先来看看大概流程
加固俯瞰

1、编写加密方法,作为工具方法用于后续的加密和解密准备。
2、编写代理Application(ProxyApplication),作为加固后的apk的伪入口。(ProxyApplication作为伪入口时,需要将加密apk进行解密并重新加载于classLoader中)
3、对需要加密的apk的AndroidManifest文件的Application:name 标签经行更改为ProxyApplication,并用标签声明真正的Application入口和版本号。
4、将1、2步的文件打包成aar包。
5、解压aar包(于aarTemp文件夹),并将解压后的jar文件,编译成dex文件(Entrance.dex)(安卓虚拟机可识别的机器码文件)。
6、解压需要加密的apk(于apkTemp文件夹),遍历解压后的文件夹,取出所有dex文件,用1步中的加密方法对所有dex文件进行加密,并替换原本没加密的dex。
*注:Entrance.dex在aarTemp内,没被加密
7、将aarTemp中的dex文件,复制到apkTemp文件中,并将apkTemp压缩成apk文件。
8、对齐 & 签名(才能正常使用)
附上相关的代码
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第四步:解压arr(包含加密解密工具和ProxyApplication.java)
File aarFile = new File("core/build/outputs/aar/core-debug.aar");
File aarTemp = new File("lib/temp");
Zip.unZip(aarFile, aarTemp);
// 生成classes.dex
File classesJar = new File(aarTemp, "classes.jar");
File classesDex = new File(aarTemp, "classes.dex");
Process process = null;
//dx --dex --output out.dex in.jar
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("cmd /c dx --dex --output " + classesDex.getAbsolutePath()
+ " " + classesJar.getAbsolutePath());
process.waitFor();
if (process.exitValue() != 0) {
System.out.println("dex error");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//第六步:解压apk
File apkFile = new File("app/build/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk");
File apkTemp = new File("lib/Apktemp");
Zip.unZip(apkFile, apkTemp);
ArrayList<File> dexFiles = new ArrayList<>();
for (File file : apkTemp.listFiles()) {
if (file.getName().endsWith("dex")) {
dexFiles.add(file);
}
}
//加密apk里面的dex
AES.init(AES.DEFAULT_PWD);
for (File dexFile : dexFiles) {
try {
byte[] bytes = Utils.getBytes(dexFile);
byte[] encrypt = AES.encrypt(bytes);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(apkTemp,
"secret-" + dexFile.getName()));
fos.write(encrypt);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
dexFile.delete();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
classesDex.renameTo(new File("lib/Apktemp", "classes.dex"));
File unSignedApk = new File("app/build/outputs/apk/debug/app-unsigned.apk");
//第七步:把apkTemp压缩成unsightApk
try {
Zip.zip(apkTemp, unSignedApk);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//第八步:对齐 签名
File alignedApk = new File("app/build/outputs/apk/debug/app-unsigned-aligned.apk");
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("cmd /c zipalign -v -p 4 " + unSignedApk.getAbsolutePath()
+ " " + alignedApk.getAbsolutePath());
process.waitFor();
if (process.exitValue() != 0) {
System.out.println("zipalign error");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
File signedApk=new File("app/build/outputs/apk/debug/app-signed-aligned.apk");
File jks=new File("mykeystore.jks");
try {
process=Runtime.getRuntime().exec("cmd /c apksigner sign --ks "+jks.getAbsolutePath()
+" --ks-key-alias key0 --ks-pass pass:11111111 --key-pass pass:11111111 --out "
+signedApk.getAbsolutePath()+" "+alignedApk.getAbsolutePath());
process.waitFor();
if(process.exitValue()!=0){
System.out.println("sign error");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("over ");
}
}
这里详细讲讲ProxyApplication:
探讨1:作为唯一没加密的dex文件内的ProxyApplication如何把加密的dex文件,加载到类加载器(ClassLoader)中?
