目录
一. 前言
前面两篇文章《(一)Spring 核心之面向切面编程(AOP)—— 配置及使用》和《(二)Spring 核心之面向切面编程(AOP)—— 切面的实现》主要介绍了 Spring AOP 原理解析的切面实现过程,如加载配置,将切面类的所有切面方法根据使用的注解生成对应 Advice,并将 Advice 连同切入点匹配器和切面类等信息一并封装到Advisor。本文在此基础上继续介绍postProcessAfterInitialization 的方法,即代理(JDK 代理和 CGLIB 代理)的创建过程。
二. 代理的创建
2.1. 创建前准备
创建代理的方法是 postProcessAfterInitialization,如果 Bean 被子类标识为代理,则使用配置的拦截器创建一个代理。
/**
* Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is
* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.
* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 如果不是提前暴露的代理
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}wrapIfNecessary() 方法主要用于判断是否需要创建代理,如果 Bean 能够获取到 advisor 才需要创建代理:
/**
* Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access
* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is
*/
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 如果bean是通过TargetSource接口获取
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
// 如果bean是切面类
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// 如果是aop基础类?是否跳过?
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 重点:获取所有advisor,如果没有获取到,那说明不要进行增强,也就不需要代理了。
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 重点:创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}2.2. 获取所有的 Advisor
我们看下获取所有 advisor 的方法 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean():
@Override
@Nullable
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}通过 findEligibleAdvisors() 方法获取 advisor,如果获取不到返回 DO_NOT_PROXY(不需要创建代理),findEligibleAdvisors() 方法如下:
/**
* Find all eligible Advisors for auto-proxying this class.
* @param beanClass the clazz to find advisors for
* @param beanName the name of the currently proxied bean
* @return the empty List, not {@code null},
* if there are no pointcuts or interceptors
* @see #findCandidateAdvisors
* @see #sortAdvisors
* @see #extendAdvisors
*/
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 和上文一样,获取所有切面类的切面方法生成Advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 找到这些Advisor中能够应用于beanClass的Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 如果需要,交给子类拓展
