1.集合框架的概念
Java集合框架(Java Collections Framework简称JCF)是为表示和操作集合,而规定的一种统一的标准的体系结构。集合框架包含三大块内容:对外的接口、接口的实现和对集合运算的算法。数组和集合的区别:数组是定长的,集合是不定长的。
2.Collection集合
2.1 Collection集合默认可以存储任何类型的元素
2.2 Collection可以重复添加,并且可以存储空值null
2.3 不能根据下标获取单个元素
2.4 Collection的方法使用
Collection coll = new ArrayList();//定义Collection接口变量,指向其实现对象Arraylist
coll.add("a");//添加String类型的a
coll.add(5);//添加整形的5
coll.add('b');//添加char类型的b
Collection colls = new ArrayList(2);
colls.add(2);
colls.add(3);
coll.addAll(colls);
System.out.println(coll);
boolean b = coll.containsAll(colls);//判断coll中是否包含colls中的所有元素
System.out.println(b);
int size = coll.size();//获取coll的长度
System.out.println(size);
coll.remove(5);//删除2这个元素
coll.removeAll(colls);//批量删除coll中的colls的元素
System.out.println(coll);
boolean empty = coll.isEmpty();//判断coll是否为空
System.out.println(empty);
coll.clear();//清除coll中的所有元素
boolean empty1 = coll.isEmpty();
System.out.println(empty1);
3.List
3.1 List集合是有序集合: 数据的添加和存储次序一致, List集合可以存储重复的数据, List集合中的数据可以通过下标访问
3.2 ArrayList实现类的用法
3.2.1 实现了list接口,可以动态扩展,可以使用下标进行访问数据,查找较快,删除和插入较慢,ArrayList的底层就是数组,对数组进行了封装,多线程访问的时候是不安全的。
List list = new ArrayList(5);//创建长度为五的Arraylist对象
list.add("a");//在集合中添加一个String类型的a
list.add(5);//在集合中添加一个整形的数字5
list.add('a');//添加一个char类型的a
list.add(new Date());//添加一个Date类型的数据
list.add("a");//可以添加重复的数据
//当添加的内容超过数组的长度后会自动扩容
list.add("不是秋天的邱");
System.out.println(list);//输出集合的内容
list.set(3,"好一个秋");//将设置下标为3的内容为好一个秋
list.remove(new Date());//移除集合中的Date数据
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(1);//移除下标为1的内容
List listTwo = new ArrayList(2);
listTwo.add("秋天的秋");
listTwo.add(1,"湫湫湫湫");
list.addAll(listTwo);//将集合listTwo中的所有内容添加到list集合中
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.contains("不是秋天的邱"));//查找集合中是否存在“不是秋天的秋”
System.out.println(list.containsAll(listTwo));
list.get(2);//获取下标为2的内容
list.indexOf("a");//查找a首次出现的位置
System.out.println(list.size());//输出集合的长度
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());//判断集合是否为空
int i = list.hashCode();//返回list的哈希码值
System.out.println(i);
list.clear();//清空集合
3.3LinedList和Vector实现类的用法
LinkedList: 具有List的特征,底层以链表结构实现,可以进行头尾元素的添加删除
Vetor: 与ArrayList功能一致,在多线程环境下,比ArrayList安全。查询效率高,增加删除效率低,性能比较低。
LinedList的用法:
LinkedList linkedList=new LinkedList();
linkedList.add("a");//添加字符型的a
linkedList.add(5);//添加整型数据
linkedList.add(new Date());//添加时间类型数据
linkedList.addFirst(1);//在头部添加数据
linkedList.addLast("尾");//在尾部添加数据
linkedList.set(2,"hello");//在下标为2的地方插入元素
System.out.println(linkedList.get(2));//获取下标为2的元素内容
linkedList.getFirst();//获取第一个数据 即linkedlist【0】
linkedList.getLast();//获取最后一个元素的内容
LinkedList linked = new LinkedList(); //LinkedList不能指定长度
linked.add(11);
linked.add(10);
linkedList.addAll(linked);//批量添加元素 即添加linked中是所有元素
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.remove(2);//删除下标为2的元素的内容
System.out.println(linkedList);
System.out.println(linked);
linkedList.addAll(0,linked);//在下标为2的地方放批量插入数据
System.out.println(linkedList);
linkedList.removeFirst();//删除头部元素
linkedList.removeLast();//删除尾部元素
System.out.println(linkedList);
4 set
4.1.set是无序且不能重复的,他是一个接口,它包含HashSet和TreeSet两个部分。底层逻辑是hashMap
4.2.HashSet的使用方法如下:
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();//默认的长度是16
HashSet hashSet1 = new HashSet(5);//可以指定长度
HashSet hashSet2 = new HashSet(15,0.7f);
//其中15表示长度,0.7表示负载因子,即当资源使用达到70%的时候会自动扩容
hashSet.add(1);//添加数字1
hashSet.add("A");
hashSet.add("B");
hashSet.add('A');
hashSet.add("A");
System.out.println(hashSet);//当添加的内容有重复时会自动舍弃,因为hashset是不可重复的,根据输出来看hashSet是无序的
hashSet1.add("张学良");
