一、深入对象
• 创建对象三种方式
• 构造函数
• 实例成员&静态成员
1.创建对象三种方式

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const obj = new Object()
obj.uname = '老师'
console.log(obj)
const obj1 = new Object({ uname: 'pink' })
console.log(obj1)
</script>
</body>
</html>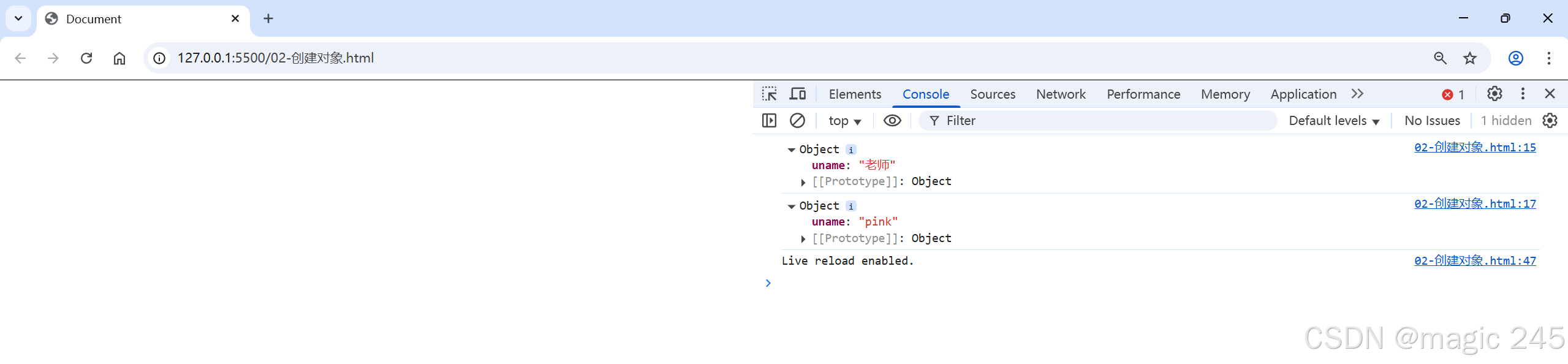
2.构造函数



<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 创建一个猪 构造函数
function Pig(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname
this.age = age
}
// console.log(new Pig('佩奇', 6))
// console.log(new Pig('乔治', 3))
const p = new Pig('佩奇', 6)
console.log(p)
// const pepa = { uname: '佩奇', age: 6 }
// const obj = new Object()
function Goods(name, price, count) {
this.name = name
this.price = price
this.count = count
this.sayhi = function () { }
}
const mi = new Goods('小米', 1999, 20)
console.log(mi)
const hw = new Goods('华为', 3999, 59)
console.log(hw)
console.log(mi === hw)
mi.name = 'vivo'
console.log(mi)
console.log(hw)
// const date = new Date('2022-4-8')
// console.log(date)
// 静态成员
Goods.num = 10
console.log(Goods.num)
Goods.sayhi = function () { }
</script>
</body>
</html>


3.实例成员&静态成员
⑴实例成员:
- 定义:实例成员(属性或方法)属于对象实例,每个实例都有自己的副本。
- 特点:通过
new创建实例后,通过this关键字访问。
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
// 实例属性(Instance Properties)
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 实例方法(Instance Methods)
sayHello() {
return `Hello, my name is ${this.name} and I'm ${this.age} years old.`;
}
}
// 创建实例
const alice = new Person("Alice", 30);
const bob = new Person("Bob", 25);
// 访问实例成员
console.log(alice.name); // 输出: Alice
console.log(alice.sayHello()); // 输出: Hello, my name is Alice and I'm 30 years old.
console.log(bob.name); // 输出: Bob
console.log(bob.sayHello()); // 输出: Hello, my name is Bob and I'm 25 years old.⑵静态成员(Static Members)
- 定义:静态成员(属性或方法)属于类本身,所有实例共享同一个静态成员。
- 特点:通过类名直接访问,无需实例化。
class MathHelper {
// 静态属性(Static Property)
static PI = 3.14159;
// 静态方法(Static Method)
static calculateCircleArea(radius) {
return MathHelper.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
// 直接通过类名访问静态成员
console.log(MathHelper.PI); // 输出: 3.14159
console.log(MathHelper.calculateCircleArea(5)); // 输出: 78.53975
// 不能通过实例访问静态成员(会报错)
// const helper = new MathHelper();
// helper.PI; // 报错!二、内置构造函数
• Object
• Array
• String
• Number



