前言
上篇文章对shared_ptr进行了简单的仿写,在这篇文章中,将引入它的小弟weak_ptr,两者之间的关系将由本文来解析。
普通的shared_ptr仿写:【点击这里查看】
一、对带有weak_ptr的shared_ptr进行仿写
1. 成员组成内存结构简图
这种shared_ptr的成员变量有三个:
- 直接指向对象的指针_Ptr;
- 指向引用计数类型的指针_Rep;
- 删除器类型。
接下来实现引用计数类和删除器类。
(一)删除器类型
1.删除单个对象
template<class _Ty>
class MyDeletor
{
public:
MyDeletor() = default;
void operator()(_Ty* ptr) const
{
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
delete ptr;// one
}
}
};
2.删除一组对象
template<class _Ty>
class MyDeletor<_Ty[]>
{
public:
MyDeletor() = default;
void operator()(_Ty* ptr) const
{
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
delete[]ptr; // array
}
}
};
(二)引用计数类型
有三个成员变量:
- 指向对象的指针_Ptr;
- shared_ptr的引用计数;
- weak_ptr的引用计数。
构造函数:
- 让值类型指针指向 参数所指向的对象;
- shared_ptr和weak_ptr的引用计数都置为1。
_Incref():对shared_ptr的引用计数扩容(+1);
_Incwref():对weak_ptr的引用计数扩容(+1);
#include<atomic>
template<class _Ty>
class RefCnt
{
public:
_Ty* _Ptr; // Obj;
std::atomic_int _Uses; // shared_ptr;
std::atomic_int _Weaks; // weak_ptr;
public:
RefCnt(_Ty* p) :_Ptr(p), _Uses(1), _Weaks(1) {}
~RefCnt() {}
void _Incref() { _Uses += 1; }
void _Incwref() { _Weaks += 1; }
};
my_shared_ptr类的设计
1. 构造函数