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
// 对Advisor排序
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}获取所有切面类的切面方法生成 Advisor:
/**
* Find all candidate Advisors to use in auto-proxying.
* @return the List of candidate Advisors
*/
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available");
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}找到这些 Advisor 中能够应用于 beanClass 的 Advisor:
/**
* Determine the sublist of the {@code candidateAdvisors} list
* that is applicable to the given class.
* @param candidateAdvisors the Advisors to evaluate
* @param clazz the target class
* @return sublist of Advisors that can apply to an object of the given class
* (may be the incoming List as-is)
*/
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 通过Introduction实现的advice
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
// 是否能够应用于clazz的Advice
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}2.3. 创建代理的入口方法
获取所有 advisor 后,如果有 advisor,则说明需要增强,即需要创建代理,创建代理的方法如下:
/**
* Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,
* already pre-configured to access the bean
* @return the AOP proxy for the bean
* @see #buildAdvisors
*/
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
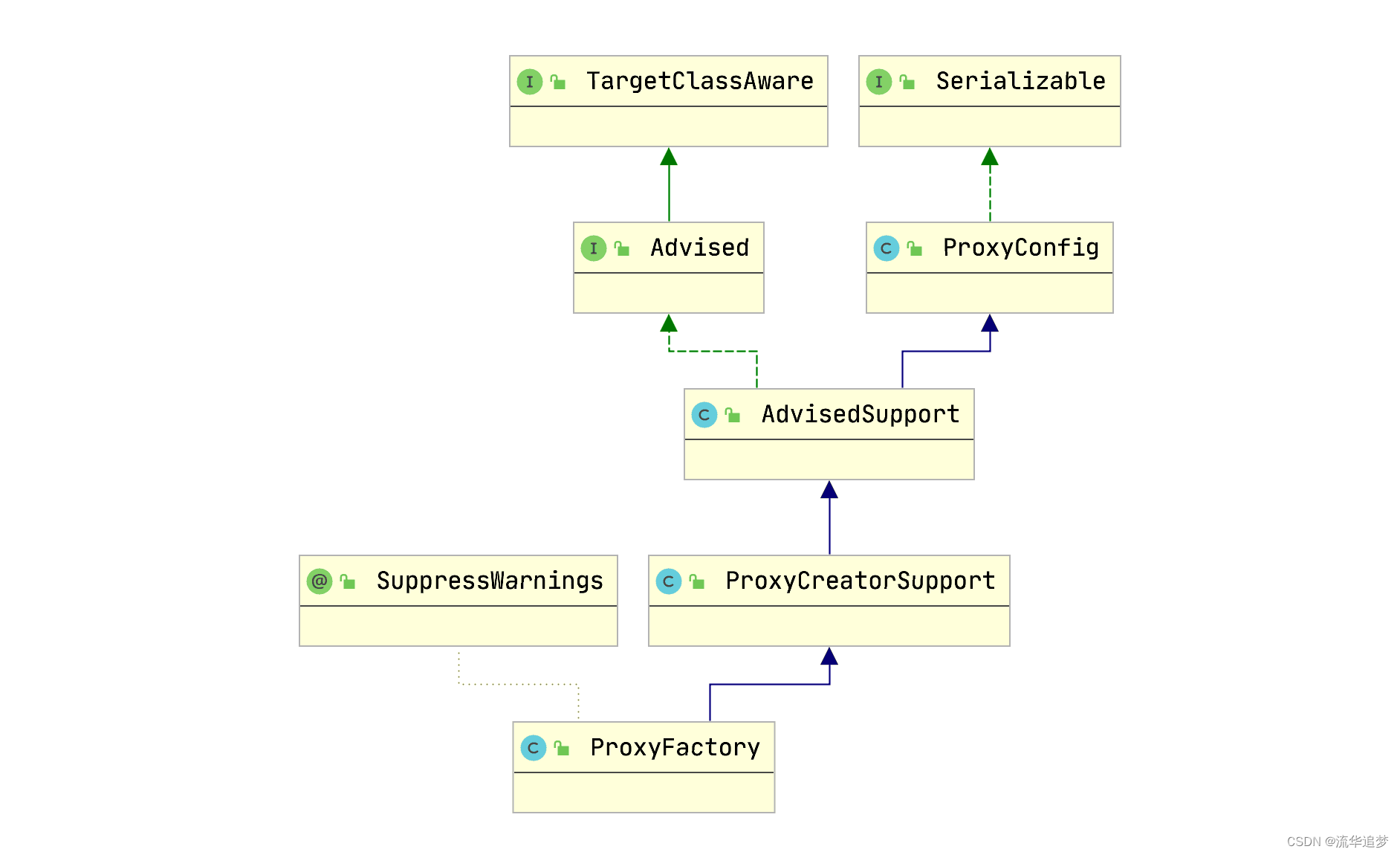
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
// Explicit handling of JDK proxy targets (for introduction advice scenarios)
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(beanClass)) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the proxy's interfaces only.
for (Class<?> ifc : beanClass.getInterfaces()) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);
}
}
}
else {
// No proxyTargetClass flag enforced, let's apply our default checks...
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader
ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader();
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) {
