题目:
本题要求你实现一个稍微更值钱一点的 AI 英文问答程序,规则是:
-
无论用户说什么,首先把对方说的话在一行中原样打印出来;
-
消除原文中多余空格:把相邻单词间的多个空格换成 1 个空格,把行首尾的空格全部删掉,把标点符号前面的空格删掉;
-
把原文中所有大写英文字母变成小写,除了 I;
-
把原文中所有独立的 can you、could you 对应地换成 I can、I could—— 这里“独立”是指被空格或标点符号分隔开的单词;
-
把原文中所有独立的 I 和 me 换成 you;
-
把原文中所有的问号 ? 换成惊叹号 !;
-
在一行中输出替换后的句子作为 AI 的回答。
输入格式:
输入首先在第一行给出不超过 10 的正整数 N,随后 N 行,每行给出一句不超过 1000 个字符的、以回车结尾的用户的对话,对话为非空字符串,仅包括字母、数字、空格、可见的半角标点符号。
输出格式:
按题面要求输出,每个 AI 的回答前要加上 AI: 和一个空格。
输入样例:
6
Hello ?
Good to chat with you
can you speak Chinese?
Really?
Could you show me 5
What Is this prime? I,don 't know输出样例:
Hello ?
AI: hello!
Good to chat with you
AI: good to chat with you
can you speak Chinese?
AI: I can speak chinese!
Really?
AI: really!
Could you show me 5
AI: I could show you 5
What Is this prime? I,don 't know
AI: what Is this prime! you,don't know测试点:
测试点1注意单独的I要变成you
测试点4有多个can you 或 could you 要处理
注意不能让下面两条相互影响:
- 把原文中所有独立的
can you、could you对应地换成I can、I could—— 这里“独立”是指被空格或标点符号分隔开的单词; - 把原文中所有独立的
I和me换成you;
试试下面的样例!
样例输入:
2
can I ?
can you
样例输出:
can I ?
AI: can you!
can you
AI: I can
额外输入样例:
2
,6666 , , 6666666666 ?
can I 额外输出样例:
,6666 , , 6666666666 ?
AI: ,6666,, 6666666666!
can I
AI: can you额外输入样例:
1
lcan youl can you can you lcould youl could you ? 额外输出样例:
lcan youl can you can you lcould youl could you ?
AI: lcan youl I can I can lcould youl I could!代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int is_cap(char ch)
{
if(ch>='A' && ch<='Z')
return 1;
return 0;
}
int is_zm(char ch)
{
if((ch>='A' && ch<='Z') || (ch>='a' && ch<='z') ||(ch>='0' && ch<='9'))
return 1;
return 0;
}
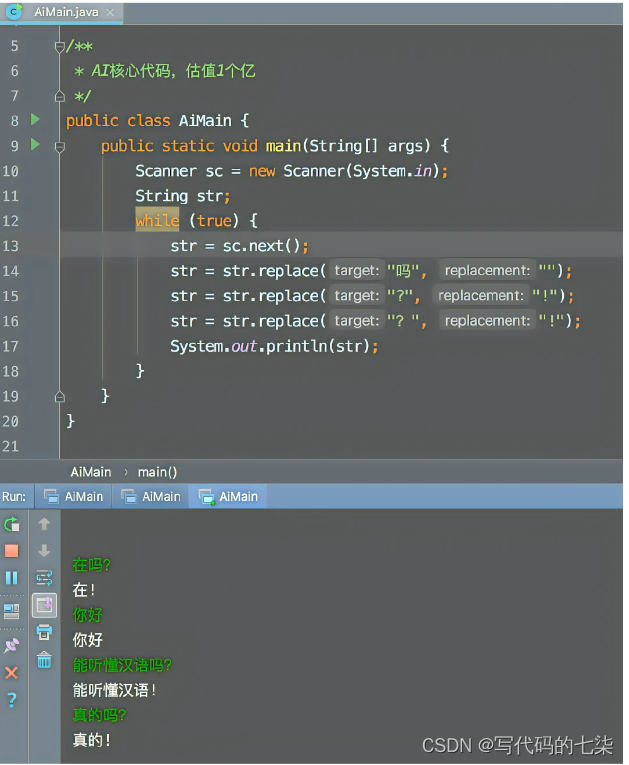
int main()
{
int n = 0;
char arr[1006] = {0};
char arr2[1006] = {0};
scanf("%d",&n);
getchar();
while(n--)
{
gets(arr);
printf("%s\n",arr);
int len = strlen(arr);
int i = 0;
while(arr[i]==' ')//首空格
{
arr[i] = '@';
i++;
}
i = len-1;
while(arr[i]==' ')//尾空格
{
arr[i] = '@';
i--;
}
for(i = 0;i<len;i++)
{
if(is_cap(arr[i]) && arr[i]!='I')//大写转小写
arr[i]+=32;
if(arr[i]==' ' && is_zm(arr[i+1])==0)//去除多余空格
arr[i] = '@';
if(arr[i]=='?')