1.Object

学习三个常用静态方法(静态方法就是只有构造函数Object可以调用的)
⑴. 作用:Object.keys 静态方法获取对象中所有属性(键)


⑵ 作用:Object.values 静态方法获取对象中所有属性值

⑶作用:Object. assign 静态方法常用于对象拷贝

使用:经常使用的场景给对象添加属性

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const o = { uname: 'pink', age: 18 }
// 1.获得所有的属性名
console.log(Object.keys(o)) //返回数组['uname', 'age']
// 2. 获得所有的属性值
console.log(Object.values(o)) // ['pink', 18]
// 3. 对象的拷贝
const oo = {}
Object.assign(oo, o)
console.log(oo)
Object.assign(o, { gender: '女' })
console.log(o)
</script>
</body>
</html>

2. Array


⑴作用:reduce 返回函数累计处理的结果,经常用于求和等



数组.reduce( (累计值, 当前元素) => { ... }, 初始值 )- 初始值:计算的起点(比如求和的初始值是
0) - 累计值:每一步计算的中间结果
- 当前元素:数组中正在处理的元素
常见用法:求和
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 1. 直接求和
const total = numbers.reduce( (acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0 )
console.log(total) // 10
// 2. 计算对象数组的总价
const goods = [
{ price: 100 },
{ price: 200 },
{ price: 300 }
]
const sum = goods.reduce( (acc, item) => acc + item.price, 0 )
console.log(sum) // 600
⑵.员工涨薪计算成本