ProxyApplication三部曲:
1.获得加密apk。
2.解压zip并解密dex文件。
3把新dex文件索引存在类加载器中。
上述过程中,涉及到把dex文件加载到类加载器中,下面简单理解下类加载机制。
前提:android的ClassLoader有两种类型系统类加载器和自定义加载器。
1)BootClassLoader:
安卓系统启动时候会使用BCL来预加载常用类。
2)DexClassLoader
加载dex文件和包含dex文件的压缩包
3)PathClassLoader
加载系统类和应用程序的类
4) InMemoryClassLoader:
androidO新增的,用于加载内存中的dex
·
·ClassLoader是一个抽象类,定义了classloader的主要功能。BootClassLoader是它的内部类
·SecureClassLoader不是ClassLoader的实现类,拓展了ClassLoader的权限方面的功能
·BaseDexClassLoader继承ClassLoader,但是是抽象类,PathClassLoader, DexClassLoader, InMemoryClassLoader都继承它,并各自实现类功能
·双亲委托模式
(讲人话:首先判断该类是否已经加载,如无,不是从自身查找,而是委托到父加载器中找是否有加载目的Class,若无依次向父类递归,直至最顶层ClassLoader类。如果找到了,就直接返回Class,若果没找到就继续依次向下子加载器findClass…)
优点:
1.避免重复加载
2.保护安全性。
(沙雕A建一个 类名为 android.view.View的自定义类,可能造成系统原本的View不可用。但其实还有一层保护,虚拟机把两个类名一致的且被同一个类加载器加载的类,虚拟机才会认为他们是同一个类)
来一个demo打印看看应用的类加载器是什么:

这里可以看到PathClassLoader作为加载器。
ClassLoader的加载过程:
ClassLoader.java
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
//找该类是否被加载过了
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
//先判断父类是否存在
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
//如果不存在就在自层找
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
//在委托流程中没找到该类,就会执行该句
c = findClass(name);
}
}
//如果已加载就直接返回
return c;
}
BaseDexClassLoader.java
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
//调用pathList的findClass
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
ClassNotFoundException cnfe = new ClassNotFoundException(
"Didn't find class \"" + name + "\" on path: " + pathList);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
cnfe.addSuppressed(t);
}
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
先看看pathList是什么对象
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* dexFile must be an in-memory representation of a full dexFile.
*
* @param dexFiles the array of in-memory dex files containing classes.
* @param parent the parent class loader
*
* @hide
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(ByteBuffer[] dexFiles, ClassLoader parent) {
// TODO We should support giving this a library search path maybe.
super(parent);
//在构造器内初始化 是一个DexPathList对象
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexFiles);
}
接下来看看DexPathList对象怎么存放已加载的class
/**
* Construct an instance.
*
* @param definingContext the context in which any as-yet unresolved
* classes should be defined
*
* @param dexFiles the bytebuffers containing the dex files that we should load classes from.
*/
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, ByteBuffer[] dexFiles) {
...
this.definingContext = definingContext;
// TODO It might be useful to let in-memory dex-paths have native libraries.
this.nativeLibraryDirectories = Collections.emptyList();
this.systemNativeLibraryDirectories =
splitPaths(System.getProperty("java.library.path"), true);
this.nativeLibraryPathElements = makePathElements(this.systemNativeLibraryDirectories);
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<IOException>();
//把所有存进来的dex文件存储在dexElements对象
this.dexElements = makeInMemoryDexElements(dexFiles, suppressedExceptions);
if (suppressedExceptions.size() > 0) {
this.dexElementsSuppressedExceptions =
suppressedExceptions.toArray(new IOException[suppressedExceptions.size()]);
} else {
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions = null;
}
}
接下来看看dexElements 是何方神圣!?
这是dexElements的对象声明
/**
* List of dex/resource (class path) elements.
* Should be called pathElements, but the Facebook app uses reflection
* to modify 'dexElements' (http://b/7726934).
*/
private Element[] dexElements;
重点来了:
/**
* Element of the dex/resource path. Note: should be called DexElement, but apps reflect on
* this.
*/
/*package*/ static class Element {
/**
* A file denoting a zip file (in case of a resource jar or a dex jar), or a directory
* (only when dexFile is null).
