目录
1.2. configureHeadlessProperty
1.4. DefaultApplicationArguments
2.2. ConfigurableEnvironment和Environment
2.3.2. configurePropertySources
2.4. ConfigurationPropertySources.attach
2.5. DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd
一. SpringApplication.run代码概览
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}SpringApplication的run方法运行 Spring 应用程序,方法内有几个核心对象:bootstrapContext、context、environment。其中最核心的为context,创建并刷新一个新的ApplicationContext,方法prepareContext(),refreshContext(),afterRefresh()都是围绕context处理,而refreshContext()是run方法中核心中的核心,预估需要多章节才能讲完。
1.1. bootstrapContext
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.initialize(bootstrapContext));
return bootstrapContext;
}public interface ConfigurableBootstrapContext extends BootstrapRegistry, BootstrapContext {
}DefaultBootstrapContext是ConfigurableBootstrapContext的默认实现。ConfigurableBootstrapContext是一个BootstrapContext,它还通过BootstrapRegistry接口提供配置方法。BootstrapContext是一个简单的引导上下文,在启动和Environment后处理期间可用,直到准备好ApplicationContext。BootstrapContext提供对单例的惰性访问,这些单例的创建成本可能很高,或者需要在ApplicationContext可用之前共享。
public interface BootstrapContext {
/**
* 如果类型已注册,则从上下文中返回一个实例。如果之前没有访问过该实例,则会创建它。
* @param <T> 实例类型
* @param type 实例类型
* @throws IllegalStateException 如果类型尚未注册
*/
<T> T get(Class<T> type) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 如果类型已注册,则从上下文中返回一个实例。如果之前没有访问过该实例,则会创建它。
* @param <T> 实例类型
* @param type 实例类型
* @param other 如果类型尚未注册,则使用的实例
*/
<T> T getOrElse(Class<T> type, T other);
/**
* 如果类型已注册,则从上下文中返回一个实例。如果之前没有访问过该实例,则会创建它。
* @param <T> 实例类型
* @param type 实例类型
* @param other 如果类型尚未注册,则要使用的实例的Supplier
*/
<T> T getOrElseSupply(Class<T> type, Supplier<T> other);
/**
* 如果类型已注册,则从上下文中返回一个实例。如果之前没有访问过该实例,则会创建它。
* @param <T> 实例类型
* @param type 实例类型
* @param exceptionSupplier 将返回要抛出的异常的Supplier
* @throws IllegalStateException 如果类型尚未注册抛出的异常
*/
<T, X extends Throwable> T getOrElseThrow(Class<T> type, Supplier<? extends X> exceptionSupplier) throws X;
/**
* 如果给定类型存在注册,则返回true。
* @param <T> 实例类型
* @param type 实例类型
*/
<T> boolean isRegistered(Class<T> type);
}
在引入依赖的spring.factories中不包含BootstrapRegistryInitializer的实例,所以得到的BootstrapContext内容如下:
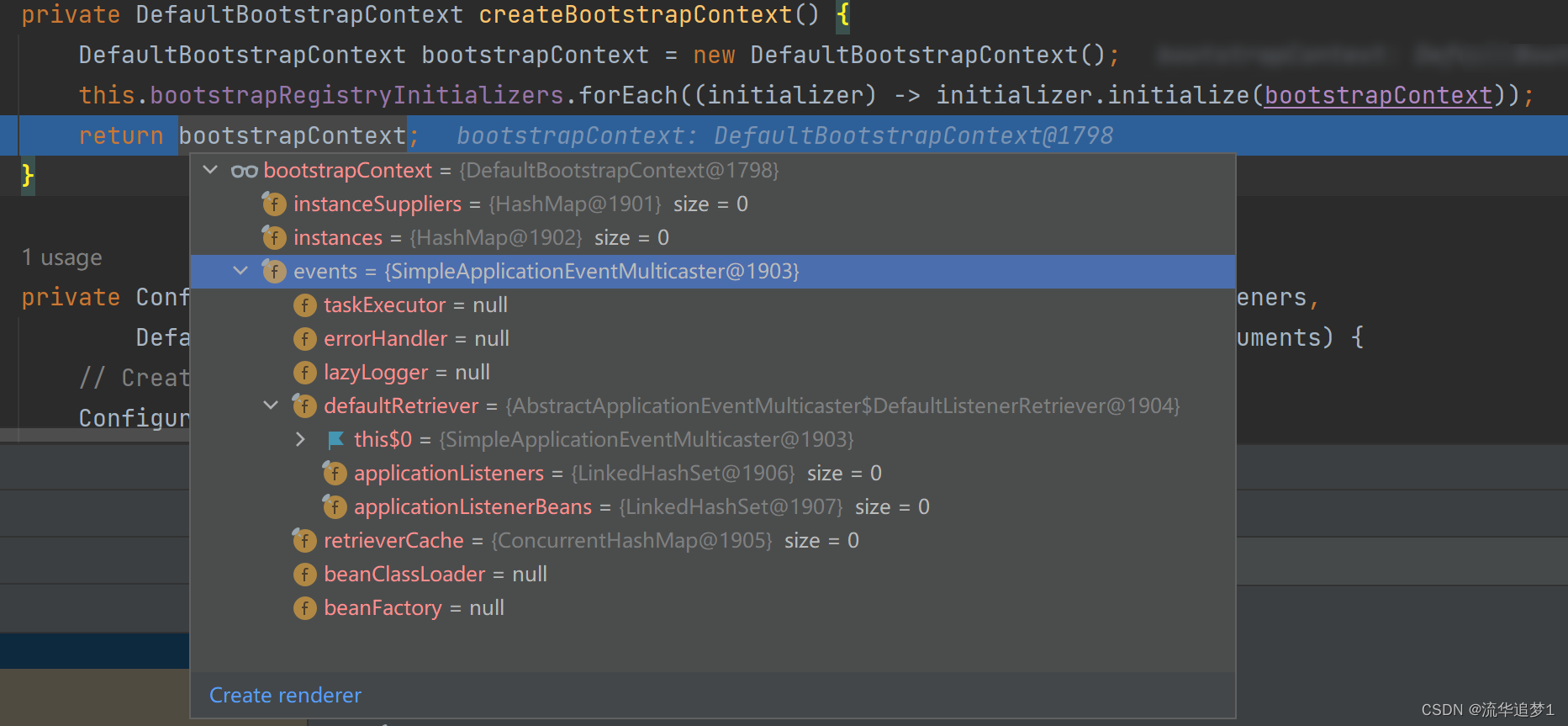
1.2. configureHeadlessProperty
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
System.setProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS,
System.getProperty(SYSTEM_PROPERTY_JAVA_AWT_HEADLESS, Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}configureHeadlessProperty设置系统属性java.awt.headless的值,如果原先没有设置,则设置为true。
java.awt.headless是J2SE的一种模式,用于在缺失显示屏、鼠标或者键盘时的系统配置。对于后端服务来讲,很多都是需要将这个属性设置为true的。
1.3. getRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args),
this.applicationStartup);
}SpringApplicationRunListeners是SpringApplicationRunListener的集合,SpringApplicationRunListener是SpringApplication中run方法的侦听器。SpringApplicationRunListener通过SpringFactoriesLoader加载,并且应该声明一个接受SpringApplication实例和String[]参数的公共构造函数。每次运行都会创建一个新的SpringApplicationRunListener实例。
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
/**
* 在 run 方法第一次启动时立即调用。可用于非常早的初始化。
*/
default void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
}
/**
