目录
一. 前言
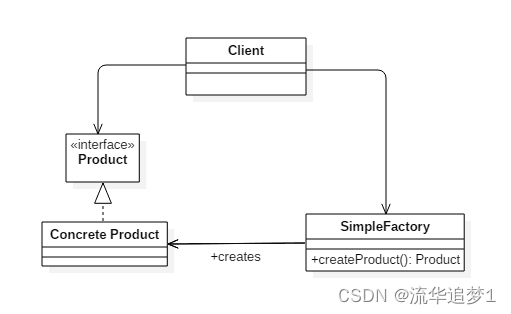
简单工厂不是设计模式,更像是一种编程习惯。它把实例化的操作单独放到一个类中,这个类就成为简单工厂类,让简单工厂类来决定应该用哪个具体子类来实例化,这样做能把客户类和具体子类的实现解耦,客户类不再需要知道有哪些子类以及应当实例化哪个子类。
二. 实现
public interface Product {
}
/**
* 具体产品1
*/
public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
}
/**
* 具体产品2
*/
public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
}
/**
* 具体产品3
*/
public class ConcreteProduct3 implements Product {
}以下的 Client 类中包含了实例化的代码,这是一种错误的实现,如果在客户类中存在实例化代码,就需要将代码放到简单工厂中。
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int type = 1;
Product product;
if (type == 1) {
product = new ConcreteProduct1();
} else if (type == 2) {
product = new ConcreteProduct2();
} else {
product = new ConcreteProduct3();
}
// do something with the product
}
}以下的 SimpleFactory 是简单工厂实现,它被所有需要进行实例化的客户类调用。
public class SimpleFactory {
public Product createProduct(int type) {
if (type == 1) {
return new ConcreteProduct1();
} else if (type == 2) {
return new ConcreteProduct2();
}
return new ConcreteProduct3();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();
Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);
// do something with the product
}
}




 简单工厂模式是一种编程习惯,用于将对象实例化的责任从客户类转移到专门的工厂类,以减少代码耦合。文章通过示例展示了如何通过SimpleFactory创建不同类型的Product(ConcreteProduct1,ConcreteProduct2,ConcreteProduct3),强调了将实例化逻辑移出Client类的重要性。
简单工厂模式是一种编程习惯,用于将对象实例化的责任从客户类转移到专门的工厂类,以减少代码耦合。文章通过示例展示了如何通过SimpleFactory创建不同类型的Product(ConcreteProduct1,ConcreteProduct2,ConcreteProduct3),强调了将实例化逻辑移出Client类的重要性。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