classLoader = ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).getOriginalClassLoader();
}
return proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader);
}proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader):
/**
* Create a new proxy according to the settings in this factory.
* <p>Can be called repeatedly. Effect will vary if we've added
* or removed interfaces. Can add and remove interceptors.
* <p>Uses the given class loader (if necessary for proxy creation).
* @param classLoader the class loader to create the proxy with
* (or {@code null} for the low-level proxy facility's default)
* @return the proxy object
*/
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}2.4. 依据条件创建代理(JDK 或 CGLIB)
DefaultAopProxyFactory.createAopProxy:
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() &&
(config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}要点如下:
- config.isOptimize() 是通过 optimize 设置,表示配置是自定义的,默认是 false;
- config.isProxyTargetClass() 是通过 <aop:config proxy-target-class="true" /> 来配置的,表示优先使用 cglib 代理,默认是 false;
- hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config) 表示是否目标类实现了接口。
三. 动态代理要解决什么问题
3.1. 什么是代理
代理模式(Proxy Pattern):为另一个对象提供一个替身或占位符以控制对这个对象的访问。具体请参见《设计模式 - 代理模式》。
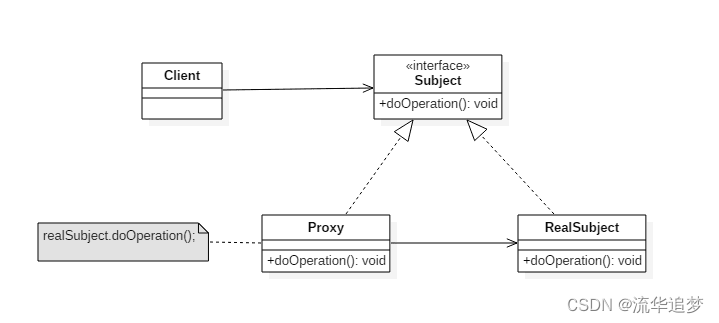
举个简单的例子:我(Client)如果要买(doOperation)房,可以找中介(Proxy)买房,中介直接和卖方(Target)买房。中介和卖方都实现买卖(doOperation)的操作。中介就是代理(Proxy)。
3.2. 什么是动态代理
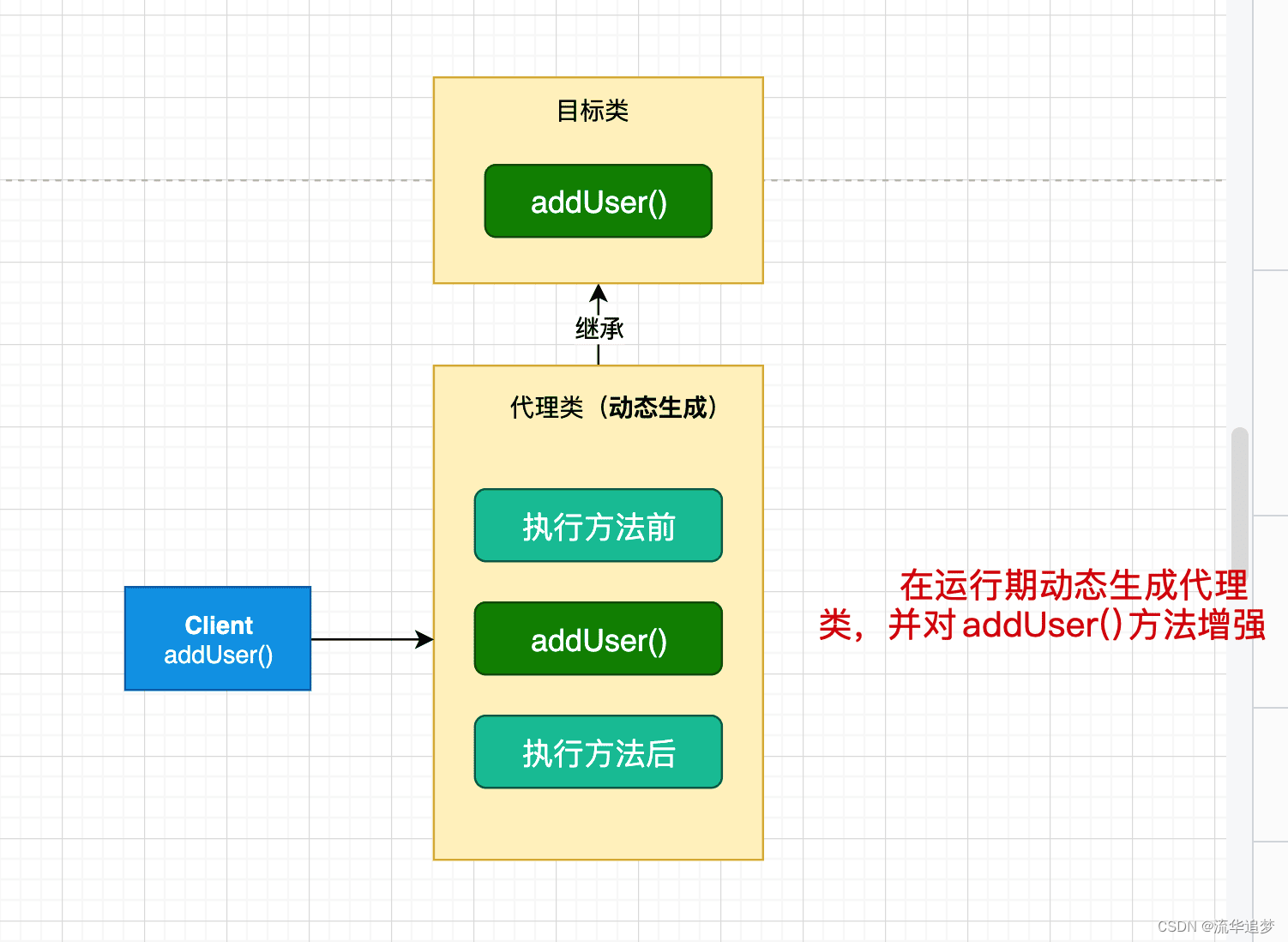
动态代理就是:在程序运行期间,创建目标对象的代理对象,并对目标对象中的方法进行功能性增强的一种技术。
在生成代理对象的过程中,目标对象不变,代理对象中的方法是目标对象方法的增强方法。可以理解为运行期间,对象中方法的动态拦截,在拦截方法的前后执行功能操作。
四. 总结
Spring 默认在目标类实现接口时是通过 JDK 代理实现的,只有非接口的是通过 CGLIB 代理实现的。当设置 proxy-target-class 为 true 时在目标类不是接口或者代理类时优先使用 CGLIB 代理实现。





 本文详细阐述了SpringAOP中的代理创建过程,包括使用postProcessAfterInitialization创建代理,以及如何根据条件选择JDK代理或CGLIB代理。重点讲解了动态代理的概念和Spring在不同情况下的代理策略。
本文详细阐述了SpringAOP中的代理创建过程,包括使用postProcessAfterInitialization创建代理,以及如何根据条件选择JDK代理或CGLIB代理。重点讲解了动态代理的概念和Spring在不同情况下的代理策略。


















 4245
4245

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










