蓝桥杯Java知识点
转载于(https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_63593632/article/details/121850686)
A.快速输入输出
输入-PrintWriter
和System.out.print用法差不多,只是要用PrintWriter类创建一个对象,最后通过.flush()将缓冲区的内容输出到控制台(我喜欢创建一个out,相当于用System.out.print了)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
out.print(1);
out.println(2);
int m=3;
out.printf("%d",m);
out.flush();//记住写
//in.close();
}
}
输入-BufferedReader
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str[]=br.readLine().split(" ");//读入一整行
int len=str.length;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) System.out.println(str[i]);
//in.close();
//输入
//1 2 3
//输出
//1
//2
//3
}
}
快读模板
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static FastReader in=new FastReader();
public static void main(String[] args) {
//编辑代码区
out.flush();
}
}
class FastReader{
StringTokenizer st;
BufferedReader br;
public FastReader(){
br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
String next(){
while (st==null||!st.hasMoreElements()){
try {
st=new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
String nextLine() {
String str = "";
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
}
B.数组
Arrays类的常用方法
sort()(2种)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
int[] arr = {3,2,1,5,4};
Arrays.sort(arr);//对数组进行升序排列
Arrays.sort(arr,0,3);//[0,3),小标0开始。 从小标0开始(包括)到下标为3(不包括)的区间进行排序
String str = Arrays.toString(arr); // Arrays类的toString()方法能将数组中的内容全部打印出来
System.out.print(str);
//输出:[1, 2, 3, 5, 4]
}
}
binarySearch()
返回指定元素的索引值(下标),数组必须是先排好序的
int[] arr = {10,20,30,40,50};
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 30));
//输出:2 (下标索引值从0开始)
C.包装类
Integer常用方法
Integer.toString(k,r)进制转换
将十进制的数k转换为r进制的数。返回一个String
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
int r =2;
System.out.println(Integer.toString(10,r)); //转r进制
r=8;
System.out.println(Integer.toString(10,r)); //转r进制
r=16;
System.out.println(Integer.toString(10,r)); //转r进制
//输出
//1010
//12
//a
}
}
Integer.parseInt(str,r)
将r进制的数字字符串str转换为十进制,并返回十进制的数
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("10001",2));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("21",8));
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("11",16));
//输出结果
17
17
17
Integer.parseInt(str)
将字符串数字转化成整形数字
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String s="123";
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(s));
//输出
//123
}
}
String类
基本数据类型与String类型相互转换
基本数据类型转String
方法一
int num = 10;
String str = num + "";
//输出
10
方法二(用String.valueOf()方法)
float fl = 12.3f;
double db = 23.5;
String str = String.valueOf(fl);
String str1 = String.valueOf(db);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str1);
//输出
12.3
23.5
String类型转其他类型
public class NewJavaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "234"; //不能写非数字字符
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(num+1);
String str2 = "true"; //只有写true输出才为true,其他的都为false,写1也为false
boolean fl = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2);
System.out.println(fl);
}
}
//输出
235
true
String类常用方法
1.equals()
判断两字符串是否相等,返回Boolean类型
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String s="123";
String ss="123";
