编译器根据类创造一个对象时就会对类中的成员变量分配相应的空间,同时也会为成员赋值,这个过程叫初始化,在对象使用结束后就会做相关的清理工作这两步就需要类的构造函数和析构函数完成。
1.构造函数
构造函数在类中都有默认生成,在定义该类的对象时,系统会自动调用相应的构造函数,初始化对象的成员,如果自己定义了构造函数,编译器就会就只会调用自定义的构造函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class date
{
public:
//构造函数
/*date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}*/
void printf()
{
cout<<_year<<"-"<<_month<<"-"<<_day<<endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
date d1;
d1.printf();
return 0;
}
创建一个日期类,先屏蔽自定义的构造函数,使用系统默认生成的构造函数,并打印d1并查看结果
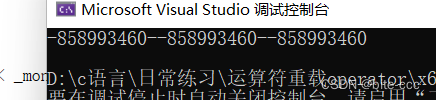
为什么是乱码,难道系统没有调用构造函数?其实并不是, 在系统生成的默认构造函数中对内置类型(int char int* char*....)不做处理,对自定义类型(class struct )调用对应的构造函数,所以有些成员变量就需要我们自己设计构造函数,日期类就需要自己设计构造函数
1. date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
2. date()
{
_year = 1;
_month = 1;
_day = 1;
}
构造函数支持函数重载,但是全缺省和无参函数不能一起出现,会出现调用的二义性。
构造函数的特征:
1.函数名与类名相同
2.没有返回值
3.支持函数重载
4.自定义了构造函数,编译器就不调用自动生成的构造函数了
5.默认生成的构造函数对内置类型不做处理,对自定义类型做处理
2.析构函数
析构函数也是类的一种特殊的成员函数,它的功能与构造函数功能相反,用于撤销对象时的一种清理工作,如释放分配给对象分配的内存空间等。
与构造函数相同,析构函数的调用也是系统自动调用的,函数名是类名前面加~,没有返回类型没有参数,所以不能支持函数重载。
与构造函数类似,析构函数可以用户自定义,也可以由系统自动生成,如果用户没有自定义,系统就调用默认生成的析构函数,如果用户自定义了析构函数系统就不再调用默认的析构函数。
~date()
{
_year=0;
_month=0;
_day=0;
}
切记析构函数不是销毁对象而是完成对象中的清理工作!
3.拷贝构造函数
拷贝构造函数顾名思义也是构造函数,就是拷贝已经存在的类的对象,再去生成一个这个类的对象
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class date
{
public:
date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
date(const date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
void printf()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
date d1(2022,9,27);
d1.printf();
date d2(d1);
d2.printf();
return 0;
}
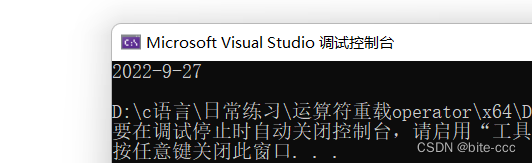
运行结果:

设计拷贝函数需要注意使用的是引用而不是传值,如果改为传值就会出现报错

拷贝构造函数的本质就是拷贝对象,假如我们的拷贝构造函数的实参是d1,我们在调用拷贝构造函数就需要把实参d1传给d,传递的过程实质就是把形参d1传给形参d,然而对于形参d1的拷贝本身就构成了拷贝构造的条件,所以传值传参就会形成无穷的递归,编译器为了防止出现这样的情况就会自身检查并报错,所以要用传引用传参。
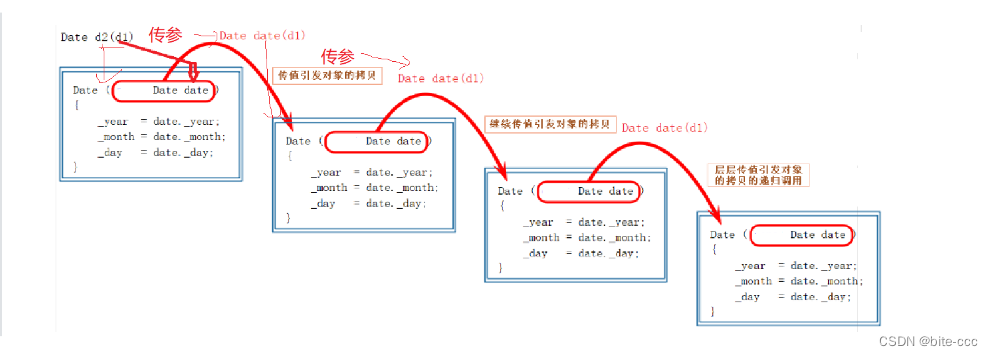
正确的写法:
date(const date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
加const 是为了防止把引用的对象修改了,加const缩小权限,保护被引用的对象
4.运算符重载
创建对象后如何比较两个对象的大小,< > =只能用来比较数的大小而不能比较对象

Date& operator+=(int day)
{
date& operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while(_day > getday(_year, _month))//天数大于本月的天数
{
_month += 1;//月+1
_day -= getday(_year, _month);//-本月的天数
}
while (_month > 12)
{
_year += 1;
_month = 1;
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
date& operator+(int day)
{
date ret;
_day += day;
return ret;
}
// 日期-天数
date& operator-(int day)
{
date ret;
_day -= day;
return ret;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)//防止传参传个负数。
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 前置++
Date& operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date operator++(int)
{
Date ret = *this;
*this += 1;
return ret;
}
// 后置--
Date operator--(int)
{
Date ret = *this;
*this -= 1;
return ret;
}
// 前置--
Date& operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)
{
if ((_year > d._year) ||
(_year > d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year > d._year && _month > d._month && _day > d._day))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)
{
if (_year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return(*this == d) || (*this > d);
}
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数。
int operator-(const Date& d)
{
//找最小和最大
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
//统计相差的天数。
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return flag * n;
}




 本文详细介绍了C++中的构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数以及运算符重载的概念和用法。通过实例展示了如何自定义这些函数,以及它们在对象生命周期中的作用,特别是对于内置类型和自定义类型的处理。此外,还讨论了拷贝构造函数的重要性,以及如何避免在实现过程中出现的无限递归问题。最后,演示了如何重载比较运算符,使得类对象可以进行大小比较。
本文详细介绍了C++中的构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数以及运算符重载的概念和用法。通过实例展示了如何自定义这些函数,以及它们在对象生命周期中的作用,特别是对于内置类型和自定义类型的处理。此外,还讨论了拷贝构造函数的重要性,以及如何避免在实现过程中出现的无限递归问题。最后,演示了如何重载比较运算符,使得类对象可以进行大小比较。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