* 在环境准备好,且在创建ApplicationContext之前调用。
*/
default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
}
/**
* 在创建和准备ApplicationContext后,但在加载源之前调用。
*/
default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 在加载应用程序上下文但在刷新之前调用。
*/
default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 上下文已刷新,应用程序已启动,但尚未调用CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners。
* @param timeTaken 启动应用程序所用的时间,如果未知,则为null
* @since 2.6.0
*/
default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
started(context);
}
/**
* 上下文已刷新,应用程序已启动,但尚未调用CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners。
*/
@Deprecated
default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 在 run 方法完成之前立即调用,此时应用程序上下文已刷新并且所有CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners已被调用。
* @param timeTaken 启动应用程序所用的时间,如果未知,则为null
* @since 2.6.0
*/
default void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
running(context);
}
/**
* 在 run 方法完成之前立即调用,此时应用程序上下文已刷新并且所有CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners已被调用。
*/
@Deprecated
default void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 当运行应用程序发生故障时调用。
* @since 2.0.0
*/
default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
}
}listeners.starting
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction,
Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {
StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);
this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);
if (stepAction != null) {
stepAction.accept(step);
}
step.end();
}StartupStep记录有关在ApplicationStartup期间发生的特定阶段或操作的指标。StartupStep的生命周期如下:1.该步骤是通过调用the application startup来创建和启动的,并被分配一个唯一的id。2.我们可以在处理过程中使用StartupStep.Tags附加信息。3.我们需要标记步骤的end()。
实现可以跟踪“执行时间”或其他步骤的度量。
public interface StartupStep {
/**
* 返回启动步骤的名称。
*/
String getName();
/**
* 在应用程序启动中返回此步骤的唯一 ID。
*/
long getId();
/**
* 如果可用,返回父步骤的id。父步骤是创建当前步骤时最近启动的步骤。
*/
@Nullable
Long getParentId();
/**
* 将StartupStep.Tag添加到步骤。
*/
StartupStep tag(String key, String value);
/**
* 将StartupStep.Tag添加到步骤。
*/
StartupStep tag(String key, Supplier<String> value);
/**
* 返回此步骤的StartupStep.Tag集合。
*/
Tags getTags();
/**
* 记录步骤的状态以及可能的其他指标,例如执行时间。一旦结束,就不允许更改步骤状态。
*/
void end();
/**
* StartupStep.Tag的不可变集合。
*/
interface Tags extends Iterable<Tag> {
}
/**
* 用于存储步骤元数据的简单键/值关联。
*/
interface Tag {
/**
* 返回Tag名称。
*/
String getKey();
/**
* 返回Tag值。
*/
String getValue();
}
}1.4. DefaultApplicationArguments
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);ApplicationArguments提供对用于运行SpringApplication的参数的访问。DefaultApplicationArguments是ApplicationArguments的默认实现。
二. prepareEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}2.1. getOrCreateEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.applicationContextFactory.createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType);
if (environment == null && this.applicationContextFactory != ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT) {
environment = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT.createEnvironment(this.webApplicationType);
}
return (environment != null) ? environment : new ApplicationEnvironment();
