本文属于「征服LeetCode」系列文章之一,这一系列正式开始于2021/08/12。由于LeetCode上部分题目有锁,本系列将至少持续到刷完所有无锁题之日为止;由于LeetCode还在不断地创建新题,本系列的终止日期可能是永远。在这一系列刷题文章中,我不仅会讲解多种解题思路及其优化,还会用多种编程语言实现题解,涉及到通用解法时更将归纳总结出相应的算法模板。
为了方便在PC上运行调试、分享代码文件,我还建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/memcpy0/LeetCode-Conquest。在这一仓库中,你不仅可以看到LeetCode原题链接、题解代码、题解文章链接、同类题目归纳、通用解法总结等,还可以看到原题出现频率和相关企业等重要信息。如果有其他优选题解,还可以一同分享给他人。
由于本系列文章的内容随时可能发生更新变动,欢迎关注和收藏征服LeetCode系列文章目录一文以作备忘。
Given a string s, find two disjoint palindromic subsequences of s such that the product of their lengths is maximized. The two subsequences are disjoint if they do not both pick a character at the same index.
Return the maximum possible product of the lengths of the two palindromic subsequences.
A subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters. A string is palindromic if it reads the same forward and backward.
Example 1:
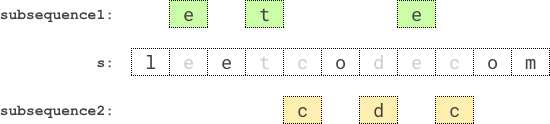
Input: s = "leetcodecom"
Output: 9
Explanation: An optimal solution is to choose "ete" for the 1st subsequence and "cdc" for the 2nd subsequence.
The product of their lengths is: 3 * 3 = 9.
Example 2:
Input: s = "bb"
Output: 1
Explanation: An optimal solution is to choose "b" (the first character) for the 1st subsequence and "b" (the second character) for the 2nd subsequence.
The product of their lengths is: 1 * 1 = 1.
Example 3:
Input: s = "accbcaxxcxx"
Output: 25
Explanation: An optimal solution is to choose "accca" for the 1st subsequence and "xxcxx" for the 2nd subsequence.
The product of their lengths is: 5 * 5 = 25.
Constraints:
2 <= s.length <= 12sconsists of lowercase English letters only.
题意:给你一个字符串 s ,请你找到 s 中两个 不相交回文子序列 ,使得它们长度的 乘积最大 。两个子序列在原字符串中如果没有任何相同下标的字符,则它们是 不相交 的。请返回两个回文子序列长度可以达到的 最大乘积 。
解法1 枚举+动态规划
由于这道题数据范围很小,我们可以枚举每一种子序列,最多有 2 12 2^{12} 212 种可能。我的做法比较粗糙:
- 枚举每一种子序列,用一个位向量加以表示;
- 判断这个位向量代表的子序列是否为回文序列;
- 如果不是,则返回第一步;否则得到这一位向量的长度 l e n 1 len_1 len1 ,再取反这一位向量,选取其他剩下的字符;
- 用动态规划求出剩下的字符中,最长的回文序列的长度 l e n 2 len_2 len2 ;
- 取所有 l e n 1 × l e n 2 len_1 \times len_2 len1×len2 中的最大值,即为题目所需结果。
整个算法的时间复杂度为 O ( 2 n × ( n + n 2 ) ) O(2^{n} \times (n+ n^2)) O(2n×(n+n2)) :
//C++ version
class Solution {
private:
int solve(const string& s) {
if (s.empty()) return 0; //判断是否为空
int n = s.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == j) dp[i][i] = 1;
else if (i + 1 == j) dp[i][j] = (s[i] == s[j] ? 2 : 1);
else dp[i][j] = max(
max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]),
(s[i] == s[j] ? 2 : 0) + dp[i + 1][j - 1]);
}
}
return dp[0][n - 1];
}
public:
int maxProduct(string s) {
if (s.size() == 2) return 1;
int n = s.size(), tot = 1 << n, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tot; ++i) { //枚举每种可能
bitset<12> fi;
int len1 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if ((i >> j) & 1) {
fi[j] = 1;
++len1;
}
}
if (len1 == 0 || len1 == n) continue;
bool flag = true;
for (int l = 0, r = n - 1; l < r; ) { //判断是否为回文子序列
while (l < r && fi[l] == 0) ++l;
while (l < r && fi[r] == 0) --r;
if (l < r) {
if (s[l] == s[r]) { ++l, --r; continue; }
else { flag = false; break; }
}
}
if (!flag) continue; //这个不是回文序列
bitset<12> se = ~fi; //取反,看哪个没有选
string temp;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (se[j]) temp += s[j];
int len2 = solve(temp); //找到se中temp的最长回文子序列
ans = max(ans, len1 * len2);
}
return ans;
}
};
//执行用时:88 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.00% 的用户
//内存消耗:26.7 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.00% 的用户
属实是暴力典范了,不过比起某些dalao来说还不够。上述代码中,枚举每一种可能的子序列,判断是否为回文子序列,不是则继续枚举——这种做法排除了许多错误方案,降低了算法的复杂度。不然直接枚举每种可能的子序列,取反得到另一子序列,然后分别计算两个子序列中最长的回文序列长度,复杂度大概是 O ( 2 n × ( 2 n 2 ) ) O(2^{n} \times (2n^2)) O(2n×(2n2)) 。不列出dalao的代码,只看一下运行效率,我只能说dalao手速太快、不拘小节:
执行用时:860 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.00% 的用户
内存消耗:273.6 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.00% 的用户
解法2 DFS暴力搜索
暴力DFS字符串 s ,对每个字符要么不选、要么插入字符序列 a 、要么插入字符序列 b 。到达字符串尾部时,分别判断字符序列 a, b 是否为回文序列,是则取这些长度乘积的最大值作为答案。 时间复杂度大概为
O
(
3
n
×
n
)
O(3^n \times n)
O(3n×n) ,好处是代码比较简洁、空间效率较高:
//C++ version
class Solution {
private:
int ans = 0, n;
bool isPindrome(const string& s) {
for (int l = 0, r = s.size() - 1; l < r; ++l, --r)
if (s[l] != s[r]) return false;
return true;
}
void dfs(int cur, const string& s, string& a, string& b) {
if (cur == n) {
int an = a.size(), bn = b.size();
if (an * bn <= ans) return;
if (isPindrome(a) && isPindrome(b)) ans = an * bn; //是回文序列且长度乘积更大
return;
}
dfs(cur + 1, s, a, b);
a.push_back(s[cur]); dfs(cur + 1, s, a, b); a.pop_back();
b.push_back(s[cur]); dfs(cur + 1, s, a, b); b.pop_back();
}
public:
int maxProduct(string s) {
n = s.size();
string a, b;
dfs(0, s, a, b);
return ans;
}
};
//执行用时:244 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了50.00% 的用户
//内存消耗:5.9 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了100.00% 的用户








 本文介绍了如何解决LeetCode上的一个算法问题,寻找字符串中两个不相交的回文子序列,使它们的长度乘积最大化。文章提供了两种解法,一种是枚举加动态规划,另一种是深度优先搜索。通过实例解释了算法思路,并给出了C++代码实现。最后,分析了不同解法的时间复杂度和空间效率。
本文介绍了如何解决LeetCode上的一个算法问题,寻找字符串中两个不相交的回文子序列,使它们的长度乘积最大化。文章提供了两种解法,一种是枚举加动态规划,另一种是深度优先搜索。通过实例解释了算法思路,并给出了C++代码实现。最后,分析了不同解法的时间复杂度和空间效率。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