System.out.println(s.equals(ss));
//输出
//true
}
}
2.contains()
判断是否包含子串,返回Boolean类型
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String s="12345";
String ss="123";
System.out.println(s.contains(ss));
//输出
//true
}
}
3.indexOf()
找子串第一次出现的下标,从下标0开始,没有找到返回-1
String s = "abcdabcedaaq";
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bc"));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("fgh"));
//输出
1
-1
4.lastIndexOf()
找子串最后一次出现的下标,没有找到返回-1
String s = "abcdbcq";
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bc"));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("fgh"));
//输出
4
-1
5.substring()
提取子串,从0开始数
String s = "abbcccdddd";
System.out.println(s.substring(2)); //从下标2开始
System.out.println(s.substring(1,5)); //从下标1到下标5(不包括5),即[1,5)
//输出
bcccdddd
bbcc
6.isEmpty()
判断字符串是否为 空,返回Boolean类型
7.replace()
替换子串,返回一个新字符串。
String s = "abcbabca";
String s1 = s.replace('a','t');//tbcbtbct,所有的字符a都被替换为t
String s1 = s.replace("ab","tttt"); //ttttcbttttca,所有的子串ab都被替换为tttt
8.split()
分割字符串,其中括号里写正则表达式。返回的是一个字符串数组。
(1)特殊情况(斜线\)
String s = "ab\\cd\\ef\\g\\h";
String[] s1 = s.split("\\\\"); //以 \ 为分割线
System.out.println(s);
int len=s1.length;
for(int i=0;i<len;++i){
System.out.println(s1[i]);
}
(2)需要加双斜线的:+、*、$、^、
String s = "ab+cdef+gh";
String[] s1 = s.split("\\+");
String s = "ab*cdef*gh";
String[] s1 = s.split("\\*");
String s = "ab$cdef$gh";
String[] s1 = s.split("\\$");
String s = "ab^cdef^gh";
String[] s1 = s.split("\\^");
//输出
ab
cdef
gh
(3)其他
String s = "ab,cde,fgh";
String[] s1 = s.split(",");
//输出
ab
cde
fgh
(4)多个符号作为分隔符,使用多个分隔符则需要借助 | 符号
String s = "ab,c+de@fgh";
String[] s1 = s.split(",|\\+|@"); //以逗号、加号、@为分隔符,之间用或(|)
9.toLowerCase()和toUpperCase()
字符串大小写转换
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
String s="abc";
String S=s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(S);
//输出
//ABC
String ss="ABC";
String SS=ss.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(SS);
//输出
//abc
in.close();
}
}
10.字符串与char[]相互转化
char[] cs = "Hello".toCharArray(); // String -> char[]
String s = new String(cs); // char[] -> String
11.replaceAll()
replace和replaceAll的第一个参数是不一样的,replace的第一个参数只能是字符或者字符串,而replaceAll的第一个参数是作为正则表达式来被方法解析的。
比如我要把一个字符串中的数字替换成字母
String s=in.next();
s=s.replaceAll("[0-9]","a");
//replaceAll第一个参数是regex正则表达式,表示数字的正则表达式是[0-9],表示字母的是[a-zA-Z]
out.print(s);
//输入:123
//输出:aaa
例题:串的处理
str[i]=str[i].replaceAll("([0-9])([a-zA-Z])","$1_$2");
//这里$1对应的是第一个小括号,$2对应第二个小括号
//这句代码就可以将一个字符串中数字和字母之间加上一个"_"
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=in.nextLine();
String str[]=s.split("\\s+");
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++){
str[i]=str[i].substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+str[i].substring(1);
str[i]=str[i].replaceAll("([0-9])([a-zA-Z])","$1_$2");
str[i]=str[i].replaceAll("([a-zA-Z])([0-9])","$1_$2");
out.print(str[i]+" ");
}
out.flush();
}
StringBuffer和StringBuilder类
由于 StringBuilder 相较于 StringBuffer 有速度优势,所以多数情况下建议使用 StringBuilder 类。
String与StringBuilder相互转化
String ss = "abcder";
StringBuilder sbs = new StringBuilder(ss); //String转换为StringBuffer
StringBuilder resbs = sbs.reverse();
String news = resbs.toString(); //StringBuffer转换为String
