一、SpringMVC简介
是一种基于JAVA实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架。
解析:
1、MVC架构模式的思想:将Web层进行指责解耦
2、基于请求驱动:请求-相应模型
3、框架的目的:简化开发
二、web.xml配置说明
1、ContextLoaderListener 初始化
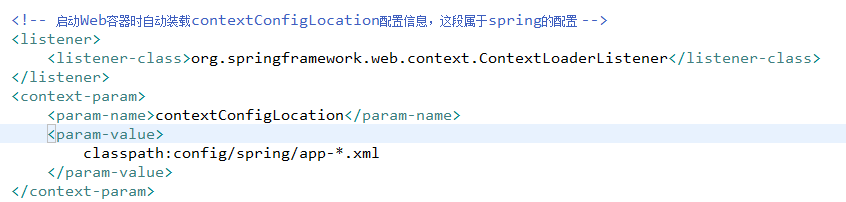
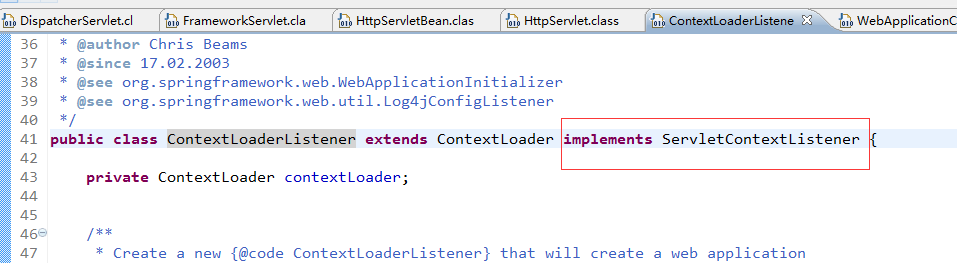
从图中我们可以看出ContextLoaderListener 实现了 ServletContextListener 所以在web容器启动时它就进行了配置信息的初始化
在我们的spring xml配置文件文件中 除了用于springmvc那部分,其他的配置都在ContextLoaderListener 中进行初始化
像这些配置文件中我们所配置的相关bean,都会在这一步被初始化到spring的bean工厂
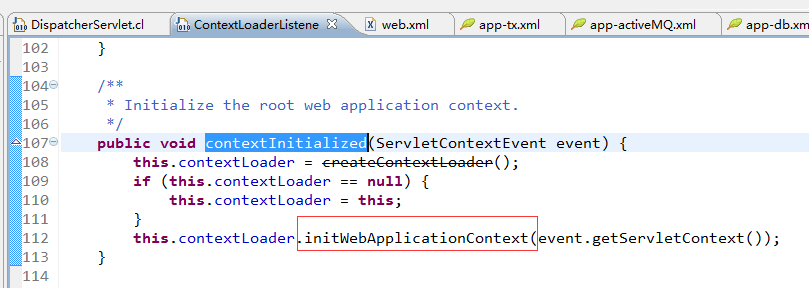
2、DispatcherServlet(分发器) 初始化
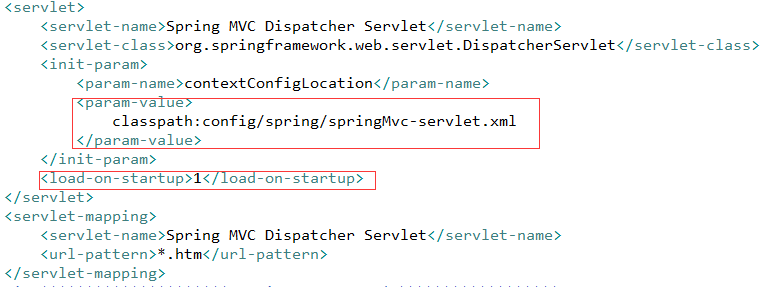
从配置中我们可以看出,它就是一个servlert 而且 load-on-startup 为1 所以在web容器启动的时候,它就被进行了初始化,
它初始化的东西就是我们在 springMvc-servlet.xml 中配置的信息。
继承关系:
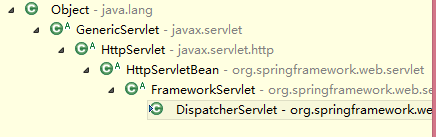
在web容器启动时将调用HttpServletBean中的init方法,该方法的主要作用是将servlet初始化参数(init-param)设置到该组件上,
而且HttpServletBean还提供给子类一个初始化扩展店,initServletBean(),该方法由FramewordServlet覆盖。
FrameworkServlet继承HttpServletBean 通过initServletBean()进行web上下文初始化,该方法主要覆盖以下两件事情:初始化web 上下文、提供子类初始化扩展点。
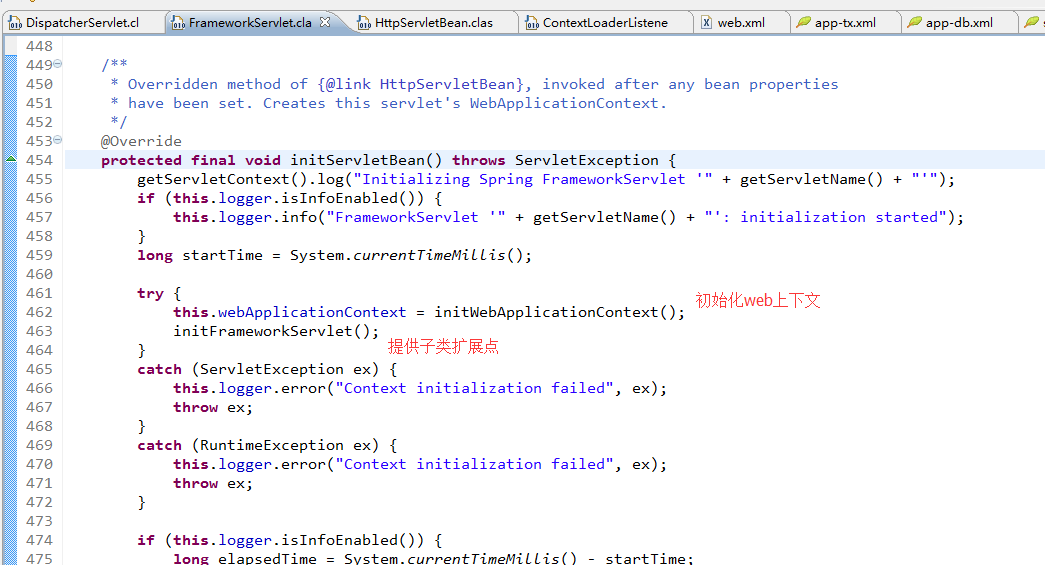
- protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
- //ROOT上下文(ContextLoaderListener加载的)
- WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
- WebApplicationContext wac = null;
- if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
- //1、在创建该Servlet注入的上下文
- wac = this.webApplicationContext;
- if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
- ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
- if (!cwac.isActive()) {
- if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
- cwac.setParent(rootContext);
- }
- configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
- }
- }
- }
- if (wac == null) {
- //2、查找已经绑定的上下文
- wac = findWebApplicationContext();
- }
- if (wac == null) {
- //3、如果没有找到相应的上下文,并指定父亲为ContextLoaderListener
- wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
- }
- if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
- onRefresh(wac);//4、刷新上下文(执行一些初始化)
- }
- if (this.publishContext) {
- String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
- getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
- if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
- }
- }
- return wac;
- }
DispatcherServlet继承FrameworkServlet,并实现了onRefresh()方法提供一些前端控制器相关的配置
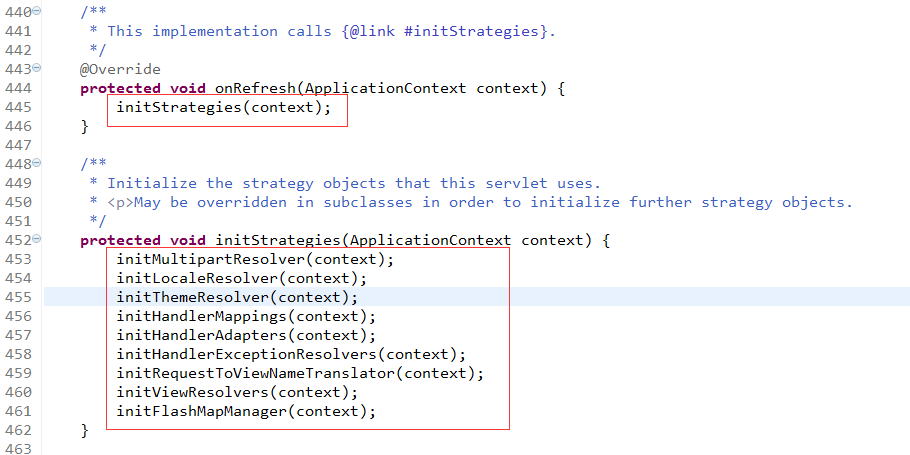
从如上代码可以看出,DispatcherServlet启动时会进行我们需要的Web层Bean的配置,如HandlerMapping、HandlerAdapter等,而且如果我们没有 配置,还会给我们提供默认的配置。
默认配置:
3、ContextLoaderListener初始化上下文 和 DispatcherServlet初始化上下文的关系
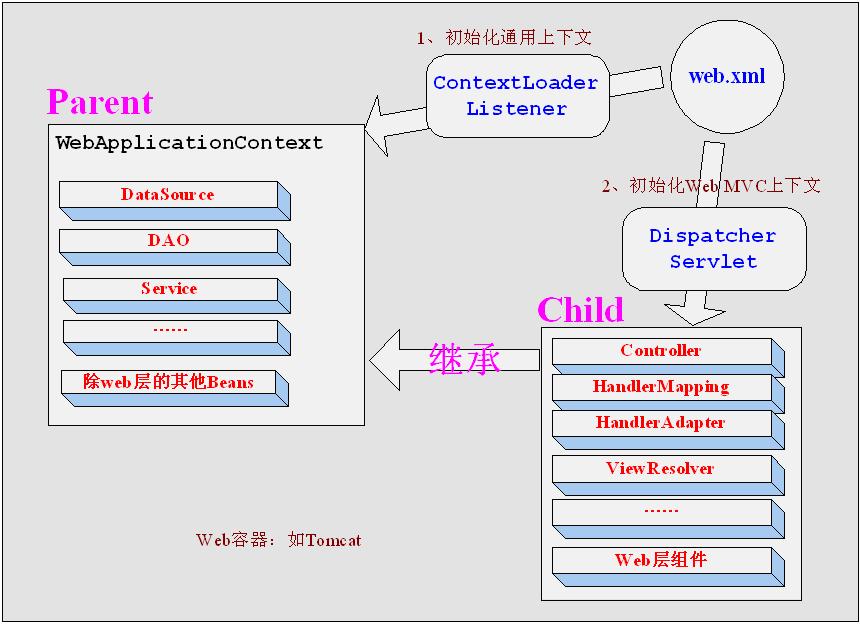
从图中我们可以看出,ContextLoaderListener 初始化的上下文bean是对整个应用程序共享的,而DispatcherServlet 初始化的
上下文只对Spring Web Mvc有效。
三、SpringMVC处理请求流程
SpringMVC框架是一个基于请求驱动的Web框架,并且使用了‘前端控制器’模型来进行设计,再根据‘请求映射规则’分发给相应的页面控制器进行处理。
具体流程:
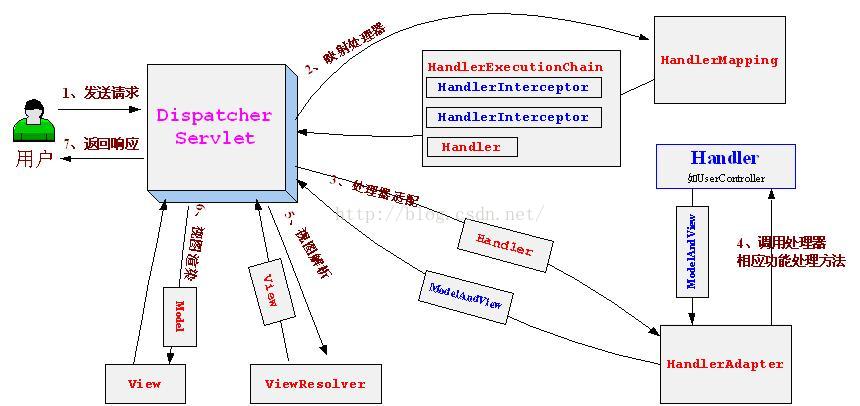
1、 首先用户 发送请求—— >DispatcherServlet , 分发器收到请求后自己不进行处理,而是委托给其他的解析器进行处理,作为统一访问点,进行全局的流程控制;
2、 DispatcherServlet —— >HandlerMapping , HandlerMapping 将会把请求映射为 HandlerExecutionChain 对象(包含一个 Handler 处理器(Controller)对象、多个 HandlerInterceptor 拦截器)对象,通过这种策略模式,很容易添加新的映射策略;
3、 DispatcherServlet —— >HandlerAdapter , HandlerAdapter 将会把处理器包装为适配器,从而支持多种类型的处理器,即适配器设计模式的应用,从而很容易支持很多类型的处理器;