}成员变量applicationContextFactory的具体类为DefaultApplicationContextFactory,DefaultApplicationContextFactory是接口ApplicationContextFactory的实现类。getOrCreateEnvironment会根据成员字段webApplicationType生成合适的ConfigurableEnvironment。
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return getFromSpringFactories(webApplicationType, ApplicationContextFactory::createEnvironment, null);
}private <T> T getFromSpringFactories(WebApplicationType webApplicationType,
BiFunction<ApplicationContextFactory, WebApplicationType, T> action, Supplier<T> defaultResult) {
for (ApplicationContextFactory candidate : SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(ApplicationContextFactory.class,
getClass().getClassLoader())) {
T result = action.apply(candidate, webApplicationType);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return (defaultResult != null) ? defaultResult.get() : null;
}类AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext和AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext都有静态内部类Factory实现了ApplicationContextFactory接口
以AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的Factory为例:
static class Factory implements ApplicationContextFactory {
@Override
public Class<? extends ConfigurableEnvironment> getEnvironmentType(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET) ? null : ApplicationServletEnvironment.class;
}
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET) ? null : new ApplicationServletEnvironment();
}
@Override
public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET) ? null
: new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
}2.2. ConfigurableEnvironment和Environment
ConfigurableEnvironment是大多数Environment类都将实现的配置接口。提供用于设置活动和默认配置文件以及操作基础属性源的工具。允许客户端通过ConfigurablePropertyResolver超级接口设置和验证所需属性、自定义转换服务等。Environment表示当前应用程序运行环境的接口,对应用程序环境的两个关键方面进行建模:配置文件和属性。
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
/**
* 指定为此Environment活动的配置文件集。在容器引导期间评估配置文件以确定是否应向容器注册bean定义。
*/
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* 将配置文件添加到当前的活动配置文件集中。
*/
void addActiveProfile(String profile);
/**
* 如果没有其他配置文件通过setActiveProfiles显式激活,则指定默认激活的配置文件集。
*/
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* 以可变形式返回此Environment的PropertySources ,允许操作在针对此Environment对象解析属性时应搜索的PropertySource对象集。
* 各种MutablePropertySources方法(例如addFirst 、 addLast 、 addBefore和addAfter允许对属性源排序进行细粒度控制。
*/
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources();
/**
* 如果当前SecurityManager允许,则返回System.getProperties()的值,否则返回一个映射实现,该实现将尝试使用对System.getProperty(String)的调用来访问各个键。
*/
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties();
/**
* 如果当前SecurityManager允许,则返回System.getenv()的值,否则返回一个映射实现,该实现将尝试使用对System.getenv(String)的调用来访问各个键。
*/
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment();
/**
* 将给定父环境的活动配置文件、默认配置文件和属性源附加到此(子)环境各自的集合中。
*/
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
}环境对象的配置必须通过ConfigurableEnvironment接口完成,该接口从所有AbstractApplicationContext子类getEnvironment()方法返回。
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* 返回为此环境显式激活的配置文件集。配置文件用于创建要按条件注册的 bean 定义的逻辑分组,例如基于部署环境。
* 可以通过将“spring.profiles.active”设置为系统属性或调用ConfigurableEnvironment.setActiveProfiles(String...)来激活配置文件。