System.out.println(news);
StringBuilder类常用方法
1、append(String str)/append(Char c):字符串连接
StringBuilder strB = new StringBuilder();
System.out.println("StringBuilder:"+strB.append("ch").append("111").append('c'));
//return "StringBuilder:ch111c"
2、toString():返回一个与构建起或缓冲器内容相同的字符串
System.out.println("String:"+strB.toString());
3、insert(int offset, String str)/insert(int offset, Char c):在指定位置之前插入字符(串)
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String s="abcde";
String ss="123";
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(ss);
sb.insert(2,s);//下标从0开始数
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//输出
//12abcde3
}
}
4、delete(int startIndex,int endIndex):删除起始位置(含)到结尾位置(不含)之间的字符串
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String s="abcdef";
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(s);
sb.delete(2,4);//从0开始数,区间为[2,4)
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//输出
//abef
}
}
5、reverse():字符串翻转
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String s="abcdef";
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(s);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//输出
//fedcba
}
}
D.Character类
Character类用于对单个字符进行操作,可以new一个对象,也可以用Character._ 来直接调用方法。
A65 a97
Character类常用方法
1.compare(char ch1,char ch2):比较ch1与ch2,若这两个相等则返回0
2.toUpperCase(char ch):将字符参数转换成大写
3. toLowerCase(char ch):将字符参数转换成小写
4. isLowerCase(char ch):判断指定字符是否是小写字符
5. isUpperCase(char ch):判断指定字符是否是大写字符
6. isLetter():是否是一个字母
7. isDigit():是否是一个数字
8. isWhitespace(char ch):判断是否是一个空白字符
9. toString():返回字符的字符串形式,字符串的长度仅为1
10.getNumericValue(char ch):将单个字符类型的数字转化成整形数字
char c1='A',c2='a';
System.out.println(Character.compare(c1,'A'));//0
System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase(c2));//A
System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase(c1));//a
System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase(c1));//true
System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase(c2));//true
System.out.println(Character.isLetter('a'));//true
System.out.println(Character.isDigit('1'));//true
System.out.println(Character.isWhitespace(' '));//true
System.out.println(Character.toString('a'));//a
int num1=s.charAt(i)-'0';
//第一种转化方式 char->int
int num2=Character.getNumericValue(s.charAt(i));
//第二种转化方式 char->int
E.Math类常用方法
一、数学常用运算
1.绝对值Math.abs()
System.out.println(Math.abs(5)); //5
System.out.println(Math.abs(-15)); //15
System.out.println(Math.abs(-16.8)); //16.8
2.平方根Math.sqrt()
返回类型为double
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(16.0)); //4.0
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(0)); //0.0
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(-0)); //0.0
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(8)); //2.8284271247461903
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(-16.0)); //NaN
3.立方根Math.cbrt()
返回类型为double
System.out.println(Math.cbrt(8.0)); //2.0
System.out.println(Math.cbrt(-8)); //-2.0
System.out.println(Math.cbrt(0)); //0.0
System.out.println(Math.cbrt(-0)); //0.0
4.幂与指数函数Math.pow(int a,int b)
返回类型为double
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,5)); //32.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(-2,5)); //-32.0