*/
private final File path;
private final DexFile dexFile;
private ClassPathURLStreamHandler urlHandler;
private boolean initialized;
/**
* Element encapsulates a dex file. This may be a plain dex file (in which case dexZipPath
* should be null), or a jar (in which case dexZipPath should denote the zip file).
*/
public Element(DexFile dexFile, File dexZipPath) {
this.dexFile = dexFile;
this.path = dexZipPath;
}
public Element(DexFile dexFile) {
this.dexFile = dexFile;
this.path = null;
}
public Element(File path) {
this.path = path;
this.dexFile = null;
}
....
}
从上面代码可以看到Element存放了dex文件的实例,和对应路径。
回来~从BaseDexClassLoader.findClass()->DexPathList.findClass()
就看看DexPathList.findClass()的实现内容
public Class<?> findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
//遍历dexElements,findClass()
for (Element element : dexElements) {
/
Class<?> clazz = element.findClass(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
看看element.findClass()
public Class<?> findClass(String name, ClassLoader definingContext,
List<Throwable> suppressed) {
return dexFile != null ? dexFile.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed)
: null;
}
dexFile.loadClassBinaryName()
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie, this, suppressed);
}
private static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader, Object cookie,
DexFile dexFile, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
Class result = null;
try {
//调用native
result = defineClassNative(name, loader, cookie, dexFile);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
}
return result;
}
native方法往下就不再分析。从这波代码分析,找到一个重要转折点dexElements(Element数组),每当找应用程序的类时,都会遍历这个数组,找到目的的dex文件,再得到目的Class。
回到加固
由此,我们把解密的dex文件通过反射合并到这个dexElements对象(Element数组)就完事。
如下图:
 上图对应以下代码:
上图对应以下代码:
public class ProxyApplication extends Application {
//定义好解密后的文件的存放路径
private String app_name;
private String app_version;
/**
* ActivityThread创建Application之后调用的第一个方法
* 可以在这个方法中进行解密,同时把dex交给android去加载
*/
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
//获取用户填入的metadata
getMetaData();
//得到当前加密了的APK文件
File apkFile=new File(getApplicationInfo().sourceDir);
//把apk解压 app_name+"_"+app_version目录中的内容需要root权限才能用
File versionDir = getDir(app_name+"_"+app_version,MODE_PRIVATE);
File appDir=new File(versionDir,"app");
File dexDir=new File(appDir,"dexDir");
Log.e("ProxyApplication", "attachBaseContext:first "+apkFile.getAbsolutePath() );
Log.e("ProxyApplication", "attachBaseContext:sec "+versionDir.getAbsolutePath() );
//得到我们需要加载的Dex文件
List<File> dexFiles=new ArrayList<>();
//进行解密(最好做MD5文件校验)
if(!dexDir.exists() || dexDir.list().length==0){
//把apk解压到appDir
Zip.unZip(apkFile,appDir);
//获取目录下所有的文件
File[] files=appDir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
String name=file.getName();