* 如果没有将配置文件明确指定为活动,则任何默认配置文件都将自动激活。
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles();
/**
* 当没有明确设置活动配置文件时,默认情况下将配置文件集返回为活动状态。
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
/**
* @deprecated as of 5.1 in favor of {@link #acceptsProfiles(Profiles)}
*/
@Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* 返回活动配置文件是否与给定的Profiles谓词匹配。
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
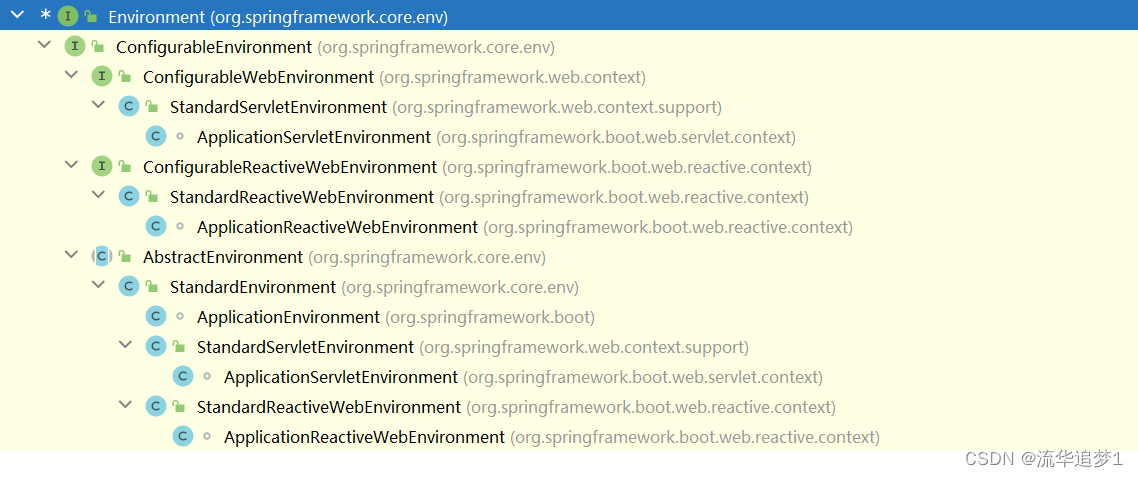
}Environment子类:
2.3. configureEnvironment
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService());
}
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}configureEnvironment方法按照environment.setConversionService -> configurePropertySources -> configureProfiles的顺序分别对属性源或配置文件进行细粒度控制。
2.3.1. setConversionService
addConversionService是SpringApplication的成员字段,默认值为true。ConfigurableEnvironment的setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService)方法继承于ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口, 该接口是PropertyResolver类型都将实现的配置接口。提供用于访问和自定义将属性值从一种类型转换为另一种类型时使用的ConversionService的工具。
PropertyResolver是用于针对任何底层源解析属性的接口
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* 返回给定的属性键是否可用于解析,即给定键的值是否不为null。
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* 返回与给定键关联的属性值,如果无法解析键,则返回null。
* @param key 要解析的属性名称
*/
@Nullable
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* 返回与给定键关联的属性值,如果无法解析键,则返回defaultValue。
* @param key 要解析的属性名称
* @param defaultValue 如果没有找到值,则返回默认值
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* 返回与给定键关联的属性值,如果无法解析键,则返回null。
* @param key 要解析的属性名称
* @param targetType 属性值的预期类型
*/
@Nullable
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 返回与给定键关联的属性值,如果无法解析键,则返回defaultValue 。
* @param key 要解析的属性名称
* @param targetType 属性值的预期类型
* @param defaultValue 如果没有找到值,则返回默认值
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* 返回与给定键关联的属性值(从不为null)
* @throws IllegalStateException 如果无法解析给定的key
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 返回与给定键关联的属性值,转换为给定的 targetType(从不为null )。
* @throws IllegalStateException 如果无法解析给定的key
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 解析给定文本中的 ${...} 占位符,用getProperty解析的相应属性值替换它们。
* 没有默认值的不可解析占位符将被忽略并保持不变。
* @param text 要解析的字符串
* @return 解析的字符串(从不为null )
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果给定字符串为null
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* 解析给定文本中的 ${...} 占位符,用getProperty解析的相应属性值替换它们。
* 没有默认值的不可解析占位符将导致抛出 IllegalArgumentException。
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果给定字符串为null或任何占位符无法解析
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}ApplicationConversionService是FormattingConversionService的一种特殊化,默认配置了适用于大多数 Spring Boot 应用程序的转换器和格式化程序。ApplicationConversionService专为直接实例化而设计,但也公开了静态addApplicationConverters和addApplicationFormatters(FormatterRegistry)实用程序方法,以便针对注册表实例临时使用。ApplicationConversionService构造方法如下:
public ApplicationConversionService() {
this(null);
}
public ApplicationConversionService(StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver) {
this(embeddedValueResolver, false);
}