hashSet1.add("吴佩孚");
hashSet1.add("孙传芳");
hashSet.addAll(hashSet1);//批量添加元素,即将hashSet1中的所有元素都添加到hashSet中,
System.out.println(hashSet);
int size = hashSet.size();//获取长度
System.out.println(size);
boolean a = hashSet.contains("A");//判断A是否在hashSet集合中
System.out.println(a);
boolean empty = hashSet.isEmpty();//判断是否为空
System.out.println(empty);
hashSet.remove("孙传芳");//移除孙传芳
System.out.println(hashSet);
//foreach方式遍历hashSet集合
for (Object o:hashSet) {
System.out.print(o+"\t");
}
System.out.println("\n"+"——————————————————————————我是分割线————————————————————————");
//使用迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator();//获取迭代器对象
while (iterator.hasNext()){//判断指针是否能够移动
System.out.print(iterator.next()+"\t");//输出当前指针所指的元素.next表示获取当前指针所指的元素
}
4.3.TreeSet的底层逻辑是二叉树,TreeSet可以实现有序集合,但是有序需要通过比较器实现
4.4.TreeSet的使用方法:和hashSet一模一样
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add("A");
treeSet.add("B");
treeSet.add("C");
treeSet.add("D");//添加元素
TreeSet treeSet1 = new TreeSet();
treeSet1.add("你好");
treeSet1.add("欢迎你");
treeSet.addAll(treeSet1);//批量添加元素
System.out.println(treeSet);
System.out.println(treeSet.size());//输出treeSet的长度
treeSet.remove("D");//删除D
4.5比较器的实现方法
当添加对象类型的数据时需要指定比较器。TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet(); 但是在创建对象时 并没有为其指定排序得规则,那么就要求该集合得元素有排序规则。 如果元素得类已经创建完成,不能修改该类得源码,这时我们又想把该类得对象放入得TreeSet容器中。 这时就需要你在创建TreeSet时指定排序得规则。
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(new Student("张三",15));
treeSet.add(new Student("李四",16));
treeSet.add(new Student("王五",18));
treeSet.add(new Student("麻叶子",15));
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}
class Student{
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Student() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
如果不指定比较器就会出现如下错误
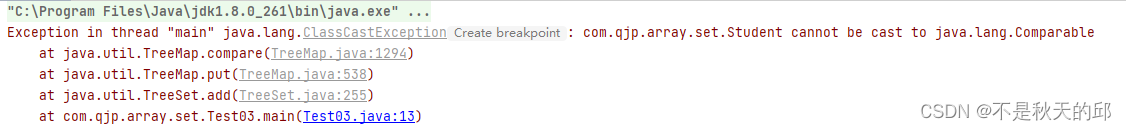
Studenmapt类需要实现Comparable接口 其次重写compareTo方法
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Student student=(Student) o;
if(this.age>student.age){
return 1;
}
if(this.age<student.age){
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet(new MyComparator());//创建TreeSet时为其导入选择器,
//其中Mycomparator是Comparator接口的实现类
5. Map,Map中的每一个元素都是属于键值对模式,如果往map中添加元素就需要同时添加key和value,Map也是一个接口,他有一个hashMap实现类。
5.1 hashMap的使用方法
Map map=new HashMap(); //创建hashMap对象,默认长度为16,负载因子为0.75
map.put("name","秋");//添加数据前边的为键 后边的为值 键不能重复,值无所谓
System.out.println(map);
map.put("age",15);
Map map1=new HashMap(15);
map1.put("k1","v1");
map1.put("k2","v2");
map.putAll(map1);
//批量添加hashMap中的所有元素,如果后边添加的元素的键值和前边的一样
//那么后边的将会覆盖前边的
boolean empty = map.isEmpty();//判断是否为空
System.out.println(empty);
Object k1 = map.get("k1");//输出键为k1的值
System.out.println(k1);
hashmap.putIfAbsent("key2","v3");//如果键值重复将不会添加此键值对
boolean k11 = map.containsKey("k1");//判断是否存在
System.out.println(k11);
Set set = map.keySet();//获取所有键 返回值为数组
System.out.println(set);
//使用foreatch遍历map
for (Object o:set) {
Object o1 = map.get(o);
System.out.println(o+"+++++++++++++++++>>>>>>>>"+o1);
}
hashmap.clear();//清空hashmap
map.remove("age2");//根据指定得key移除元素
System.out.println(map);
map.clear(); //清空map容器
System.out.println(map);
hashmap.replace("key2","v3");//替换,将键值为key2的值替换为v3
}
5.2hashMap的底层原理
5.2.1 JDK1.7使用的数据结构为:数组+链表 ,链表插入模式为头部插入,且容易造成死循环
5.2.2JDK1.8使用的数据结构是:数组+链表+红黑树 , 链表的插入模式为尾部插入。Hashmap得原理,存储元素使用得put(key,value),根据key得hash计算出相应得哈希值,根据相应得算法求出该元素在数组中得位置, 如果求出得哈希值相同,则称为哈希冲突,会根据equals来判断元素是否一致,如果equals不同,则存入单向链表上, 如果哈希碰撞得个数超过8个,则把链表转换为红黑二叉树。




















 45万+
45万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