template<class _Ty, class _Dx = MyDeletor<_Ty> >
class my_shared_ptr
{
private:
_Ty* _Ptr; // Object;
RefCnt<_Ty> * _Rep;
_Dx _mDeletor;
public:
my_shared_ptr(_Ty* p = nullptr) :_Ptr(nullptr), _Rep(nullptr)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
_Ptr = p;
_Rep = new RefCnt<_Ty>(p);
}
}
};
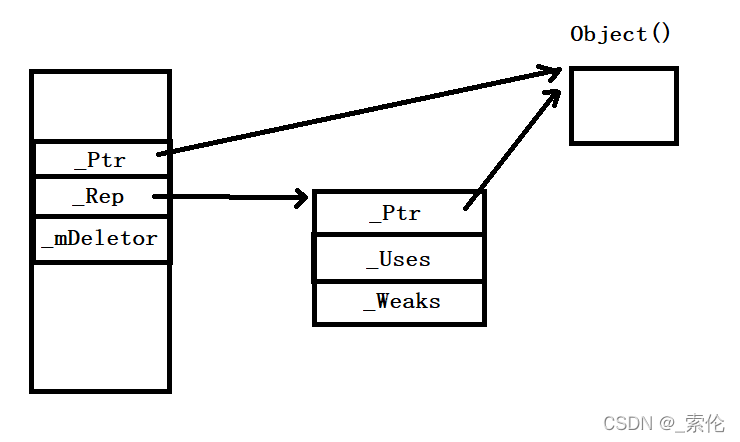
对于构造函数:
初始化列表先将两个指针置为nullptr,如果参数p不为nullptr,那么让_Ptr也指向p所指的对象;然后向堆区申请一个该值类型的引用计数对象,让_Rep指向该对象。
如图所示:
2. 析构函数
来通过判断_Rep来析构。
~my_shared_ptr()
{
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Uses == 0)
{
_mDeletor(_Ptr);
if (--_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
}
_Ptr = nullptr;
_Rep = nullptr;
}
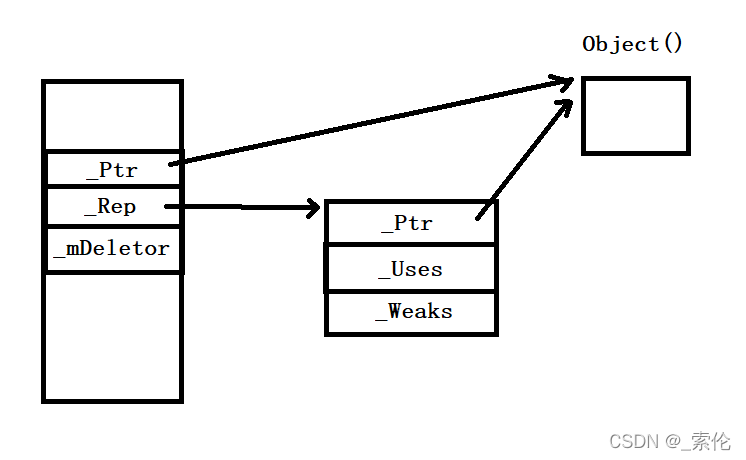
3. 拷贝构造函数
my_shared_ptr(const my_shared_ptr& _Y):_Ptr(_Y._Ptr),_Rep(_Y._Rep)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incref(); // _Uses
}
}
图解:
4. 移动构造函数
资源的转移:比较简单,只需要自身指针指向参数的指针所指之物;
再将参数的指针置为nullptr。
my_shared_ptr(my_shared_ptr&& other):_Ptr(other._Ptr),_Rep(other._Rep)
{
other._Ptr = nullptr;
other._Rep = nullptr;
}
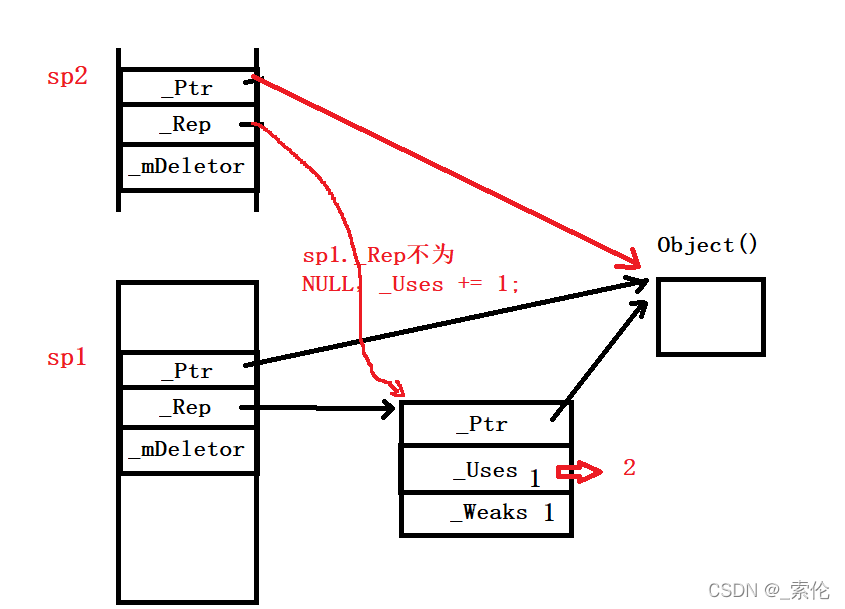
5.赋值构造函数
my_shared_ptr& operator=(const my_shared_ptr& r)
{
if (this == &r || this->_Ptr == r._Ptr) return *this;
