一、鼠标的故事
鼠标,是计算机的定位输入设备,其标准称呼应该是“鼠标器”,英文名“Mouse”,鼠标的使用是为了使计算机的操作更加简便快捷,来代替键盘那繁琐的指令。鼠标是1964年由加州大学伯克利分校博士道格拉斯·恩格尔巴特(Douglas Engelbart)发明的 ,当时道格拉斯·恩格尔巴特在斯坦福研究所(SRI)工作 [3] ,该研究所是斯坦福大学赞助的一个机构,Douglas Engelbart很早就在考虑如何使电脑的操作更加简便,用什么手段来取代由键盘输入的繁琐指令,申请专利时的名字为显示系统X-Y位置指示器。
二、Windows鼠标
微软最早的操作系统是DOS(Disk Operate System)为非图形界面,鼠标是不存在的,当时的电脑也仅仅是科研的工具。直到Windows诞生后,加上鼠标的出世才让电脑被用户更加方便地接受从而进入千家万户了。特别是互联网出现后,鼠标带领我们穿越浏览丰富多彩的页面(HTML)让我们的地球终于变成了现在的“地球村”了。
大家对于鼠标操作由生到熟是需要大量的训练才能做到的,这个过程中,Windows附带的【扫雷】和【纸牌】小游戏承担了重要的角色。在游戏娱乐的同时,大家都变成了鼠标高手。
三、鼠标的缺陷及超级鼠标
由于是定位设备,绝大多数情况下需要鼠标来来回回移动后加上点击才能通知操作系统。因此,时间长了人是更容易疲惫(相对于键盘)的。传统鼠标的几大缺陷:(1)双击的设计在某些区域和某些时候很容易出现失误,对于初学者更是一道拦路虎。(2)拖动操作很贴心直观,但是说实在的,手指长时间按住不放会让人十分紧张又疲劳的。(3)你把鼠标从屏幕的左上角精确移动到右下角需要多长时间?
正因为以上种种原因,人们眼中的电脑高手都是在键盘上运指如飞的形象了。键盘上的命令键被命名为快捷键原因只有一个:相对于双手十指同时敲击键盘快速完成任务来讲,鼠标的操作真的是又慢又累了!
四、【超级鼠标】的定位和设计
微软不愧是伟大的公司,其核心Windows的设计十分的强大与开放。这是十分幸运的事情!鼠标本身滚轮的设计加上MSDN核心函数的支持下,设计一款【超级鼠标】也不算多么难的事情了。我们推出的【超级鼠标】在多项辅助设施和脑洞大开的设计中完成如下多项功能了:
(1)不用双击 中点代替
如果传统键盘的双击操作时不时会让您出现一些错误的话,您可以用鼠标滚轮(也就是中键)点一下即可代替双击来打开文件或者程序。中点代替!
(2)穿越空间 神奇体验
鼠标向左(右)移动到屏幕最左(右)边时,自动从屏幕最右(左)边出来以便继续移动。上下移动也是如此。神奇体验!
(3)鼠标拖动 移动就行
在进行拖动操作(设计画图)时,鼠标一致按住时间长了会很累。您可以左点一下、右点一下后,移动鼠标(手指抬起)即可完成拖动。移动就行!
(4)左一滚翻 浏览方便
为传统滚轮增加一个快速档。左点一下后,不要移动鼠标滚轮滚一下就是翻一页;移动后回归传统慢速滚轮。浏览方便!
(5)左二导航 不慌不忙
左点一下、左点一下后进入专门的导航窗口,所有打开的程序、常用的程序文档、系统工具等就在鼠标附近,轻松切换管理。不慌不忙!
(6)左三惊喜 遥控奇迹
左点一下、左点一下、左点一下后进入独创的遥控平台,鼠标移动1点,远处的超级鼠标指针移动4点,让您轻松16倍操作鼠标。传统鼠标在遥控平台左点一下,就等于远处的超级鼠标在远处的超级鼠标指针处点一下。中点双击、轻松拖动、鼠标穿越、滚轮翻页、滚轮切换、滚轮关闭等功能也可以遥控使用。遥控奇迹!
(原文链接:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/moneytree/article/details/117355714)
实现的过程中用到了技术手段包括:
(1)模拟鼠标函数
The mouse_event function synthesizes mouse motion and button clicks.