private ApplicationConversionService(StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver, boolean unmodifiable) {
if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {
setEmbeddedValueResolver(embeddedValueResolver);
}
configure(this);
this.unmodifiable = unmodifiable;
}configure(this):
/**
* 使用适用于大多数SpringBoot应用程序的格式化程序和转换器配置给定的FormatterRegistry。
* @param registry 要添加到的转换器的注册表
* @throws ClassCastException 如果给定的 FormatterRegistry 无法转换为 ConversionService
*/
public static void configure(FormatterRegistry registry) {
DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(registry);
DefaultFormattingConversionService.addDefaultFormatters(registry);
addApplicationFormatters(registry);
addApplicationConverters(registry);
}DefaultConversionService提供了默认情况下使用适用于大多数环境的转换器或者格式化服务,其addDefaultConverters源码如下:
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeToCalendarConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}2.3.2. configurePropertySources
SpringApplication的configurePropertySources方法用于在此应用程序的环境中添加、删除或重新排序任何PropertySource。
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) {
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources);
}
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite
.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}MutablePropertySources是PropertySources接口的默认实现,允许操作包含的属性源并提供用于复制现有PropertySources实例的构造函数。
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource是Environment中的最后一个属性源。DefaultPropertiesPropertySource继承MapPropertySource,MapPropertySource是从Map对象读取键和值的PropertySource。
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource的addOrMerge方法用于添加新的DefaultPropertiesPropertySource或与现有的合并。
public static void addOrMerge(Map<String, Object> source, MutablePropertySources sources) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(source)) {
Map<String, Object> resultingSource = new HashMap<>();
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource propertySource = new DefaultPropertiesPropertySource(resultingSource);
if (sources.contains(NAME)) {
mergeIfPossible(source, sources, resultingSource);
sources.replace(NAME, propertySource);
}
else {
resultingSource.putAll(source);
sources.addLast(propertySource);
}
}
}在SpringApplication执行完构造方法后去调用run方法时,成员字段defaultProperties为null,调用configurePropertySources方法并不会执行DefaultPropertiesPropertySource的addOrMerge方法。
在main启动时如果有传入的args参数,则会触发CompositeProperty的addPropertySource操作,CompositeProperty迭代一组PropertySource实例的复合PropertySource实现(在多个属性源共享相同名称的情况下是必需的)。
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource用于提供最简单的方法来解析命令行参数,它的构造方法最终调用的是PropertySource的构造方法:
public class SimpleCommandLinePropertySource extends CommandLinePropertySource<CommandLineArgs> {
/**
* 创建一个新的SimpleCommandLinePropertySource具有默认名称并由给定的命令行参数String[]支持。
* @see CommandLinePropertySource#COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME
* @see CommandLinePropertySource#CommandLinePropertySource(Object)
*/
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String... args) {
super(new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser().parse(args));
}
/**
* 创建一个具有给定名称并由命令行参数的给定String[]支持的新SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 。