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr = [{
name: '张三',
salary: 10000
}, {
name: '李四',
salary: 10000
}, {
name: '王五',
salary: 20000
},
]
// 涨薪的钱数 10000 * 0.3
// const money = arr.reduce(function (prev, item) {
// return prev + item.salary * 0.3
// }, 0)
const money = arr.reduce((prev, item) => prev + item.salary * 0.3, 0)
console.log(money)
</script>
</body>
</html>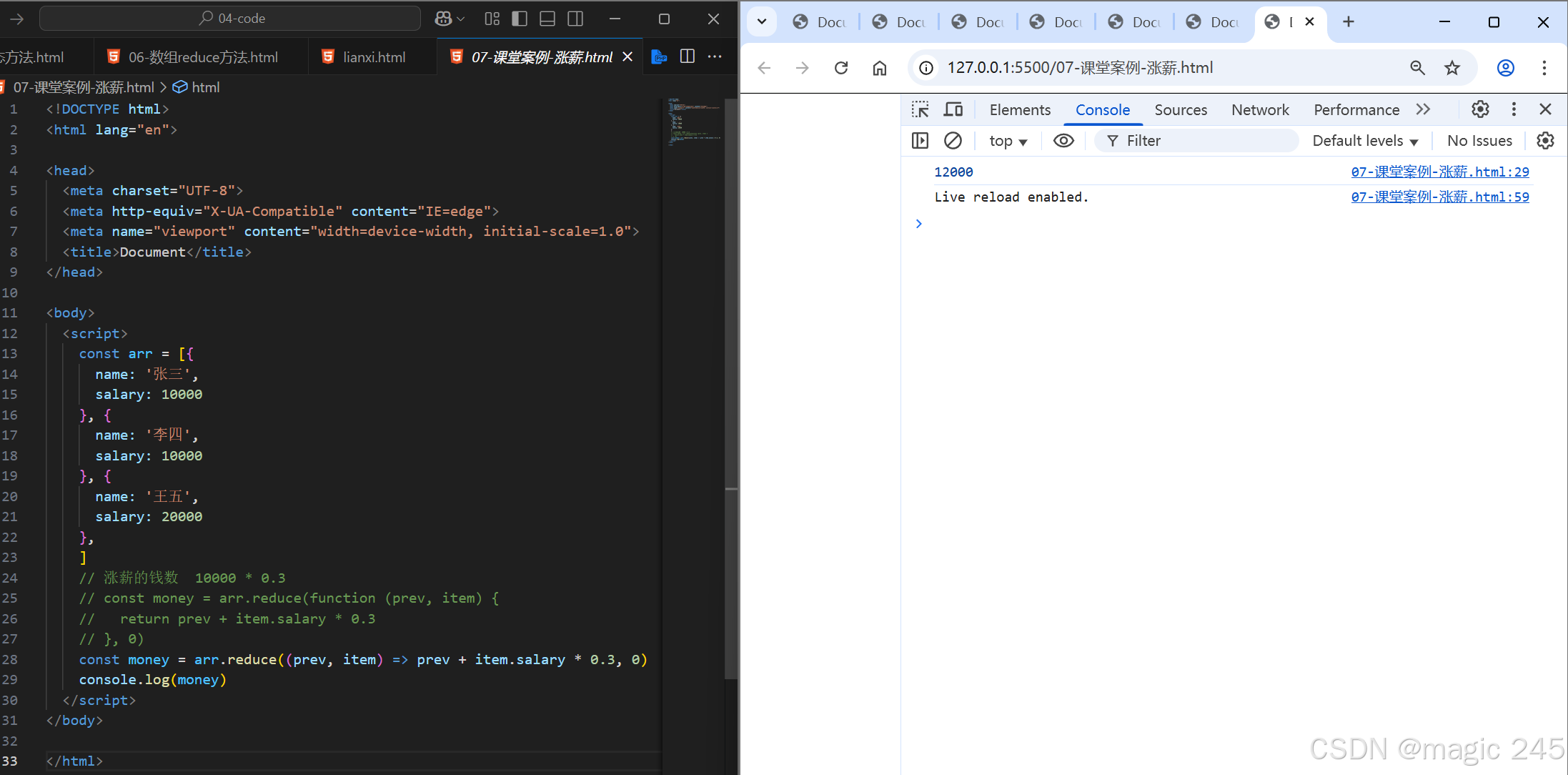
⑶ 数组常见方法-其他方法
①join('分隔符')
- 作用:将数组元素拼接为字符串
- 示例:
const fruits = ['苹果', '香蕉', '橙子']
console.log(fruits.join('/')) // 苹果/香蕉/橙子
- 说明:默认用逗号分隔,传入空字符串直接拼接
② find(条件函数)
- 作用:查找第一个符合条件的元素
- 示例:
const users = [
{ id: 1, name: '张三' },
{ id: 2, name: '李四' }
]
const user = users.find(u => u.id === 2)
console.log(user) // { id: 2, name: '李四' }
- 说明:找到即停止遍历,找不到返回
undefined
③ every(条件函数)
- 作用:检查所有元素是否都满足条件
- 示例:
const nums = [10, 20, 30]
const allOver15 = nums.every(n => n > 15)
console.log(allOver15) // false(因为10不满足)
- 说明:所有元素满足才返回
true
④some(条件函数)
- 作用:检查是否有至少一个元素满足条件
- 示例:
const nums = [5, 15, 25]
const hasOver20 = nums.some(n => n > 20)
console.log(hasOver20) // true(25满足)
- 说明:找到第一个满足的元素即停止
⑤concat(数组)
- 作用:合并多个数组
- 示例:
const arr1 = [1, 2]
const arr2 = [3, 4]
console.log(arr1.concat(arr2)) // [1, 2, 3, 4]
- 说明:不改变原数组,返回新数组
⑥sort(比较函数)
- 作用:对数组排序
- 示例:
const nums = [3, 1, 4]
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b) // 升序排列
console.log(nums) // [1, 3, 4]
- 说明:默认按字符串排序,数字需自定义比较函数
⑦splice(起始索引, 删除数量, 替换元素)
- 作用:删除 / 替换数组元素
- 示例:
const fruits = ['苹果', '香蕉', '橙子']
// 从索引1开始删除1个元素,插入'葡萄'
fruits.splice(1, 1, '葡萄')
console.log(fruits) // ['苹果', '葡萄', '橙子']
- 说明:会改变原数组,返回被删除的元素数组
⑧reverse()
- 作用:反转数组元素顺序
- 示例:
const nums = [1, 2, 3]
nums.reverse()
console.log(nums) // [3, 2, 1]
- 说明:直接修改原数组
⑨ findIndex(条件函数)
- 作用:查找第一个符合条件的元素索引
- 示例:
const users = [{ id: 101 }, { id: 102 }]
const index = users.findIndex(u => u.id === 102)
console.log(index) // 1
- 说明:找不到返回
-1
⑷.方法总结表
| 方法 | 作用 | 是否改变原数组 | 返回值类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
join | 拼接数组为字符串 | 否 | 字符串 |
find | 查找符合条件的元素 | 否 | 元素或undefined |
every | 检查所有元素是否满足条件 | 否 | 布尔值 |
some | 检查是否有元素满足条件 | 否 | 布尔值 |
concat | 合并数组 | 否 | 新数组 |
sort | 对数组排序 | 是 | 排序后的数组 |
splice | 删除 / 替换元素 | 是 | 被删除的元素数组 |
reverse | 反转数组顺序 | 是 | 反转后的数组 |
findIndex | 查找元素索引 | 否 | 索引或-1 |
这些方法在处理数组时非常实用,建议结合实际案例练习掌握!
⑸.练习