VOID mouse_event(
DWORD dwFlags, // flags specifying various motion/click variants
DWORD dx, // horizontal mouse position or position change
DWORD dy, // vertical mouse position or position change
DWORD dwData, // amount of wheel movement
DWORD dwExtraInfo // 32 bits of application-defined information
);
Parameters
dwFlags
A set of flag bits that specify various aspects of mouse motion and button clicking. The bits in this parameter can be any reasonable combination of the following values:
Value Meaning
MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE Specifies that the dx and dy parameters contain normalized absolute coordinates. If not set, those parameters contain relative data: the change in position since the last reported position. This flag can be set, or not set, regardless of what kind of mouse or mouse-like device, if any, is connected to the system. For further information about relative mouse motion, see the following Remarks section.
MOUSEEVENTF_MOVE Specifies that movement occurred.
MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTDOWN Specifies that the left button changed to down.
MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTUP Specifies that the left button changed to up.
MOUSEEVENTF_RIGHTDOWN Specifies that the right button changed to down.
MOUSEEVENTF_RIGHTUP Specifies that the right button changed to up.
MOUSEEVENTF_MIDDLEDOWN Specifies that the middle button changed to down.
MOUSEEVENTF_MIDDLEUP Specifies that the middle button changed to up.
MOUSEEVENTF_WHEEL Windows NT only: Specifies that the wheel has been moved, if the mouse has a wheel. The amount of movement is given in dwData
The flag bits that specify mouse button status are set to indicate changes in status, not ongoing conditions. For example, if the left mouse button is pressed and held down, MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTDOWN is set when the left button is first pressed, but not for subsequent motions. Similarly, MOUSEEVENTF_LEFTUP is set only when the button is first released.
dx
Specifies the mouse's absolute position along the x-axis or its amount of motion since the last mouse event was generated, depending on the setting of MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE. Absolute data is given as the mouse's actual x-coordinate; relative data is given as the number of mickeys moved.
dy
Specifies the mouse's absolute position along the y-axis or its amount of motion since the last mouse event was generated, depending on the setting of MOUSEEVENTF_ABSOLUTE. Absolute data is given as the mouse's actual y-coordinate; relative data is given as the number of mickeys moved.
dwData
If dwFlags is MOUSEEVENTF_WHEEL, then dwData specifies the amount of wheel movement. A positive value indicates that the wheel was rotated forward, away from the user; a negative value indicates that the wheel was rotated backward, toward the user. One wheel click is defined as WHEEL_DELTA, which is 120.
If dwFlags is not MOUSEEVENTF_WHEEL, then dwData should be zero.
dwExtraInfo
Specifies an additional 32-bit value associated with the mouse event. An application calls GetMessageExtraInfo to obtain this extra information.
Return Values
(2)模拟键盘函数
This function has no return value.
The keybd_event function synthesizes a keystroke. The system can use such a synthesized keystroke to generate a WM_KEYUP or WM_KEYDOWN message. The keyboard driver's interrupt handler calls the keybd_event function.
VOID keybd_event(
BYTE bVk, // virtual-key code
BYTE bScan, // hardware scan code
DWORD dwFlags, // flags specifying various function options
DWORD dwExtraInfo // additional data associated with keystroke
);
Parameters
bVk
Specifies a virtual-key code. The code must be a value in the range 1 to 254.
bScan
Specifies a hardware scan code for the key.
dwFlags
A set of flag bits that specify various aspects of function operation. An application can use any combination of the following predefined constant values to set the flags:
Value Meaning
KEYEVENTF_EXTENDEDKEY If specified, the scan code was preceded by a prefix byte having the value 0xE0 (224).
KEYEVENTF_KEYUP If specified, the key is being released. If not specified, the key is being depressed.
dwExtraInfo
Specifies an additional 32-bit value associated with the key stroke.
Return Values
This function has no return value.
Remarks
Although keybd_event passes an OEM-dependent hardware scan code to Windows, applications should not use the scan code. Windows converts scan codes to virtual-key codes internally and clears the up/down bit in the scan code before passing it to applications.
An application can simulate a press of the PRINTSCREEN key in order to obtain a screen snapshot and save it to the Windows clipboard. To do this, call keybd_event with the bVk parameter set to VK_SNAPSHOT, and the bScan parameter set to 0 for a snapshot of the full screen or set bScan to 1 for a snapshot of the active window.
