线程的创建与运行
Java中有三种创建线程的方式,分别是继承Thread类并重写run方法,实现Runnable接口的run方法,使用FutureTask方式。
一 继承Thread类并重写run方法
public class TestThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("haha.");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
TestThread thread = new TestThread();
thread.start();
}
}
如上代码,TestThread类继承了Thread类并重写了run方法,需要注意的是调用start方法后线程并没有马上执行而是进入就绪状态。使用继承的好处就是在run方法内获取当前线程直接使用this就可以,不好的地方就是java不支持多继承。
二 实现Runnable接口的run方法
public class TestRunnable implements Runnable {
int a = 0;
@Override
public void run(){
if(a > 4){
System.out.println("i'm a a child");
}else{
System.out.println("i'm a b child");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRunnable task = new TestRunnable();
new Thread(task).start();
new Thread(task).start();
}
}
如上所示,TestRunnable类实现了Runnable接口的run方法,在main方法中创建了一个TestRunnable的实例然后调用该实例的start方法启动线程。
以上两种方法共同点是任务执行完之后没有返回值
三 使用FutureTask方式
public class TestCallTask implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
return "hello";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建异步任务
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new TestCallTask() {
});
//启动线程
new Thread(futureTask).start();
//等待任务完成并返回结果
try {
String result = futureTask.get();
System.out.println(result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
如上代码中的TestCallTask类实现了Callable接口的call()方法,在main方法中首先创建了一个futureTask对象然后使用创建的对象作为任务创建了一个线程并启动,最后通过get()方法等待任务完成返回结果。
使用继承的好处是方便传参,如果使用Runnable方式则只能使用主线程里面被声明为final的变量,前两种方法无法拿到任务的返回结果而FutureTask方式可以*
线程的通知与等待
wait()方法
当一个线程调用共享变量的wait()方法时该线程会被阻塞挂起,直到1)其他线程调用该共享变量的notify()方法2)其他线程调用了该共享变量的interrupt()方法才会返回。
wait()方法被调用时只会释放当前共享变量上的锁,释放与持有都是针对该共享变量而言。
wait(long timeout)方法指定了对应线程在不被其他线程调用Notify()方法唤醒的场景下的超时时间。
package com.thread;
public class WaitFunction {
//resourceA,resourceB是共享变量
private static volatile Object resourceA = new Object();
private static volatile Object resourceB = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println("threadA get resourceA lock");
//获取资源B
synchronized (resourceB){
System.out.println("threadA get resourceB lock");
System.out.println("threadA release resourceA lock");
resourceA.wait();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//创建线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
//休眠2s
Thread.sleep(2000);
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println("threadB get resourceA lock");
System.out.println("threadB try get resourceB lock");
//获取资源B
synchronized (resourceB){
System.out.println("threadB get resourceB lock");
System.out.println("threadB release resourceA lock");
resourceA.wait();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
threadA.start();;
threadB.start();
threadA.join();
threadB.join();
}
}

如上代码,在线程B休眠2s的时间中线程A获取了资源A和资源B的锁,然后调用A的wait()方法阻塞自己之后A释放掉资源A的锁,线程B在休眠结束后会先尝试获取资源A的锁,若此时线程A还未释放资源A的锁则线程B会被阻塞,在线程B获取资源B的锁时由于线程A未释放该锁所以线程B会被阻塞。
package com.thread;
public class WaitFunction {
//resourceA,resourceB是共享变量
private static volatile Object resourceA = new Object();
private static volatile Object resourceB = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println("threadA get resourceA lock");
//获取资源B
synchronized (resourceB){
System.out.println("threadA get resourceB lock");
System.out.println("threadA release resourceA lock");
resourceA.wait();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//创建线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try{
//休眠2s
Thread.sleep(2000);
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println("threadB get resourceA lock");
System.out.println("threadB try get resourceB lock");
//获取资源B
synchronized (resourceB){
System.out.println("threadB get resourceB lock");
System.out.println("threadB release resourceA lock");
resourceA.wait();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
//模拟被其他线程中断
threadA.interrupt();
threadB.interrupt();
}
}