<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
const spec = { size: '40cm*40cm', color: '黑色' }
//1. 所有的属性值回去过来 数组
// console.log(Object.values(spec))
// 2. 转换为字符串 数组join('/') 把数组根据分隔符转换为字符串
// console.log(Object.values(spec).join('/'))
document.querySelector('div').innerHTML = Object.values(spec).join('/')
</script>
</body>
</html>
⑹.数组常见方法- 伪数组转换为真数组
静态方法Array.from()
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
<script>
// Array.from(lis) 把伪数组转换为真数组
const lis = document.querySelectorAll('ul li')
// console.log(lis)
// lis.pop() 报错
const liss = Array.from(lis)
liss.pop()
console.log(liss)
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.String

⑴. 常见实例方法
① split('分隔符')
- 作用:将字符串拆分成数组
- 示例:
const str = 'apple,banana,orange' console.log(str.split(',')) // ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
②substring(开始索引, 结束索引)
- 作用:截取字符串(含头不含尾)
- 示例:
const str = 'hello world' console.log(str.substring(0, 5)) // 'hello'
③ includes(子串)
- 作用:判断字符串是否包含指定子串
- 示例:
const str = '黑马程序员' console.log(str.includes('黑马')) // true
④toUpperCase()
- 作用:将字符串转换为大写
- 示例:
const str = 'abc' console.log(str.toUpperCase()) // 'ABC'
⑤toLowerCase()
- 作用:将字符串转换为小写
- 示例:
const str = 'XYZ' console.log(str.toLowerCase()) // 'xyz'
⑥ indexOf(子串)
- 作用:查找子串首次出现的索引
- 示例:
const str = 'javascript' console.log(str.indexOf('script')) // 4
⑦endsWith(子串)
- 作用:判断字符串是否以指定子串结尾
- 示例:
const str = 'file.txt' console.log(str.endsWith('.txt')) // true
⑧ replace(原字符串, 新字符串)
- 作用:替换字符串中的子串
- 示例:
const str = '旧内容' console.log(str.replace('旧', '新')) // '新内容'
⑨match(正则表达式)
- 作用:查找字符串中匹配正则的内容
- 示例:
const str = '价格: ¥199.90' const price = str.match(/\d+\.\d+/)[0] // '199.90'
⑵.练习 显示赠品练习


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
const gift = '50g的茶叶,清洗球'
// 1. 把字符串拆分为数组
// console.log(gift.split(',')) [,]
// 2. 根据数组元素的个数,生成 对应 span标签
// const str = gift.split(',').map(function (item) {
// return `<span>【赠品】 ${item}</span> <br>`
// }).join('')
// // console.log(str)
// document.querySelector('div').innerHTML = str
document.querySelector('div').innerHTML = gift.split(',').map(item => `<span>【赠品】 ${item}</span> <br>`).join('')
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Number

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// toFixed 方法可以让数字指定保留的小数位数
const num = 10.923
// console.log(num.toFixed())
console.log(num.toFixed(1))
const num1 = 10
console.log(num1.toFixed(2))
</script>
</body>
</html>
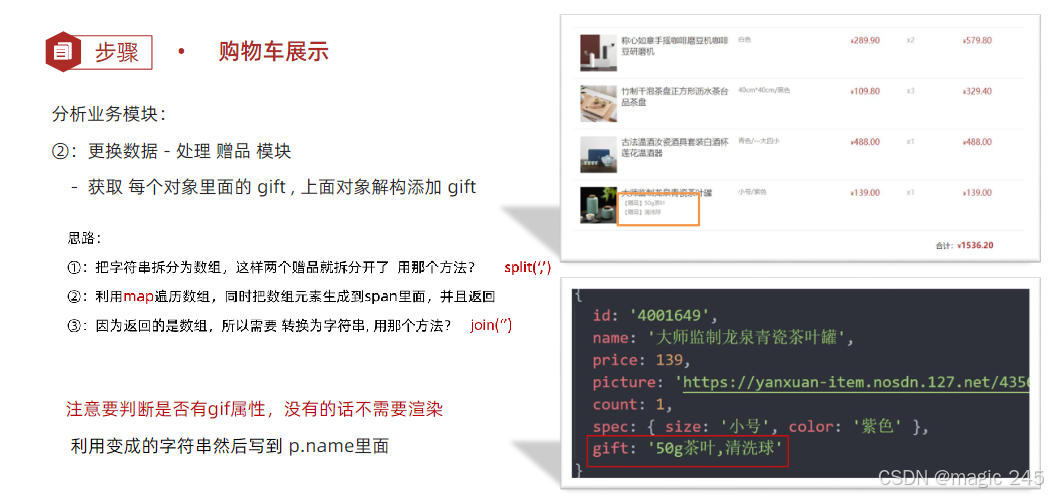
三、案例:购物车展示