if(name.endsWith(".dex") && !TextUtils.equals(name,"classes.dex")){
try{
AES.init(AES.DEFAULT_PWD);
//读取文件内容
byte[] bytes=Utils.getBytes(file);
//解密
byte[] decrypt=AES.decrypt(bytes);
//写到指定的目录
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(decrypt);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
dexFiles.add(file);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}else{
for (File file : dexDir.listFiles()) {
dexFiles.add(file);
}
}
try{
//2.把解密后的文件加载到系统
loadDex(dexFiles,versionDir);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void loadDex(List<File> dexFiles, File versionDir) throws Exception{
//1.获取pathlist
Field pathListField = Utils.findField(getClassLoader(), "pathList");
Object pathList = pathListField.get(getClassLoader());
//2.获取数组dexElements
Field dexElementsField=Utils.findField(pathList,"dexElements");
Object[] dexElements=(Object[])dexElementsField.get(pathList);
//3.反射到初始化dexElements的方法
Method makeDexElements=Utils.findMethod(pathList,"makePathElements",List.class,File.class,List.class);
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<IOException>();
Object[] addElements=(Object[])makeDexElements.invoke(pathList,dexFiles,versionDir,suppressedExceptions);
//合并数组
Object[] newElements= (Object[])Array.newInstance(dexElements.getClass().getComponentType(),dexElements.length+addElements.length);
System.arraycopy(dexElements,0,newElements,0,dexElements.length);
System.arraycopy(addElements,0,newElements,dexElements.length,addElements.length);
//替换classloader中的element数组
dexElementsField.set(pathList,newElements);
}
private void getMetaData() {
try{
ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
Bundle metaData=applicationInfo.metaData;
if(null!=metaData){
if(metaData.containsKey("app_name")){
app_name=metaData.getString("app_name");
}
if(metaData.containsKey("app_version")){
app_version=metaData.getString("app_version");
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
```java
(tinker热修复共同点:加入新dex去dexElements)
**探讨2: 初次冷启动ProxyApplication进程时,已经将ProxyApplication作为入口,后续的冷启动如何更替为真正的MyApplication作为真正的应用入口?且ProxyApplication作为初次入口时,已经初始化了有关ProxyApplication的信息,怎么更换会真正的MyApplication?**
在这里前提需要粗略了解app冷启动的流程(以在launcher上点击启动app作为起点):
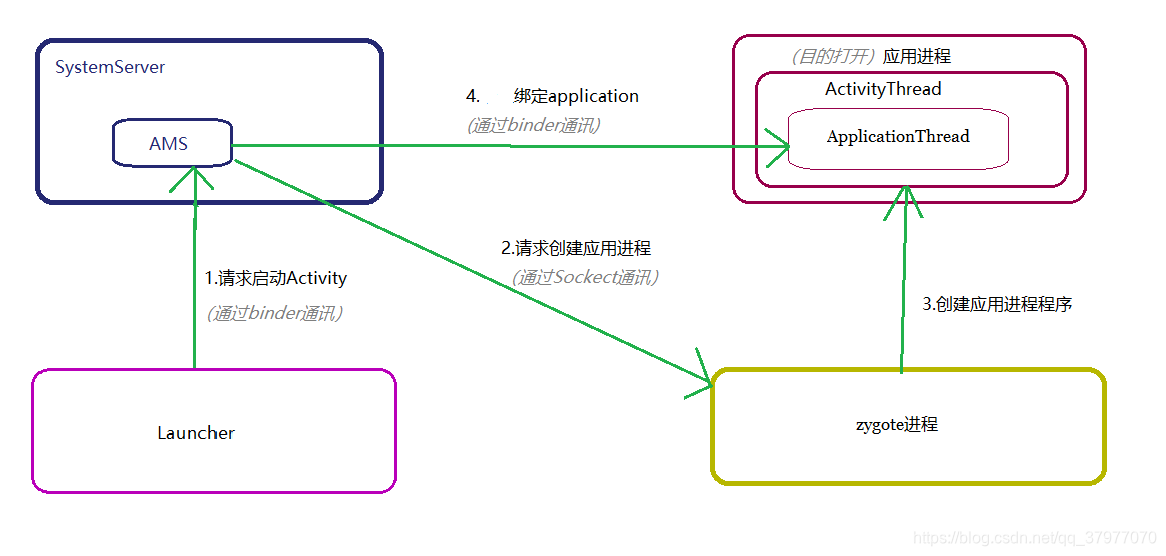
1. 首先launcher通过startActivityAsUser()请求打开activity,然后再ContextImpl里通过binder获取ActivityManager服务,调用到ActvityManagerService的startActivityAsUser()。
2. 然后AMS在启动应用进程前会进行一系列的判断。如,当前这个应用进程是否已启动,若不存在就,向Zygote启动新建进程。
3. zygote进程接收到新建进程请求后,
1)通过classLoader实例化ActivityThread对象,
2)binder线程池启动。
(_ams在判断相关打开进程前的涉及前提判断的过程和binder启动的过程复杂,且知识点较多,但与这里加固主题的重点逻辑无必要关联,就简单带过。_)
4. ActivityThread对象被初始化后,
1)开启主线程的looper循环,
2)请求ams进行绑定Application
回到加固主题的目标->在ProxyApplication初始化后,怎么将真正的MyApplication去替换ProxyApplication?