*/
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String name, String[] args) {
super(name, new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser().parse(args));
}
/**
* 获取选项参数的属性名称。
*/
@Override
public String[] getPropertyNames() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.source.getOptionNames());
}
@Override
protected boolean containsOption(String name) {
return this.source.containsOption(name);
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected List<String> getOptionValues(String name) {
return this.source.getOptionValues(name);
}
@Override
protected List<String> getNonOptionArgs() {
return this.source.getNonOptionArgs();
}
}2.4. ConfigurationPropertySources.attach
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);public static void attach(Environment environment) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment).getPropertySources();
PropertySource<?> attached = getAttached(sources);
if (attached == null || !isUsingSources(attached, sources)) {
attached = new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources));
}
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
sources.addFirst(attached);
}ConfigurationPropertySources的attach方法将ConfigurationPropertySource支持附加到指定的Environment。使环境管理的每个PropertySource适应ConfigurationPropertySource并允许经典的PropertySourcesPropertyResolver调用使用configuration property names进行解析。附加的解析器将动态跟踪来自基础Environment属性源的任何添加或删除。
在attach方法中,先判断传入的environment是否是ConfigurableEnvironment类型,满足条件则强转为ConfigurableEnvironment类型并调用getPropertySources方法。在sources中移除名称是configurationProperties的属性源,并且把attached作为最高优先级添加到sources中。
2.5. DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);public static void moveToEnd(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
moveToEnd(environment.getPropertySources());
}
public static void moveToEnd(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
PropertySource<?> propertySource = propertySources.remove(NAME);
if (propertySource != null) {
propertySources.addLast(propertySource);
}
}DefaultPropertiesPropertySource继承MapPropertySource,MapPropertySource包含直接贡献给SpringApplication的默认属性。按照惯例, DefaultPropertiesPropertySource始终是Environment中的最后一个属性源。DefaultPropertiesPropertySource的moveToEnd方法移动“defaultProperties”属性源,使其成为给定ConfigurableEnvironment中的最后一个源。
2.6. bindToSpringApplication
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
try {
Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}SpringApplication的bindToSpringApplication方法将环境绑定到SpringApplication。
Binder是一个容器对象,它绑定来自一个或多个ConfigurationPropertySources的对象。Binder的get方法从指定的环境创建一个新的Binder实例:
public static Binder get(Environment environment) {
return get(environment, null);
}
public static Binder get(Environment environment, BindHandler defaultBindHandler) {
Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> sources = ConfigurationPropertySources.get(environment);
PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver placeholdersResolver = new PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver(environment);
return new Binder(sources, placeholdersResolver, null, null, defaultBindHandler);