<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.list {
width: 990px;
margin: 100px auto 0;
}
.item {
padding: 15px;
transition: all .5s;
display: flex;
border-top: 1px solid #e4e4e4;
}
.item:nth-child(4n) {
margin-left: 0;
}
.item:hover {
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.item img {
width: 80px;
height: 80px;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.item .name {
font-size: 18px;
margin-right: 10px;
color: #333;
flex: 2;
}
.item .name .tag {
display: block;
padding: 2px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #999;
}
.item .price,
.item .sub-total {
font-size: 18px;
color: firebrick;
flex: 1;
}
.item .price::before,
.item .sub-total::before,
.amount::before {
content: "¥";
font-size: 12px;
}
.item .spec {
flex: 2;
color: #888;
font-size: 14px;
}
.item .count {
flex: 1;
color: #aaa;
}
.total {
width: 990px;
margin: 0 auto;
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
border-top: 1px solid #e4e4e4;
padding: 20px;
}
.total .amount {
font-size: 18px;
color: firebrick;
font-weight: bold;
margin-right: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="list">
<!-- <div class="item">
<img src="https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/84a59ff9c58a77032564e61f716846d6.jpg" alt="">
<p class="name">称心如意手摇咖啡磨豆机咖啡豆研磨机 <span class="tag">【赠品】10优惠券</span></p>
<p class="spec">白色/10寸</p>
<p class="price">289.90</p>
<p class="count">x2</p>
<p class="sub-total">579.80</p>
</div> -->
</div>
<div class="total">
<div>合计:<span class="amount">1000.00</span></div>
</div>
<script>
const goodsList = [
{
id: '4001172',
name: '称心如意手摇咖啡磨豆机咖啡豆研磨机',
price: 289.9,
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/84a59ff9c58a77032564e61f716846d6.jpg',
count: 2,
spec: { color: '白色' }
},
{
id: '4001009',
name: '竹制干泡茶盘正方形沥水茶台品茶盘',
price: 109.8,
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/2d942d6bc94f1e230763e1a5a3b379e1.png',
count: 3,
spec: { size: '40cm*40cm', color: '黑色' }
},
{
id: '4001874',
name: '古法温酒汝瓷酒具套装白酒杯莲花温酒器',
price: 488,
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/44e51622800e4fceb6bee8e616da85fd.png',
count: 1,
spec: { color: '青色', sum: '一大四小' }
},
{
id: '4001649',
name: '大师监制龙泉青瓷茶叶罐',
price: 139,
picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/4356c9fc150753775fe56b465314f1eb.png',
count: 1,
spec: { size: '小号', color: '紫色' },
gift: '50g茶叶,清洗球,宝马, 奔驰'
}
]
// 1. 根据数据渲染页面
document.querySelector('.list').innerHTML = goodsList.map(item => {
// console.log(item) // 每一条对象
// 对象解构 item.price item.count
const { picture, name, count, price, spec, gift } = item
// 规格文字模块处理
const text = Object.values(spec).join('/')
// 计算小计模块 单价 * 数量 保留两位小数
// 注意精度问题,因为保留两位小数,所以乘以 100 最后除以100
const subTotal = ((price * 100 * count) / 100).toFixed(2)
// 处理赠品模块 '50g茶叶,清洗球'
const str = gift ? gift.split(',').map(item => `<span class="tag">【赠品】${item}</span> `).join('') : ''
return `
<div class="item">
<img src=${picture} alt="">
<p class="name">${name} ${str} </p>
<p class="spec">${text} </p>
<p class="price">${price.toFixed(2)}</p>
<p class="count">x${count}</p>
<p class="sub-total">${subTotal}</p>
</div>
`
}).join('')
// 3. 合计模块
const total = goodsList.reduce((prev, item) => prev + (item.price * 100 * item.count) / 100, 0)
// console.log(total)
document.querySelector('.amount').innerHTML = total.toFixed(2)
</script>
</body>
</html>






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