这里需要跟进源码,有两个主要目的
1.看看ProxyApplication是怎么初始化?
2.在初始化后,怎么作为对象在后续被进程所使用?
上源码!从ams调用ActivityThread绑定Application开始看
```java
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
...
Application app;
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy savedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();
final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy writesAllowedPolicy = StrictMode.getThreadPolicy();
try {
// If the app is being launched for full backup or restore, bring it up in
// a restricted environment with the base application class.
//data.info是LoadedApk类型对象,LoadedApk这个类就是APK在内存中的表示,可以得到代码的ClassLoader,资料mDataDir,功能清单ApplicationInfo等信息
//通过LoadedApk的makeApplication()进行构建Application实例
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
// Propagate autofill compat state
app.setAutofillCompatibilityEnabled(data.autofillCompatibilityEnabled);
//把构建出来的app赋值给mInitialApplication 。
//由此找到替换目标 TODO TARGET :
// ActivityThread.java -> mInitialApplication对象
mInitialApplication = app;
// don't bring up providers in restricted mode; they may depend on the
// app's custom Application class
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) {
//这里传入app->要跟进去这里看看怎样利用app。。
installContentProviders(app, data.providers);
// For process that contains content providers, we want to
// ensure that the JIT is enabled "at some point".
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.ENABLE_JIT, 10*1000);
}
}
...
try {
//这里执行ProxyApplication的onCreat()
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
...
}
接下来先看看LoadedApk的makeApplication(),做了什么
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
...
Application app = null;
//mApplicationInfo.className;得到声明文件中的Application标签的 Name 值
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER,
"initializeJavaContextClassLoader");
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
//创建Context
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
//Instrumentation是用于管理和执行activity声明周期的工具类
//通过mActivityThread.mInstrumentation 创建application对象
//创建出来的是app对象实质是ProxyApplication -->目的替换所有用到app对象(ProxyApplication)的字段
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
//用了app去设置appContext.setOuterContext
//找到替换目标 todo TARGET :
// 替换ContextImpl的mOuterContext对象 >> ContextImpl.java ->mOuterContext对象
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate application " + appClass
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
//用了app加入mActivityThread.mAllApplications队列
//找到替换目标 todo TARGET :
//替换ActivityThread的mAllApplications队列 >> ActivityThread ->mAllApplications
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
//找到替换目标 todo TARGET :
//替换LoadedApk的mApplication对象 >> LoadedApk ->mApplication
mApplication = app;
...
}
接下来先看看ActivityThread的installContentProviders(),传入application对象做了什么
private void installContentProviders(
Context context, List<ProviderInfo> providers) {
...
//传入context到installProvider()
ContentProviderHolder cph = installProvider(context, null, cpi,
false /*noisy*/, true /*noReleaseNeeded*/, true /*stable*/);
if (cph != null) {
cph.noReleaseNeeded = true;
results.add(cph);
}
}
...
}
installProvider()
private ContentProviderHolder installProvider(context context,
ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) {
...
Context c = null;
ApplicationInfo ai = info.applicationInfo;
//ai这个获取到还是ProxyApplication的资料
//->如果context.getPackageName()
// 获得到的不是ProxyApplication就可以改变c的赋值行为
//这里可以进行重写context的getPackageName方法,
//使输出PackageName为真正的MyApplication即可
if (context.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
c = context;
} else if (mInitialApplication != null &&
mInitialApplication.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
c = mInitialApplication;
} else {
try {
//目的要进入这里进行构造c对象
c = context.createPackageContext(ai.packageName,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
...