4、 HandlerAdapter —— > 处理器功能处理方法的调用, HandlerAdapter 将会根据适配的结果调用真正的处理器的功能处理方法,完成功能处理(在调用处理器前会先执行spring的前置拦截器preHandle);并返回一个 ModelAndView 对象(包含模型数据、逻辑视图名),返回视图后会执行spring的后置拦截器postHandle;
5、 ModelAndView 的逻辑视图名—— > ViewResolver , ViewResolver 将把逻辑视图名解析为具体的 View,通过这种策略模式,很容易更换其他视图技术;
6、 View —— > 渲染 ,View 会根据传进来的 Model 模型数据进行渲染,此处的 Model 实际是一个 Map 数据结构,因此很容易支持其他视图技术(这步处理完后执行spring的完成后拦截器);
7、 返回控制权给 DispatcherServlet , 由 DispatcherServlet 返回响应给用户,到此一个流程结束。
DispatcherServlet 的分发控制主要是在doDispatch 中完成,接下来我来看下源码
- protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
- HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
- HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
- boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
- WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
- try {
- ModelAndView mv = null;
- Exception dispatchException = null;
- try {
- //步骤1、检查请求是否是multipart(如文件上传),如果是将通过MultipartResolver解析
- processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
- multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
- //步骤2、请求到处理器(页面控制器Controller)的映射,通过HandlerMapping进行映射
- mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest, false);
- if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
- noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
- return;
- }
- //步骤3、处理器适配,将我们的处理器包装成相应的适配器(从而支持多种类型的处理器)
- HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
- // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
- //304 Not Modified缓存支持
- String method = request.getMethod();
- boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
- if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