以上代码使用interrput()方法模拟线程被其他线程中断后抛出异常的场景。
Notify()与notifyAll()方法
notify()方法会唤醒一个在该共享变量上调用wait()方法后被挂起的线程,但是是随机唤醒,同时被唤醒的线程需要在获取该共享变量的监视器锁后才可以返回。
notifyAll()方法会唤醒该共享变量上的所有挂起的线程。
package com.thread;
public class TestNotify {
//resourceA是共享变量
private static volatile Object resourceA = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA) {
System.out.println("threadA begin wait");
resourceA.wait();
System.out.println("threadA begin wait");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//创建线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA) {
System.out.println("threadB begin wait");
resourceA.wait();
System.out.println("threadB end wait");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//创建线程C
Thread threadC = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA) {
System.out.println("threadC begin notify");
resourceA.notify();
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
//休眠一秒等A和B都获取到锁其中有一个挂起后再启动C
Thread.sleep(2000);
threadC.start();
threadA.join();
threadB.join();
threadC.join();
System.out.println("end sss");
}
}

如上代码,线程A和线程B共同去获取资源A的锁,其中有一个线程被阻塞挂起,之后线程C去调用资源A的notify方法唤醒被挂起的线程。但是另外一个线程还是在持有资源A的锁。
package com.thread;
public class TestNotify {
//resourceA是共享变量
private static volatile Object resourceA = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA) {
System.out.println("threadA begin wait");
resourceA.wait();
System.out.println("threadA begin wait");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//创建线程B
Thread threadB = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA) {
System.out.println("threadB begin wait");
resourceA.wait();
System.out.println("threadB end wait");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
//创建线程C
Thread threadC = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//获取资源A
synchronized (resourceA) {
System.out.println("threadC begin notify");
resourceA.notifyAll();
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
//休眠一秒等A和B都获取到锁其中有一个挂起后再启动C
Thread.sleep(2000);
threadC.start();
threadA.join();
threadB.join();
threadC.join();
System.out.println("end sss");
}
}

如上代码,当线程C调用资源A的notifyAll()方法时将所有被挂起的线程唤醒。
等待终止join()与睡眠sleep()
join()方法可以等戴先成执行结束后结束整体任务,该方法无参且无返回值。
sleep()方法是指当线程调用时会让出规定时间内的执行权不参与cpu调度但其持有的锁还是继续持有,等待时间到了之后该线程处于就绪状态参与cpu的调度。
如果子线程在sleep期间主线程中断了子线程,则子线程抛出异常。
package com.thread;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestJoinAndSleep {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//设置日期格式
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(df.format(new Date()));// new Date()为获取当前系统时间
System.out.println("threadA begin start");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
threadA.start();
threadA.join();
System.out.println(df.format(new Date()));// new Date()为获取当前系统时间
System.out.println("threadA end");
}
}
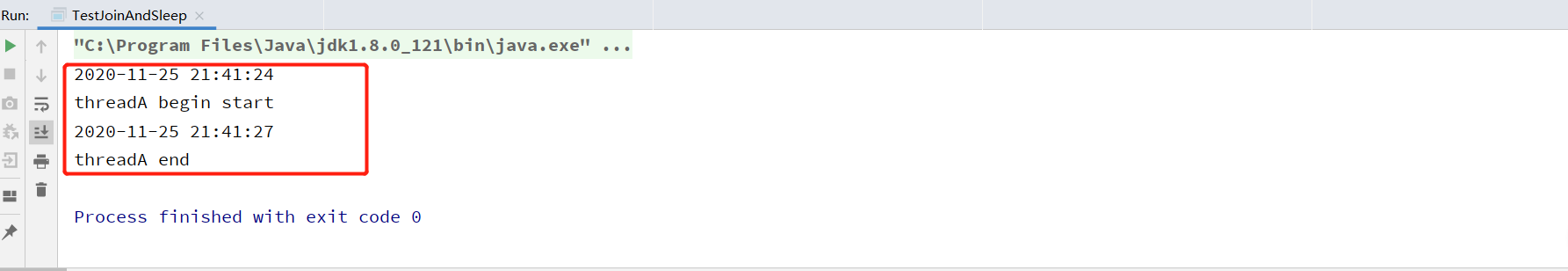
如上代码,线程A在启动之后调用sleep方法休眠3s后执行结束,而调用join方法等待线程A结束后结束任务,查看运行结果的时间可以证明。
让出cpu的yield()与中断interrput()
当一个线程调用yield方法时,当前线程会让出cpu使用权然后处于就绪状态,线程调度器会从就绪队列中获取优先级最高的一个线程来获取cpu执行权。
package com.thread;
public class TestYield implements Runnable {
TestYield() {
Thread t = new Thread(this);
t.start();
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//当i=0时让出cpu进行下一轮调度
if ((i % 5) == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "yield cpu...");
}
//当前线程让出cpu进行下一轮调度
//Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "over...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new TestYield();
new TestYield();
}
}