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,0)); //1.0
5.对数函数Math.log()与Math.log10()
System.out.println(Math.log(16)); //2.772588722239781
System.out.println(Math.log(0)); //-Infinity
System.out.println(Math.log(-0)); //-Infinity
System.out.println(Math.log(-16)); //NaN
System.out.println(Math.log10(100)); //2.0
System.out.println(Math.log10(-100)); //NaN
System.out.println(Math.log10(0)); //-Infinity
二、取整函数
1.向上取整Math.ceil()
2.向下取整Math.floor()
3.四舍五入Math.round()
System.out.println(Math.ceil(9.6)); //10.0
System.out.println(Math.ceil(0)); //0.0
System.out.println(Math.ceil(-9.6)); //-9.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(6.6)); //6.0System.out.println(Math.floor(0)); //0.0
System.out.println(Math.floor(-6.6)); //-7.0
System.out.println(Math.round(6.45)); //6
System.out.println(Math.round(0)); //0
System.out.println(Math.round(-6.45)); //-6
三、最大值与最小值
1.最大值Math.max(int a,int b)
取两者之间较大的一个值
System.out.println(Math.max(3,5.5)); //5.5
System.out.println(Math.max(4,8)); //8
System.out.println(Math.max(4.7,6.5)); //6.5
System.out.println(Math.max(-5,-8)); //-5
2.最小值Math.min(int a,int b)
取两者之间较小的一个值
System.out.println(Math.min(4.7,8.8)); //4.7
System.out.println(Math.min(3,6)); //3
System.out.println(Math.min(2,0.0)); //0.0
System.out.println(Math.min(-5,-7.6)); //-7.6
四、随机数
Math.random()
返回带有正号的double值,大于等于0.0且小于1.0 。 从该范围均匀分布伪随机地生成返回值。
//生成指定区间[a , b)随机数公式:
//Math.random()*(b-a) + a
System.out.println(Math.random()); //随机生成[0,1)区间double类型的数
System.out.println(Math.random()*90+10); //随机生成[10,100)区间double类型的数
BigInteger类
使用时需要导入 import java.math.BigInteger;
使用 BigInteger 类,首先要创建一个 BigInteger 对象。
常用方法


//加法
BigInteger add1 = new BigInteger("10");
System.out.println(add1.add(new BigInteger("20")));
//减法
BigInteger sub1 = new BigInteger("10");
System.out.println(sub1.subtract(new BigInteger("20")));
//除法
BigInteger div1 = new BigInteger("10");
System.out.println(div1.divide(new BigInteger("20")));
//乘法
BigInteger mul1 = new BigInteger("10");
System.out.println(mul1.multiply(new BigInteger("20")));
//取模
BigInteger remain1 = new BigInteger("10");
System.out.println(remain1.remainder(new BigInteger("8")));
//快速幂取模
BigInteger mod = new BigInteger ("10");
BigInteger pow = new BigInteger ("20");
System.out.println(pow.modPow(pow,mod));
//比较两个数字的大小,小于返回-1,大于返回1,等于0的时候返回0
BigInteger comp1 = new BigInteger("10");
System.out.println(comp1.compareTo(new BigInteger("18")));
//n次幂的运算
BigInteger power1 = new BigInteger("2");
System.out.println(power1.pow(10));
//返回较小的数
BigInteger min1 = new BigInteger("2");
System.out.println(min1.min(new BigInteger("-23")));
//返回较大的数
BigInteger max1 = new BigInteger("2");
System.out.println(max1.max(new BigInteger("-23")));
//返回该类型的数字的值
BigInteger val = new BigInteger("123");
System.out.println(val.intValue());
//返回最大公约数
BigInteger gcd1 = new BigInteger("12");
System.out.println(gcd1.gcd(new BigInteger("6")));
介绍BigInteger的读入方法——nextBigInteger(),从控制台读入一个BigInteger型数据,类似于读入int型的nextInt();
public void test() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // 读入
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 读入一个int;
BigInteger m = sc.nextBigInteger(); // 读入一个BigInteger;