- long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
- }
- if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
- return;
- }
- }
- //执行处理器相关的拦截器的前置理(HandlerInterceptor.preHandle)
- if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
- return;
- }
- //步骤4、由适配器执行处理器(调用处理器相应功能处理方法)
- mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
- if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
- return;
- }
- applyDefaultViewName(request, mv);
- //执行处理器相关的拦截器的后处理(HandlerInterceptor.postHandle)
- mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- dispatchException = ex;
- }
- //这里面执行了处理器相关拦截器的完成后处理(HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion)
- processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
- }
- catch (Error err) {
- triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err);
- }
- finally {
- if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
- // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
- if (mappedHandler != null) {
- mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
- }
- }
- else {
- // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
- if (multipartRequestParsed) {
- cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
- }
- }
- }
- }




 本文介绍了Spring MVC框架的基本概念,包括其MVC设计模式、请求驱动类型的特点及简化开发的目标。详细阐述了web.xml配置文件中ContextLoaderListener与DispatcherServlet的作用及初始化过程,并概述了Spring MVC处理请求的具体流程。
本文介绍了Spring MVC框架的基本概念,包括其MVC设计模式、请求驱动类型的特点及简化开发的目标。详细阐述了web.xml配置文件中ContextLoaderListener与DispatcherServlet的作用及初始化过程,并概述了Spring MVC处理请求的具体流程。
















 2471
2471

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