如上代码,开了两个线程每个线程的功能都一样,分别在i=0时调用yield方法让出cpu进行下一轮调度。该方法一般用在调试或者测试的场景下帮助复现并发竞争条件导致的问题。
sleep与yield方法的区别在于,当线程调用sleep时线程会被挂起调度器不回调用,而调用yield时线程只是让出cpu没有被挂起。
线程中断的方法有三个,分别如下:
void interrupt() :中断线程,给线程设置中断标志并挂起线程
boolean isInterrupt():检测当前线程是否中断
boolean interrupt():检测是否中断,如果发现线程中断则清除标志
package com.thread;
public class TestInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "hello");
}
}
});
//启动子线程
threadA.start();
//主线程休眠2S
Thread.sleep(1000);
//中断子线程
System.out.println("main thread interrupt threadA");
threadA.interrupt();
//等待子线程执行结束
threadA.join();
System.out.println("main over");
}
}
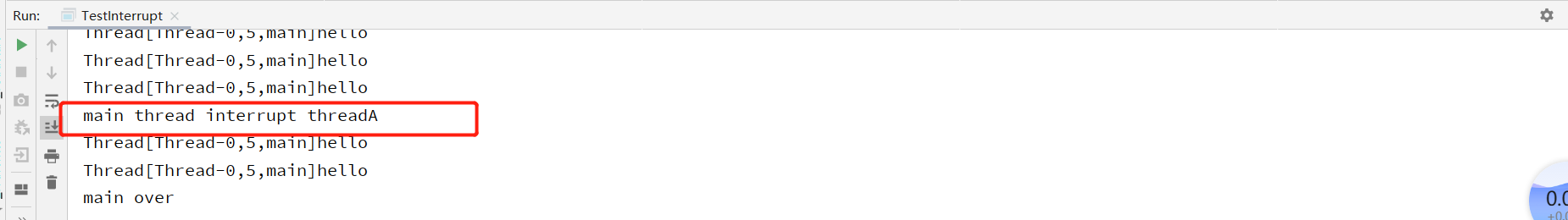
如上代码,主线程在等待子线程启动后中断子线程,子线程中断后返回等待结束。
package com.thread;
public class TestInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建线程A
Thread threadA = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(;;){
}
}
});
//启动子线程
threadA.start();
//设置中断标志
threadA.interrupt();
//获取中断标志
System.out.println("isInterrput:" + threadA.isInterrupted());
//获取标志并重置
System.out.println("isInterrput:" + threadA.interrupted());
//获取标志并重置
System.out.println("isInterrput:" + Thread.interrupted());
//获取中断标志
System.out.println("isInterrput:" + threadA.isInterrupted());
threadA.join();
System.out.println("main over");
}
}
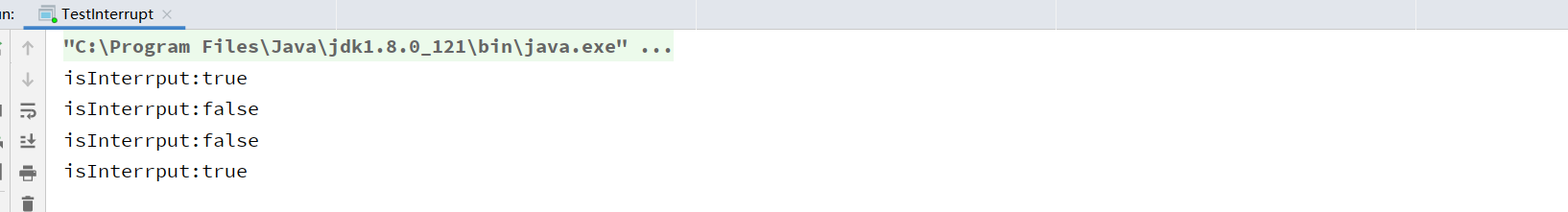
如上代码,在设置中断标志后打印出来,然后重置中断标志在打印。





 本文总结了Java中线程的创建与运行,包括继承Thread、实现Runnable和使用FutureTask三种方式。接着介绍了线程的通知与等待机制,如wait、notify和notifyAll方法,以及join和sleep方法的使用。还探讨了yield方法和线程中断的操作,如interrupt、isInterrupted和interrupted方法的作用。
本文总结了Java中线程的创建与运行,包括继承Thread、实现Runnable和使用FutureTask三种方式。接着介绍了线程的通知与等待机制,如wait、notify和notifyAll方法,以及join和sleep方法的使用。还探讨了yield方法和线程中断的操作,如interrupt、isInterrupted和interrupted方法的作用。
















 1067
1067

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








