#字符串的创建
创建字符串
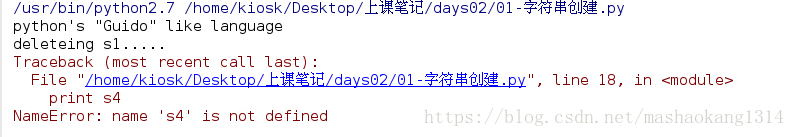
s4="python\'s \"Guido\" like language"
#\为转义字符
print s4
**删除字符串**
print "deleteing s1....."
#删除内存空间的数据;
del s4
print s4 #再输出报错,因为字符串已经被删除
运行结果
输出字符串的格式
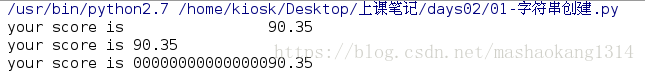
#20.2该数据占二十位并保留两位小数
print "your score is %20.2f" % 90.345678
#20.2该数据占二十位并保留两位小数,并向左对齐
print "your score is %-20.2f" % 90.345678
#20.2该数据占二十位并保留两位小数,若转化位数不够时,用0进行填补
print "your score is %020.2f" % 90.345678
运行结果
输出半径为3的圆的面积
import math
name = 'circle'
radius = 3
#元组
print "the %s radius is %s, value is %.2f" %(name,radius,math.pi*radius**2)
运行结果
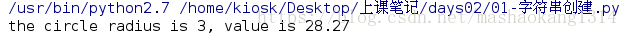
radius = 3
#字典
infortion = {
'name' : 'circle',
'radius' : radius,
'value' : math.pi*radius**2
}
print "the %(name)s radius is %(radius)s value is %(value).2f" % infortion
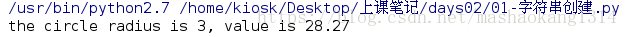
##字符串的特性
索引
s = "hello"
#正向索引
print s[0]
#反向索引
print s[-1]
输出索引的字符

切片
切片
s[start?step]
如果start不存在,默认从头开始切片
如果end不存在,默认从start切到字符串结束
如果start,end都存在,从start开始,end-1结束
s = "hello world"
print s[:3] #hel
print s[1:] #ello world
print s[1:3] #el
print s[1:3][::-1]
切片结果
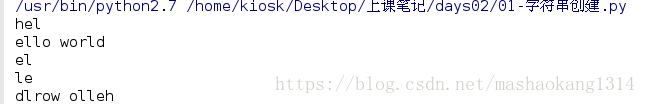
反转字符串
s = "hello world"
print s[::-1]
s1=s
#切片时,字符串s2的id地址和s1,s相同;
s2=s[::-1]
#id是查看s字符串在内存中的地址
print id(s),id(s1),id(s2)

重复和连接
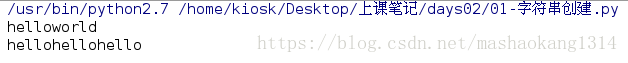
#重复和连接
s="hello" + "world"
print s
s1="hello" * 3
print s1
成员操作符
# 成员操作符
s = 'hello'
print 'el' in s # 返回值为bool值;
print 'el' not in s

##字符串的常用方法
###字符的判断
s = “123HELLO”
print s.isdigit() 判断是否为数字
print s.isupper() 判断是否有大写字母
print s.isalnum() 判断是否有数字或字 母
print s.isalpha() 判断是否有字母
print s.islower() 判断是否有小写字母
print s.isspace() 判断是否有空格
istitle是否是标题; 第一个字母大写, 剩下小写;
print “Hello1”.istitle()
###字符串以什么开头和以什么结尾方法
url1 = "http://www.python.org/2/"
url2 = "https://www.python.org/2/"
url3 = "ftp://www.python.org/2/"
url4 = "file:///www"
if url1.startswith('http://') or url1.startswith('https://'):
print "%s 使用了http或者https协议" %(url1)
else:
print "%s 没有使用http协议" %(url1)
filename = "hello.log"
if filename.endswith('.log'):
print "%s 是日志文件" %(filename)
else:
print "%s 不是日志文件" %(filename)
运行结果

###字符串位置调整
s = " hello "
print s.ljust(30) # left 向左调整
print s.rjust(30) # right
print s.center(30)
运行结果

###字符串去空格
s = ' hello '
print s.strip() # 去掉左边和右边的空格
print s.lstrip() # 去掉左边
print s.rstrip() # 去掉右边

###字符串大小写转换
s = "rOot"
print s.upper()
print s.lower()

###字符串分割split与字符串连接join
ip = "172.25.254.199"
# ['172', '25', '254', '199'] 列表
# split方法: 将字符串按照指定分隔符分割,默认以空格分割;
reversed_ip = ip.split('.')[::-1]
print str(reversed_ip)
# join方法: 将;列表中的所有字符串连接;
print ".".join(reversed_ip)
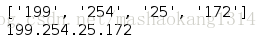
s = 'hello'
# count查看某个子串出现的次数;
print s.count('l')
# indexc查看某个子串的索引值, 直接报错;
print s.index('l')
print s.rindex('l')
# find查找子串的索引值,如果不存在返回-1;
print s.find('l')
print s.rfind('l')
s = 'h e l l o'
# replace除了替换之外, 还可以删除字符串中间的空格;
print s.replace(' ', '')
###内置方法
s = 'hello'
#count 查看某个字符串出现的次数
print s.count('l')
#index 查看某个字符串的索引值,若不存在直接报错
print s.index('l')
print s.rindex('l')
#find 查找字串的索引值,若不存在则返回-1
print s.find('o')
print s.rfind('o')
s = 'h e l l o'
#replace 除了替换之外,还可以删除字符串中间的空格
print s.replace(' ','')
#查看字符串的储存地址
print id(s)
#查看字符串的类型
print type(s)
#求绝对值
print abs(-1)
print abs(10)
print abs(0)
#比较大下
print cmp(2,1) #1
print cmp(1,2) #-1
print cmp(1,1) #0
print min(1,2,43,52)
print max(43,5432,2,454)
#求和
print sum((2,4,5,53,4,3))
print sum(range(10))
#求1~10之间所有偶数的和
print sum(range(0,11,2))
#字符串的长度
s = ‘hello world’
print len(s)
#字符串的个数
li = [‘hello’,‘xiao’,‘mi’]
print len(li)
#排序
s = “aefjhgq”
print sorted(s)
for i in reversed(s):
# print不换行: print 字符串,
print i,

#合并字符串也可以合并列表
str1 = ‘abc’
str2 = ‘123’
print zip(str1, str2)






 本文详细介绍了Python中字符串的创建、删除、格式化输出等基本操作,并深入探讨了字符串的索引、切片、反转等特性。此外,还讲解了字符串的各种常用方法,包括判断、位置调整、去空格、大小写转换、分割与连接等。
本文详细介绍了Python中字符串的创建、删除、格式化输出等基本操作,并深入探讨了字符串的索引、切片、反转等特性。此外,还讲解了字符串的各种常用方法,包括判断、位置调整、去空格、大小写转换、分割与连接等。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