}
经过上述代码找到了四处需要替换的对象变量和一处重写方法。
整理:
- 新建一个真的的MyApplication对象,以用来替换ProxyApplication对象
- ActivityThread.java -> mInitialApplication对象
- ContextImpl.java ->mOuterContext对象
- ActivityThread的mAllApplications队列 >> ActivityThread ->mAllApplications
- LoadedApk的mApplication对象 >> LoadedApk ->mApplication
- context.getPackageName()重写
->如何新建MyApplication对象,这里可以模仿源码如何新建ProxyApplication对象步骤进行构造
新建Application对象在Instrumentation.java实现:
public Application newApplication(ClassLoader cl, String className, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = getFactory(context.getPackageName())
.instantiateApplication(cl, className);
app.attach(context);
return app;
}
跟进instantiateApplication(): AppComponentFactory.java
public @NonNull Application instantiateApplication(@NonNull ClassLoader cl,
@NonNull String className)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
//通过classLoader,获得类,然后进行newInstance
return (Application) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
所以我们可以类似方法获得Application对象
//得到attachBaseContext(context) 传入的上下文 ContextImpl
Context baseContext = getBaseContext();
//创建用户真实的application (MyApplication)
Class<?> delegateClass = Class.forName(app_name);
realApplication = (Application) delegateClass.newInstance();
//得到attach()方法
Method attach = Application.class.getDeclaredMethod("attach", Context.class);
attach.setAccessible(true);
attach.invoke(realApplication, baseContext);
->关于对象替换可以通过反射进行实现。这里需要找到一个入口点,获取哪个对象进行着手?
在ProxyApplication.java中可以获得context对象,通过Context的实现类ContextImpl找到下列对象。

由此,通过context来作为入手进行反射。
附上ProxyApplication.java全代码,包含替换目标对象的代码
public class ProxyApplication extends Application {
//定义好解密后的文件的存放路径
private String app_name;
private String app_version;
/**
* ActivityThread创建Application之后调用的第一个方法
* 可以在这个方法中进行解密,同时把dex交给android去加载
*/
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
//获取用户填入的metadata
getMetaData();
//得到当前加密了的APK文件
File apkFile = new File(getApplicationInfo().sourceDir);
//把apk解压 app_name+"_"+app_version目录中的内容需要boot权限才能用
File versionDir = getDir(app_name + "_" + app_version, MODE_PRIVATE);
File appDir = new File(versionDir, "app");
File dexDir = new File(appDir, "dexDir");
//得到我们需要加载的Dex文件
List<File> dexFiles = new ArrayList<>();
//进行解密(最好做MD5文件校验)
if (!dexDir.exists() || dexDir.list().length == 0) {
//把apk解压到appDir
Zip.unZip(apkFile, appDir);
//获取目录下所有的文件
File[] files = appDir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
String name = file.getName();
if (name.endsWith(".dex") && !TextUtils.equals(name, "classes.dex")) {
try {
AES.init(AES.DEFAULT_PWD);
//读取文件内容
byte[] bytes = Utils.getBytes(file);
//解密
byte[] decrypt = AES.decrypt(bytes);
//写到指定的目录
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(decrypt);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
dexFiles.add(file);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} else {
for (File file : dexDir.listFiles()) {
dexFiles.add(file);
}
}
try {
//2.把解密后的文件加载到系统
loadDex(dexFiles, versionDir);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void loadDex(List<File> dexFiles, File versionDir) throws Exception {
//1.获取pathlist
Field pathListField = Utils.findField(getClassLoader(), "pathList");
Object pathList = pathListField.get(getClassLoader());
//2.获取数组dexElements
Field dexElementsField = Utils.findField(pathList, "dexElements");
Object[] dexElements = (Object[]) dexElementsField.get(pathList);
//3.反射到初始化dexElements的方法
Method makeDexElements = Utils.findMethod(pathList, "makePathElements", List.class, File.class, List.class);
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<IOException>();
Object[] addElements = (Object[]) makeDexElements.invoke(pathList, dexFiles, versionDir, suppressedExceptions);
//合并数组
Object[] newElements = (Object[]) Array.newInstance(dexElements.getClass().getComponentType(), dexElements.length + addElements.length);
System.arraycopy(dexElements, 0, newElements, 0, dexElements.length);
System.arraycopy(addElements, 0, newElements, dexElements.length, addElements.length);
//替换classloader中的element数组
dexElementsField.set(pathList, newElements);
}
private void getMetaData() {
try {
ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
getPackageName(), PackageManager.GET_META_DATA);
Bundle metaData = applicationInfo.metaData;
if (null != metaData) {