arr[i] = '!';
}
int j = 0;
for(i = 0;i<len;i++)
{
if(arr[i]!='@')
arr2[j++]=arr[i];//去除空格后的字符串
}
arr2[j] = '\0';//添加‘\0’
len = j;
for(i = 0;i<len;i++)
{
//单独的I变为you
if(i==0 && arr2[i]=='I' && is_zm(arr2[i+1])==0)
arr2[i] = '@';//在开头
else if(i==len-1 && arr2[i]=='I' && is_zm(arr2[i-1])==0)
arr2[i]='@';//在末尾
else if(arr2[i]=='I' && is_zm(arr2[i-1])==0 && is_zm(arr2[i+1])==0)
arr2[i]='@';//在中间
// me -> you
if(i==0 && arr2[i] == 'm' && arr2[i+1] == 'e' && is_zm(arr2[i+2])==0)
arr2[i] = '@';//开头
else if(i==len-2 && arr2[i] == 'm' && arr2[i+1] == 'e' && is_zm(arr2[i-1])==0)
arr2[i] = '@';//末尾
else if(is_zm(arr2[i-1])==0 && arr2[i]=='m' && arr2[i+1]=='e' && is_zm(arr2[i+2])==0)
arr2[i] = '@';//中间
}
char* ch2 = NULL;
//can you -> I can
while(1)
{
ch2 = strstr(arr2,"can you");
if(ch2==NULL)
break;
else
{
if(ch2-arr2==0 && is_zm(*(ch2+7)==0))
*ch2 = '#';//开头
else if(ch2-arr2==len-7 && is_zm(*(ch2-1))==0)
*ch2 = '#';//末尾
else if(is_zm(*(ch2-1))==0 && is_zm(*(ch2+7))==0)
*ch2 = '#';//中间
else//防止无限循环
*ch2 = 'C';//先改成大写
}
}
//could you -> I could
while(1)
{
ch2 = strstr(arr2,"could you");
if(ch2==NULL)
break;
else
{
if(ch2-arr2==0 && is_zm(*(ch2+9)==0))
*ch2 = '%';//开头
else if(ch2-arr2==len-9 && is_zm(*(ch2-1))==0)
*ch2 = '%';//末尾
else if(is_zm(*(ch2-1))==0 && is_zm(*(ch2+9))==0)
*ch2 = '%';//中间
else//防止无限循环
*ch2 = 'C';//先改成大写
}
}
//printf("AI: %s\n",arr2);
///*
printf("AI: ");
for(int k = 0;k<len;k++)
{
if(arr2[k]!='#' && arr2[k]!='%' && arr2[k]!='@')
{
if(arr2[k]=='C')
printf("c");//改回来
else
printf("%c",arr2[k]);
}
else if(arr2[k]=='@' && arr2[k+1]=='e')
{
k++;
printf("you");
}
else if(arr2[k]=='@')
printf("you");
else if(arr2[k]=='#')
{
k+=6;
printf("I can");
}
else if(arr2[k]=='%')
{
k+=8;
printf("I could");
}
}
printf("\n");
//*/
}
return 0;
}2024-4-4 更新c++代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int is_(char ch)
{
if('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z') return 1;
else if('A' <= ch && ch <= 'Z') return 2;
else if('0' <= ch && ch <= '9') return 3;
else return 0;
}
void strip(string& str)
{
int i = 0;
while(i < str.size() && str[i] == ' ') i++;
str.erase(0,i);
i = str.size() - 1;
while(i >= 0 && str[i] == ' ') i--;
str.erase(i + 1);
i = str.find(" ");
while(i != -1)
{
str.erase(i,1);
i = str.find(" ");
}
for(i = 0;i < str.size();i++)
{
if(i && !is_(str[i]) && str[i - 1] == ' ')
str.erase(i - 1,1);
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 0;
cin >> n;
string str;
getline(cin,str);
while(n--)
{
getline(cin,str);
cout << str << endl;
strip(str);//去空格
for(int i = 0;i < str.size();i++)//大写变小写
if(is_(str[i]) == 2 && str[i] != 'I')
str[i] += 32;
else if(str[i] == '?') str[i] = '!';//? 变 !