}Binder的构造方法:
public Binder(Iterable<ConfigurationPropertySource> sources, PlaceholdersResolver placeholdersResolver,
List<ConversionService> conversionServices, Consumer<PropertyEditorRegistry> propertyEditorInitializer,
BindHandler defaultBindHandler, BindConstructorProvider constructorProvider) {
Assert.notNull(sources, "Sources must not be null");
for (ConfigurationPropertySource source : sources) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Sources must not contain null elements");
}
this.sources = sources;
this.placeholdersResolver = (placeholdersResolver != null) ? placeholdersResolver : PlaceholdersResolver.NONE;
this.bindConverter = BindConverter.get(conversionServices, propertyEditorInitializer);
this.defaultBindHandler = (defaultBindHandler != null) ? defaultBindHandler : BindHandler.DEFAULT;
if (constructorProvider == null) {
constructorProvider = BindConstructorProvider.DEFAULT;
}
ValueObjectBinder valueObjectBinder = new ValueObjectBinder(constructorProvider);
JavaBeanBinder javaBeanBinder = JavaBeanBinder.INSTANCE;
this.dataObjectBinders = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(valueObjectBinder, javaBeanBinder));
}ConfigurationPropertySource是ConfigurationProperties的来源。ConfigurationPropertySources的get(Environment environment)返回一组先前已attached到Environment的ConfigurationPropertySource实例。
三. createApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);SpringApplication的createApplicationContext是用于创建ApplicationContext的策略方法,和创建Environment类似。默认情况下,此方法将尊重任何显式设置的应用程序上下文类或工厂,然后再回退到合适的默认值。此方法返回的应用程序上下文是尚未刷新的。
private ApplicationContextFactory applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);
}成员变量applicationContextFactory的具体类为DefaultApplicationContextFactory,DefaultApplicationContextFactory是接口ApplicationContextFactory的实现类。createApplicationContext会根据成员字段webApplicationType生成合适的ConfigurableApplicationContext。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET) ? null
: new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.REACTIVE) ? null
: new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();
}createApplicationContext方法执行完毕后,接着调用GenericApplicationContext的setApplicationStartup方法:
public void setApplicationStartup(ApplicationStartup applicationStartup) {
super.setApplicationStartup(applicationStartup);
this.beanFactory.setApplicationStartup(applicationStartup);
}beanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory的实例。SpringApplication的createApplicationContext是通过创建GenericApplicationContext的无参构造方法创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的。
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}DefaultListableBeanFactory是Spring的ConfigurableListableBeanFactory和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的默认实现,是一个基于 bean 定义元数据的成熟 bean 工厂,可通过后处理器进行扩展。典型用法是在访问 bean 之前首先注册所有 bean 定义(可能从 bean 定义文件中读取,按名称查找Bean是本地bean定义表中的一种低成本操作,它对预先解析的bean定义元数据对象进行操作。)。
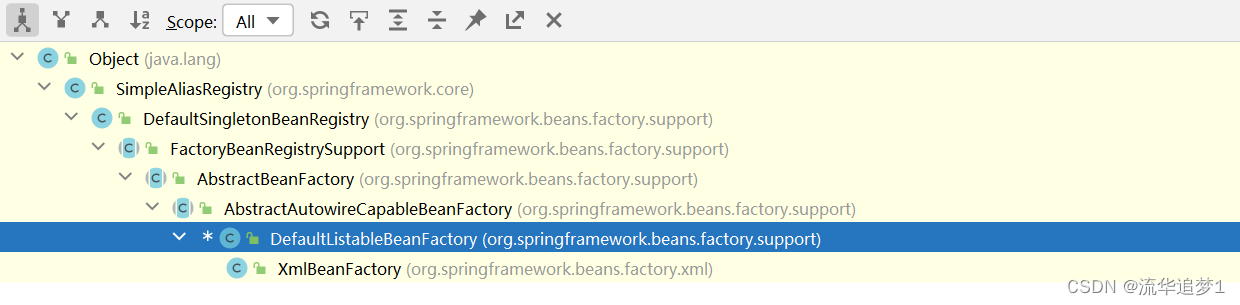