if (metaData.containsKey("app_name")) {
app_name = metaData.getString("app_name");
}
if (metaData.containsKey("app_version")) {
app_version = metaData.getString("app_version");
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 开始替换application
*/
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e("proxyApp", "onCreate: " + Log.getStackTraceString(new Throwable()));
super.onCreate();
try {
bindRealApplicatin();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 让代码走入if中的第三段中
*
* @return
*/
@Override
public String getPackageName() {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(app_name)) {
return "";
}
return super.getPackageName();
}
@Override
public Context createPackageContext(String packageName, int flags) throws PackageManager.NameNotFoundException {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(app_name)) {
return super.createPackageContext(packageName, flags);
}
try {
bindRealApplicatin();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return realApplication;
}
boolean isBindReal;
Application realApplication;
private void bindRealApplicatin() throws Exception {
if (isBindReal) {
return;
}
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(app_name)) {
return;
}
//得到attachBaseContext(context) 传入的上下文 ContextImpl
Context baseContext = getBaseContext();
//创建用户真实的application (MyApplication)
Class<?> delegateClass = Class.forName(app_name);
realApplication = (Application) delegateClass.newInstance();
//得到attach()方法
Method attach = Application.class.getDeclaredMethod("attach", Context.class);
attach.setAccessible(true);
attach.invoke(realApplication, baseContext);
// ContextImpl---->mOuterContext(app) 通过Application的attachBaseContext回调参数获取
Class<?> contextImplClass = Class.forName("android.app.ContextImpl");
//获取mOuterContext属性
Field mOuterContextField = contextImplClass.getDeclaredField("mOuterContext");
mOuterContextField.setAccessible(true);
mOuterContextField.set(baseContext, realApplication);
// ActivityThread--->mInitialApplication ContextImpl的mMainThread属性
Field mMainThreadField = contextImplClass.getDeclaredField("mMainThread");
mMainThreadField.setAccessible(true);
Object mMainThread = mMainThreadField.get(baseContext);
Class<?> activityThreadClass = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Field mInitialApplicationField = activityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mInitialApplication");
mInitialApplicationField.setAccessible(true);
mInitialApplicationField.set(mMainThread, realApplication);
// ActivityThread--->mAllApplications(ArrayList) ContextImpl的mMainThread属性
Field mAllApplicationsField = activityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mAllApplications");
mAllApplicationsField.setAccessible(true);
ArrayList<Application> mAllApplications = (ArrayList<Application>) mAllApplicationsField.get(mMainThread);
mAllApplications.remove(this);
mAllApplications.add(realApplication);
// LoadedApk------->mApplication ContextImpl的mPackageInfo属性
Field mPackageInfoField = contextImplClass.getDeclaredField("mPackageInfo");
mPackageInfoField.setAccessible(true);
Object mPackageInfo = mPackageInfoField.get(baseContext);
Class<?> loadedApkClass = Class.forName("android.app.LoadedApk");
Field mApplicationField = loadedApkClass.getDeclaredField("mApplication");
mApplicationField.setAccessible(true);
mApplicationField.set(mPackageInfo, realApplication);
//修改ApplicationInfo className LooadedApk
Field mApplicationInfoField = loadedApkClass.getDeclaredField("mApplicationInfo");
mApplicationInfoField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationInfo mApplicationInfo = (ApplicationInfo) mApplicationInfoField.get(mPackageInfo);
mApplicationInfo.className = app_name;
realApplication.onCreate();
isBindReal = true;
}
}
验收:
可以在四大组件中调用getApplication() 、getApplicationContext() 打印出来看看ProxyApplication是否已经被替换成MyApplication。
例如:





(*注:广播接收器onReceive(Context context, Intent intent),参数里的context,是ReceiverRestrictedContext类型继承ContextWrapper,不可用于registerReceiver和bindService,详细分析可看我的另外一篇博文:[framework]了解android的各种Context )
恭喜你,加固学习分享,终于看完了!再看一遍好吗, pleaseeeeeeee!!
转自:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_37977070/article/details/108495821
























 562
562

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