str.insert(0,"@");str += '@';//方便处理
for(int i = 1;i < str.size() - 1;i++)//所有独立的 I 和 me 换成 you;
if(str[i] == 'I' && !is_(str[i - 1]) && !is_(str[i + 1]))
str.erase(i,1),str.insert(i,"*");//防止相互影响
for(int i = 1;i < str.size() - 1;i++)
if(i + 1 < str.size() - 1 && str[i] == 'm' && str[i + 1] == 'e' && !is_(str[i - 1]) && !is_(str[i + 2]))
str.erase(i,2),str.insert(i,"*");//防止相互影响
int t = str.find("can you");
int len = strlen("can you");
while(t != -1 && !is_(str[t - 1]) && !is_(str[t + len]))
{
str.erase(t,len);
str.insert(t,"I can");
t = str.find("can you");
}
t = str.find("could you");
len = strlen("could you");
while(t != -1 && !is_(str[t - 1]) && !is_(str[t + len]))
{
str.erase(t,len);
str.insert(t,"I could");
t = str.find("could you");
}
t = str.find("*");
while(t != -1)
{
str.erase(t,1);
str.insert(t,"you");
t = str.find("*");
}
str.erase(0,1);str.erase(str.size() - 1,1);
cout << "AI: " << str << endl;
}
return 0;
}
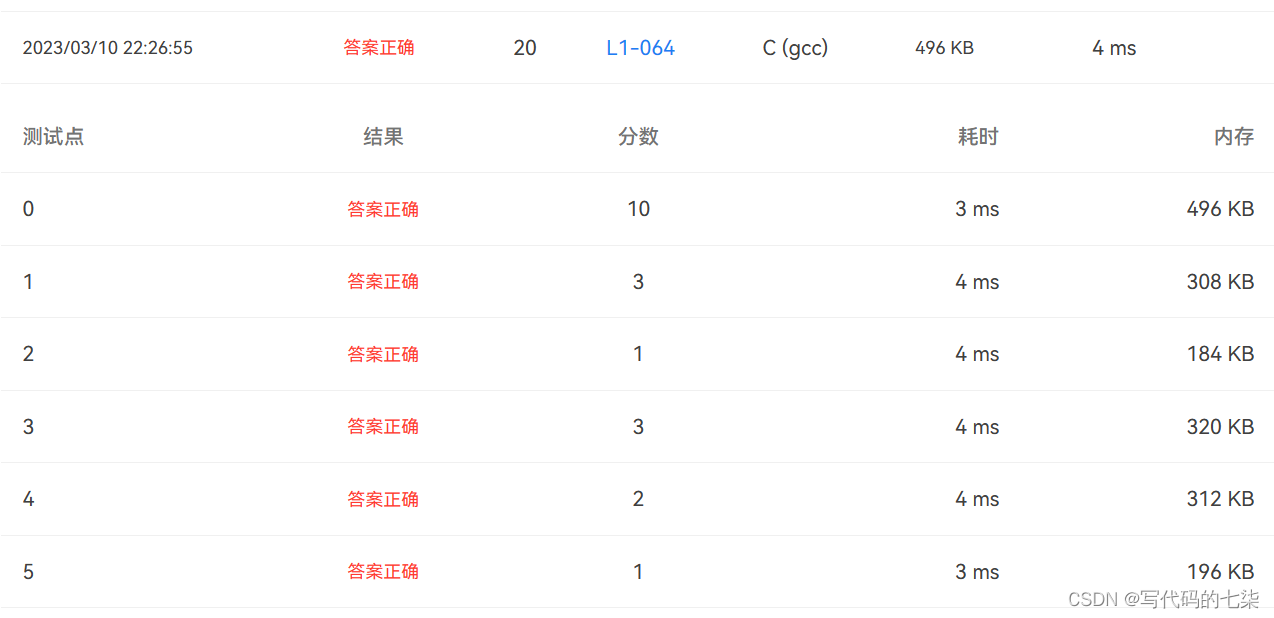
结果:





















 1156
1156

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








