目录
G-多吃蘑菇_第20届上海大学程序设计联赛春季赛G 搜索/回溯/图论
A-如何才能穿过传送门_第20届上海大学程序设计联赛春季赛(同步赛) (nowcoder.com)模拟
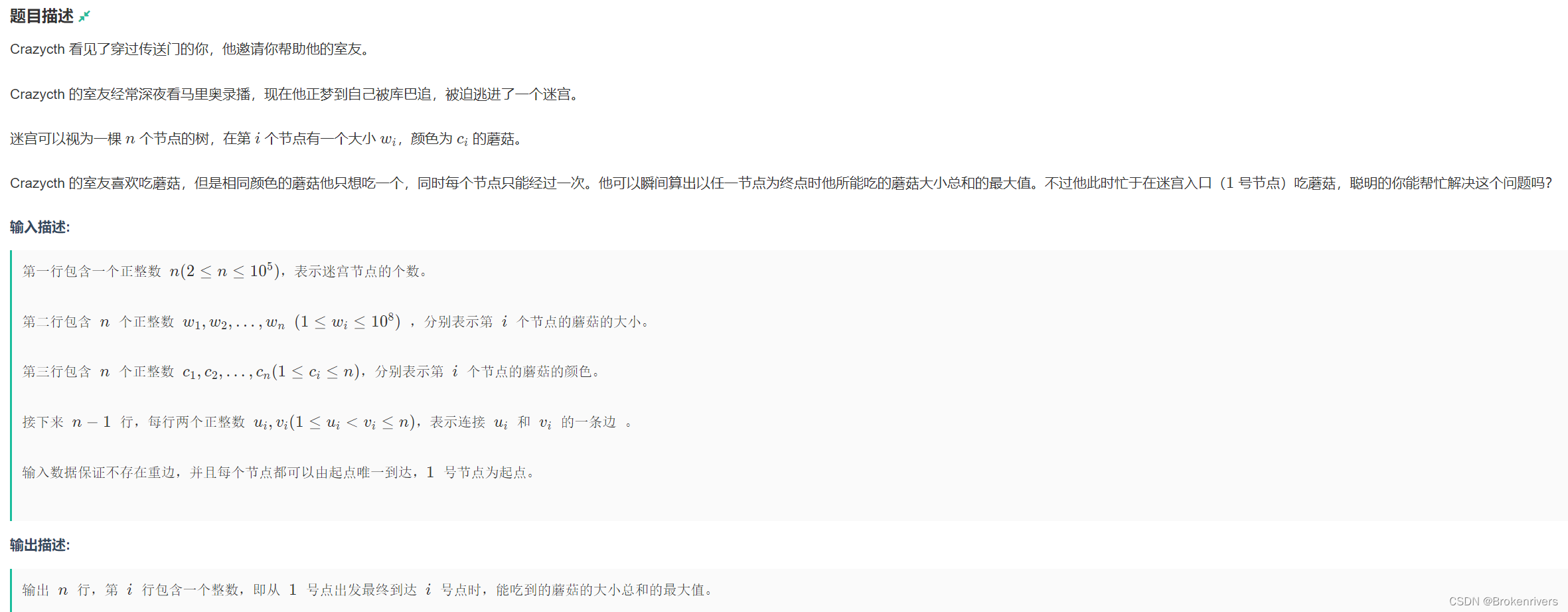
G-多吃蘑菇_第20届上海大学程序设计联赛春季赛G 搜索/回溯/图论
//#include<bits/std c++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<math.h>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<limits.h>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define f first
#define s second
#define ll long long
#define int ll
#pragma warning (disable:4996);
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int T, n, m, q;
int w[N];//重量
int c[N];//节点颜色
int dp[N];//答案
int cnt[N];//每个状态下当前颜色对应重量的最大值
vector<int>gra[N];//邻接表
void dfs(int now,int fa, int sum) {//总的思路是遍历整棵数,同时填上对应节点的答案
dp[now] = sum;//填入当前节点的答案,dp表示选中颜色的蘑菇大小总和
for (int x : gra[now]) {//遍历子树
if (x!=fa) {
int t = cnt[c[x]];//当前颜色能拿的最大重量
if (t < w[x]) {
cnt[c[x]] = w[x];//更新该颜色的最大重量
dfs(x, now, sum + (w[x] - t));
cnt[c[x]] = t;//这条路走完了回溯颜色去另一条路
}
else {
dfs(x, now, sum);//继续遍历
}
}
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(NULL);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // !ONLINE_JUDGE
cin >> n;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
cin >> w[j];
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> c[j];
}
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
int t1, t2;
cin >> t1 >> t2;
gra[t1].push_back(t2);
gra[t2].push_back(t1);
}
cnt[c[1]] = w[1];//初始化
dfs(1, -1, w[1]);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cout << dp[j] << endl;
return 0;
}之前好像写过一个和这个差不多的搜索题目。
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-902B/origin
思路:关键点是子树的颜色都与该子树的根节点相同,所以搜索的时候不必去填补颜色,只需要判断该根节点的颜色即可 。然后记录根节点颜色继续向下遍历子树。
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<math.h>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<limits.h>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<unordered_set>
#define ll long long
#define int ll
#pragma warning (disable:4996);
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4+10;
int T;
int cmp(int a, int b) {
return a > b;
}
vector<int>tree[N];
int mp[N];
int n;
int ans = 0;
void dfs(int dep,int f,int c) {//dep当前节点编号,f表示根节点,c为根节点的颜色