See Also
GetAsyncKeyState, GetKeyState, MapVirtualKey, SetKeyboardState
(3)钩子函数
void __stdcall SetHookmo(HWND hMainWin,bool nCode)
{
if(nCode) // 安放HOOK
{
hWndMain=hMainWin;
hKeyHookmo=SetWindowsHookEx(WH_MOUSE,(HOOKPROC)HookProcmo,hInstance,0);
}
else // 卸下HOOK
UnhookWindowsHookEx(hKeyHookmo);
}
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LRESULT CALLBACK HookProcmo(int nCode,WPARAM wParam,LPARAM lParam)
{
POINT pint;
AnsiString tmp,tmp3,tmpn,mb,tmp2;
int nMaxCount=40;
MOUSEHOOKSTRUCT *ml;
ml=(MOUSEHOOKSTRUCT *)lParam;
}
(4)DLL调用
static HINSTANCE hDLL; // DLL句柄
typedef void __stdcall (*DLLFUN)(HWND,bool);
typedef void __stdcall (*DLLFUN1)(HWND,bool,int);
DLLFUN DLLSetHook;
DLLFUN1 DLLSetHook1;
hDLL=LoadLibrary((LPCTSTR)"qshkn.dll"); // DLL文件名:qshkn.dll
if(hDLL==NULL)
{ ShowMessage("DLL: 不能加载!程序退出。"); exit(1); }
DLLSetHook =(DLLFUN)GetProcAddress(hDLL,"SetHookmo");
if(DLLSetHook==NULL)
{ ShowMessage("DLL: 函数没找到!程序退出。"); FreeLibrary(hDLL); exit(1); }
DLLSetHook(this->Handle,true);
(5)Timer控件的使用
定时器用来协调多种事件及其响应处理过程。比如探测鼠标位置,改变鼠标位置等。以下为鼠标穿越的源代码。
::GetCursorPos(&mp);