while(sc.hasNext()){
System.out.print("sc.hasNext()=" + sc.hasNext());
}
}
F.Java集合类
ArrayList


HashSet

 注意HashSet没有带索引的方法,比如get方法
注意HashSet没有带索引的方法,比如get方法
例题:明明的随机数
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Integer>set=new HashSet<>();
ArrayList<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();
int n=in.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)a[i]=in.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(!set.contains(a[i])){//利用Hashset集合元素的不可重复性来过滤
set.add(a[i]);
list.add(a[i]);
}
}
Collections.sort(list);
out.println(list.size());
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
}
out.flush();
}
HashMap

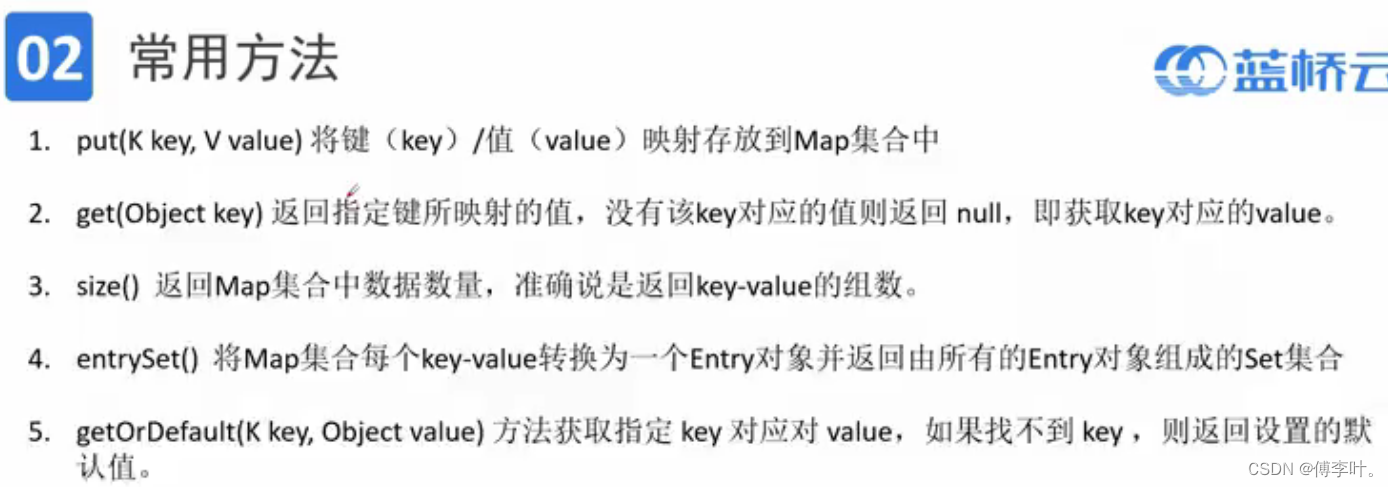
例题

public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=in.nextInt();
HashMap<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int a=in.nextInt();
map.put(a,map.getOrDefault(a,0)+1);
}
int max=0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {//Hashmap的遍历
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
max = Math.max(max, value);
}
ArrayList<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();
for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>entry:map.entrySet()){
Integer key=entry.getKey();
Integer value=entry.getValue();
if(value==max)list.add(key);
}
Collections.sort(list);
for(int i:list)out.print(i+" ");
out.flush();
}
Stack

例题
代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=in.nextInt();
String s=in.next();
char s1[]=s.toCharArray();
Stack<Character>stack=new Stack<>();
boolean flag=true;
for(char c:s1){
if(c=='(')stack.push(c);
else if(c==')'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
stack.pop();
}
else {
flag=false;//如果stack集合的左括号全部用完,但是又出现右括号,就不符合了
break;
}
}
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())flag=false;//还有一种情况就是结尾是(,也是不符合的
if(flag==true) out.print("Yes");
else out.println("No");
out.flush();
}
Queue与PriorityQueue
 优先队列PriorityQueue比一般的Queue多出一个作用是
优先队列PriorityQueue比一般的Queue多出一个作用是
在元素进入队列后,出队时是按照从小到大的优先级出队
public static void main(String[] args) {
//优先队列默认从小到大出队
PriorityQueue <Integer>q=new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(3);
q.add(1);
q.add(2);
out.println(q.poll());//1
out.println(q.poll());//2
out.println(q.poll());//3
//优先队列从大到小出队
PriorityQueue <Integer>q1=new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->b-a);
q1.add(3);
q1.add(1);
q1.add(2);
out.println(q1.poll());//3
out.println(q1.poll());//2
out.println(q1.poll());//1
out.flush();
}
例题
最优操作(优先队列)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=in.nextInt();
int m=in.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
//先创建一个优先队列,满足从小到大的顺序
PriorityQueue<Integer>q=new PriorityQueue<>();
long sum=0;//sum用来存储数组和
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
a[i]=in.nextInt();
q.add(a[i]);//把数组放入优先队列里
sum+=a[i];//先把数组和算出来
}
while (m-->0){
int x=in.nextInt();
int y=in.nextInt();
while (x-->0){
//如果这个队列的头(也就是队列中的最小值)小于给出的y的时候,
// 就可以把头弹出去,然后把y加进去,这是最优解(贪心的思想)
if(q.peek()<y){
sum-=q.poll();//然后更新sum的值就行了
sum+=y;
q.add(y);
}
else break;
}
}
out.println(sum);
out.flush();
}























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