if (mp[dep] != c)//如果根节点与该节点对应的颜色不同则染色且ans++
ans++;
for (auto x : tree[dep]) {//遍历该根节点的子树
if (x != f) {//不能回走,向下遍历子树
dfs(x, dep, mp[dep]);
}
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(NULL);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // !ONLINE_JUDGE
cin >> n;
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j++) {
int t;
cin >> t;
tree[t].push_back(j);//无向边,邻接矩阵存储
tree[j].push_back(t);
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> mp[j];//记录每个节点对应的颜色
}
dfs(1, -1, -1);//-1与正常值区分
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
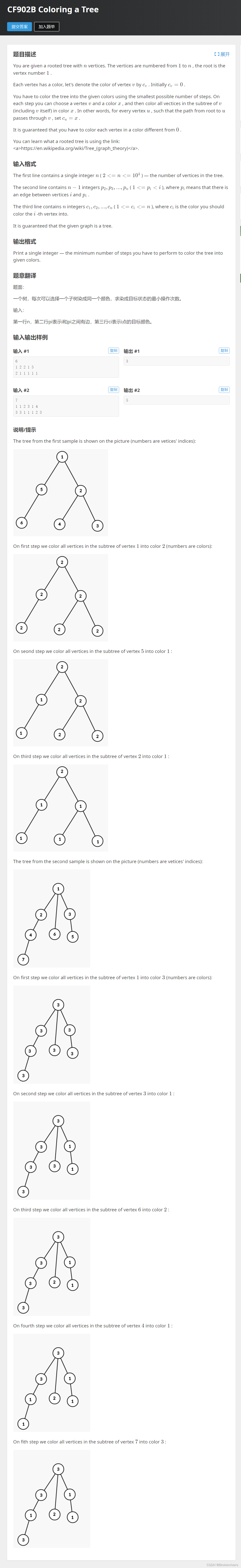
}A A-如何才能穿过传送门_第20届上海大学程序设计联赛春季赛(同步赛) (nowcoder.com)
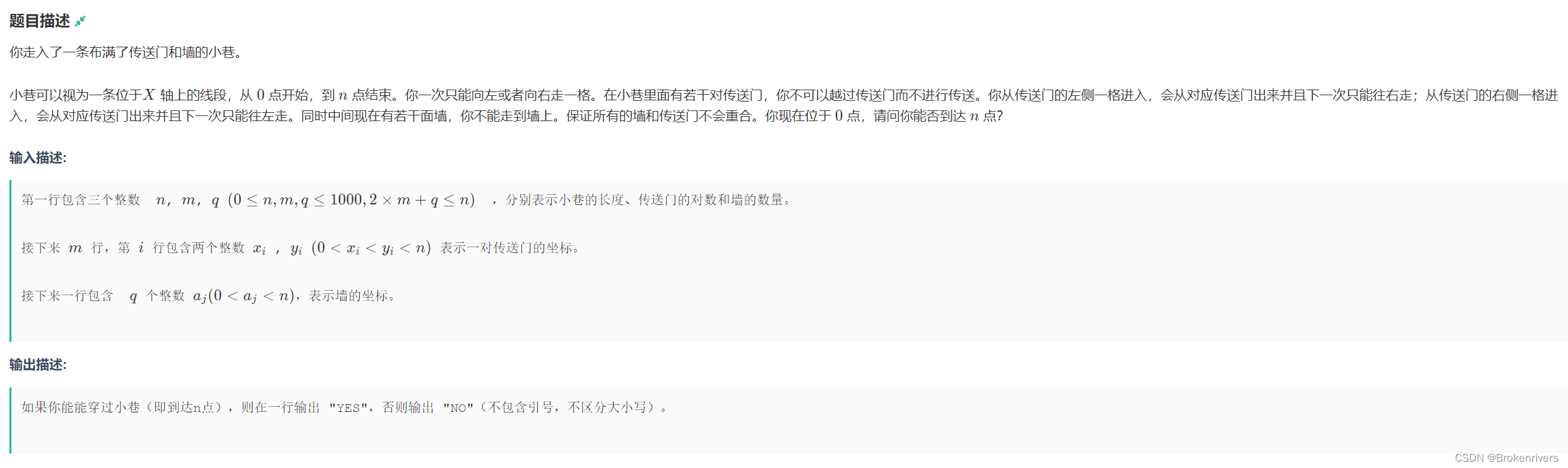
模拟一下其实就好了,标记传送门和障碍物。模拟每次路径上出现的可能,遇到传送门则跳转同时判断毕竟之路上有无障碍物。我也不懂为啥比赛没写出来..
//#include<bits/std c++.h>
#include <iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<math.h>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<limits.h>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
#define f first
#define s second
#define ll long long
#define int ll
#pragma warning (disable:4996);
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int T, n, m, q;
struct node {
int x, y;
}ppp[N];
int nx[N];
int p[N];
int w[N];
int v[N];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cout.tie(NULL);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif // !ONLINE_JUDGE
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
int t1, t2;
cin >> t1 >> t2;
v[t1] = 1, v[t2] = 1;
nx[t1] = t2;
nx[t2] = t1;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= q; j++) {
int t;
cin >> t;
v[t] = 2;
}
int ok = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (v[j] == 1) {
j = nx[j];
}
else if(v[j]==2) {
ok = 1;
}
}
if (ok) {
puts("NO");
}
else
puts("YES");
return 0;
}



 本文讲述了在第20届上海大学程序设计联赛中,涉及两个问题:G-多吃蘑菇通过搜索/回溯/图论解决颜色分配问题,A-如何穿越传送门涉及模拟算法处理路径选择和传送门操作。展示了两种算法策略,包括子树颜色一致性和模拟路径分析。
本文讲述了在第20届上海大学程序设计联赛中,涉及两个问题:G-多吃蘑菇通过搜索/回溯/图论解决颜色分配问题,A-如何穿越传送门涉及模拟算法处理路径选择和传送门操作。展示了两种算法策略,包括子树颜色一致性和模拟路径分析。
















 254
254

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








