
#总成绩
SumScore = Chinese + Math + English
#平均成绩
AvgScore = SumScore / 3
#百分比
ChinesePercent = ( Chinese / SumScore ) * 100
print("%s的平均成绩为%.2f" %(ID,AvgScore))
print("语文成绩占总成绩的%.2f%%" %ChinesePercent)





 本文探讨了变量命名规范,包括见名知意原则、驼峰命名法等,并通过实例展示了Python中不同类型变量的输入输出操作,如整数、浮点数及字符串的处理。
本文探讨了变量命名规范,包括见名知意原则、驼峰命名法等,并通过实例展示了Python中不同类型变量的输入输出操作,如整数、浮点数及字符串的处理。
















 917
917

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