DefaultListableBeanFactory的层次性关系:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory是实现默认bean创建的抽象bean工厂超类,具有RootBeanDefinition类指定的全部功能。除了 AbstractBeanFactory的createBean方法外,还实现了AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口。AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory提供 bean 创建(使用构造函数解析)、属性填充、连接(包括自动连接)和初始化。处理运行时bean引用、解析托管集合、调用初始化方法等。AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory支持自动装配构造函数、按名称的属性和按类型的属性(其子类要实现的主要模板方法是resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor, String, Set, TypeConverter) ,用于按类型自动装配。如果工厂能够搜索其bean定义,匹配的 bean通常将通过这样的搜索来实现。对于其他工厂风格,可以实现简化的匹配算法)。
AbstractBeanFactory是BeanFactory实现的抽象基类,提供ConfigurableBeanFactory SPI的全部功能。AbstractBeanFactory可以用作bean 工厂实现的基类,它从一些后端资源获取bean定义(其中bean定义访问是一项昂贵的操作)。此类提供单例缓存(通过其基类DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry、单例/原型确定、FactoryBean处理、别名、合并子bean定义的bean定义和bean销毁(通过org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean接口,自定义销毁方法)。此外,它可以通过实现org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory接口来管理bean工厂层次结构(在未知bean的情况下委托给父级)。
子类实现的主要模板方法是getBeanDefinition和createBean,分别检索给定bean名称的bean定义和为给定bean定义创建 bean 实例。这些操作的默认实现可以在DefaultListableBeanFactory和AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory中找到。
四. prepareContext
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.setEnvironment源码(如果引入了spring-boot-starter-webflux依赖,则为AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext):
public void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
super.setEnvironment(environment);
this.reader.setEnvironment(environment);
this.scanner.setEnvironment(environment);
}AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext的成员字段reader和scanner在构造方法被调用时进行赋值:
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader顾名思义就是基于注解的BeanDefinition读取器,ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner是基于ClassPath路径下的BeanDefinition扫描器。
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader会注册ConfigurationClassPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、EventListenerMethodProcessor、DefaultEventListenerFactory这些类
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner通过可配置的类型过滤器检测候选类,默认过滤器包括使用 Spring 的@Component 、 @Repository 、 @Service或@Controller原型注解的类。
五. refreshContext
refreshContext是springBoot启动源码中最复杂的部分了,里面的内容也非常多,将会拆分很多个章节去说。
请参见
六. callRunners
afterRefresh()是个空方法。然后走到下面listeners.started(context),处理各个listener。最后callRunners
这里面重要的就是callRunners。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}从beanFactory中获取ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner修饰的类的对象,并加入runners中.然后再排序。




 SpringApplication的run方法是启动SpringBoot应用的核心,它涉及到环境配置、ApplicationContext创建、监听器调用等多个步骤。在run方法中,首先创建BootstrapContext,配置headless属性,获取run监听器。然后,准备环境,包括创建和配置Environment,设置属性源,以及绑定到SpringApplication。接着,创建ApplicationContext,调用prepareContext方法进行进一步的初始化。最后,刷新ApplicationContext,调用runners执行。整个过程涉及到了SpringBoot启动的多个重要环节。
SpringApplication的run方法是启动SpringBoot应用的核心,它涉及到环境配置、ApplicationContext创建、监听器调用等多个步骤。在run方法中,首先创建BootstrapContext,配置headless属性,获取run监听器。然后,准备环境,包括创建和配置Environment,设置属性源,以及绑定到SpringApplication。接着,创建ApplicationContext,调用prepareContext方法进行进一步的初始化。最后,刷新ApplicationContext,调用runners执行。整个过程涉及到了SpringBoot启动的多个重要环节。


















 1532
1532

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