mx=mp.x;
my=mp.y;
if(mx<=1)
{
SetCursorPos(Screen->Width+mxmax-6,my);
}
if(mx>=Screen->Width+mxmax-2)
{
if(my>Screen->Height)
my=Screen->Height-20;
SetCursorPos(6,my);
}
if(mx==Screen->Width+1&&my>Screen->Height)
{
SetCursorPos(Screen->Width-12,Screen->Height-360);
}
if(my<=1)
{
if(mx<=Screen->Width)
SetCursorPos(mx,Screen->Height-6);
else
SetCursorPos(mx,mymax-6);
}
if(mx<=Screen->Width&&my>=Screen->Height-1)
{
SetCursorPos(mx,6);
}
if(mx>Screen->Width&&my>=mymax-1)
{
SetCursorPos(mx,6);
}
五、【超级鼠标】界面及下载
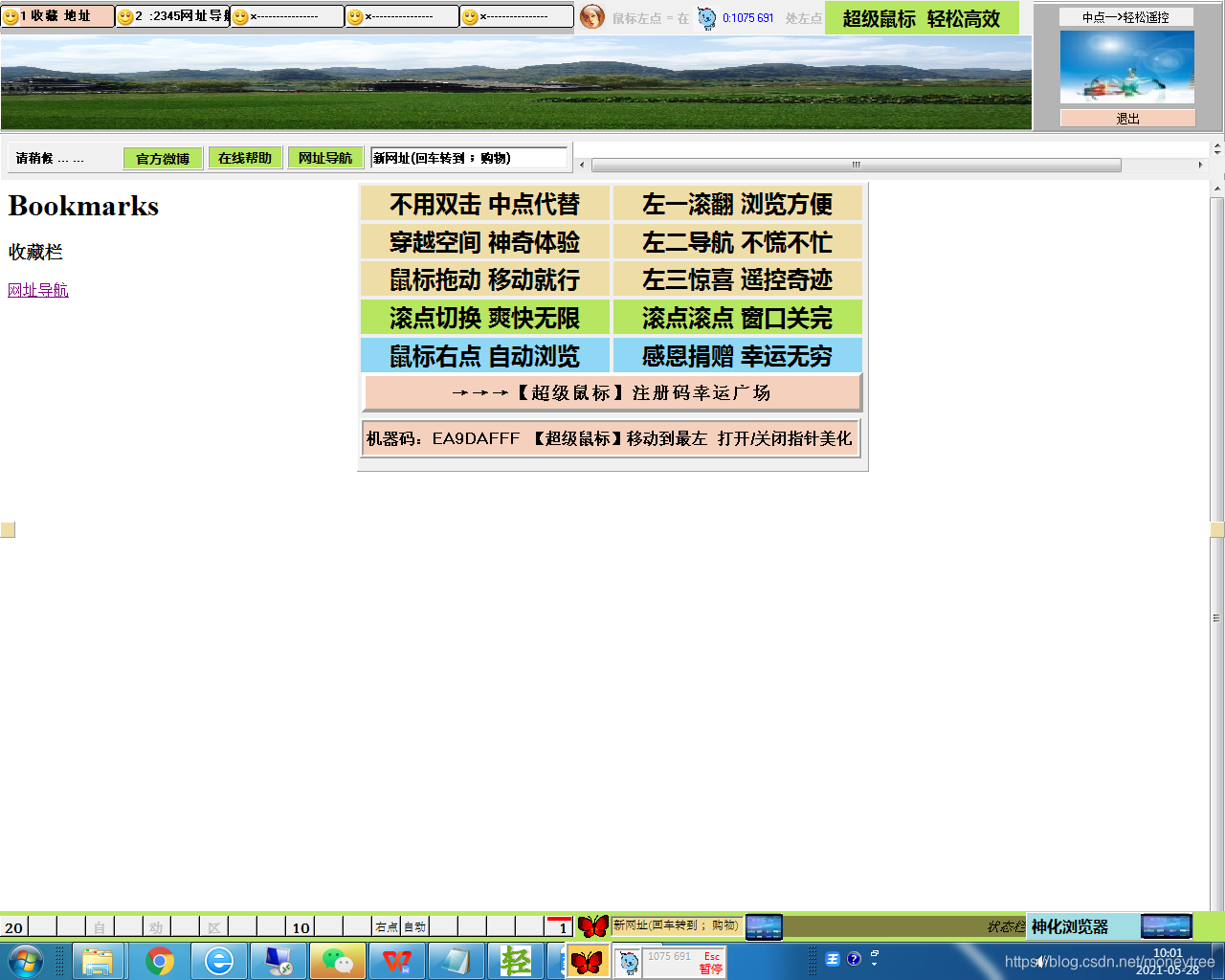
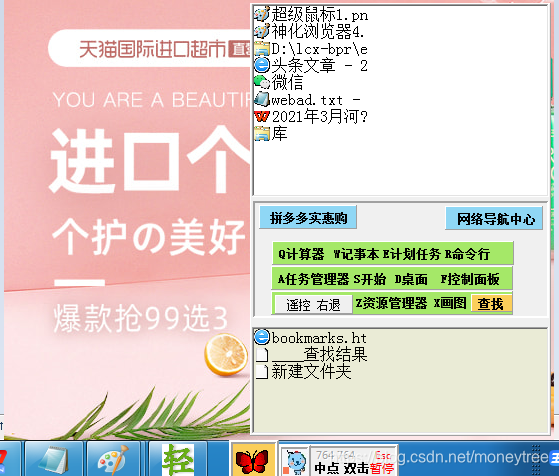

【超级鼠标】免费下载:https://download.youkuaiyun.com/download/moneytree/19150437
六、感谢观看
如果【超级鼠标】能帮到您了,请打赏点赞,我们会把【超级鼠标】做得更好,并送出幸运大奖!让程序员轻松优秀起来,为中华民族的精英们加油!!【幸运名人堂】等着大家光临!!!





 本文介绍了鼠标的起源、在Windows系统中的应用,指出传统鼠标存在易使人疲劳、操作易失误等缺陷。随后详细阐述了超级鼠标的多项功能,如中点代替双击、鼠标穿越等,还介绍了实现超级鼠标用到的模拟鼠标函数、模拟键盘函数等技术手段,并给出了下载链接。
本文介绍了鼠标的起源、在Windows系统中的应用,指出传统鼠标存在易使人疲劳、操作易失误等缺陷。随后详细阐述了超级鼠标的多项功能,如中点代替双击、鼠标穿越等,还介绍了实现超级鼠标用到的模拟鼠标函数、模拟键盘函数等技术手段,并给出了下载链接。

















 1163
1163

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