if (_Ptr != nullptr && --_Rep->_Uses == 0)
{
_mDeletor(_Ptr);
if (--_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
}
_Ptr = r._Ptr;
_Rep = r._Rep;
if (_Ptr != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incref(); // _Uses;
}
return *this;
}
- 防止自赋值:当this指针和参数相同时,或两者的_Ptr指向同一对象,则直接返回。
- 如果_Ptr指向不为nullptr,且对shared_ptr的引用计数减一后为0,则先删除指向的对象,此时引用计数类型并未删除;
- 再对weak_ptr的引用计数减一,若为0,说明引用计数类型也没有存在的必要,这时候对其删除。
- 这时候再让当前的两个指针指向参数的指针所指向的资源
- 如果当前_Ptr指向的对象不为nullptr,则对shared_ptr的引用计数加一。
- 返回当前对象(*this)。
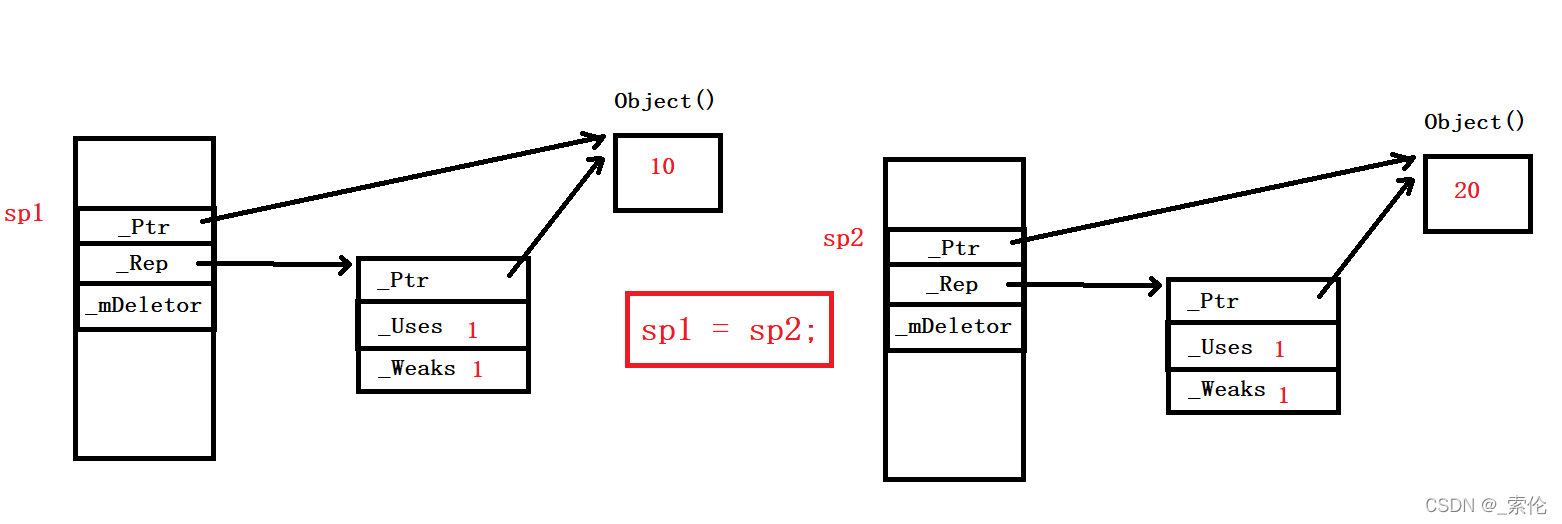
示例1:
如果是这种比较复杂的情况,就需要先把sp1所指向的对象析构掉。
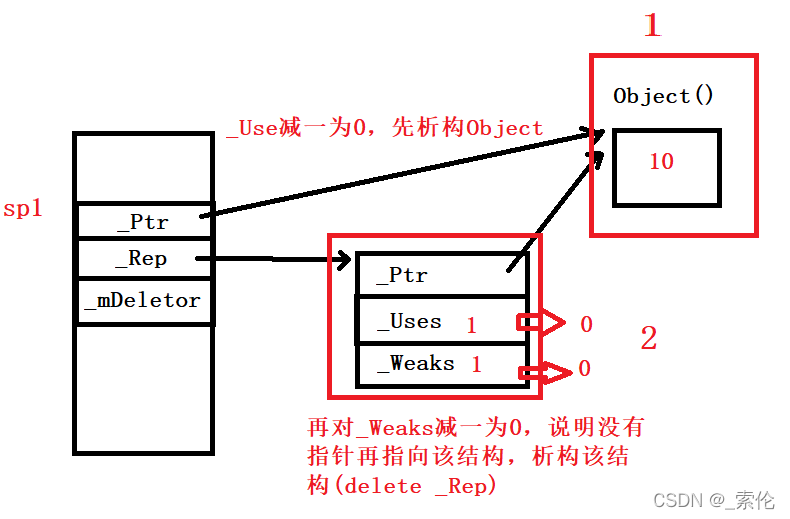
6. 移动赋值函数
my_shared_ptr& operator=(my_shared_ptr&& other)
{
if (this == &other) return *this;
if (_Ptr != nullptr && other._Ptr != nullptr && _Ptr == other._Ptr)
{
this->_Rep->_Uses -= 1;
other._Ptr = nullptr;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
if (_Ptr != nullptr && --_Rep->_Uses == 0)
{
_mDeletor(_Ptr);
if (--_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
}
_Ptr = other._Ptr;
_Rep = other._Rep;
other._Ptr = nullptr;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
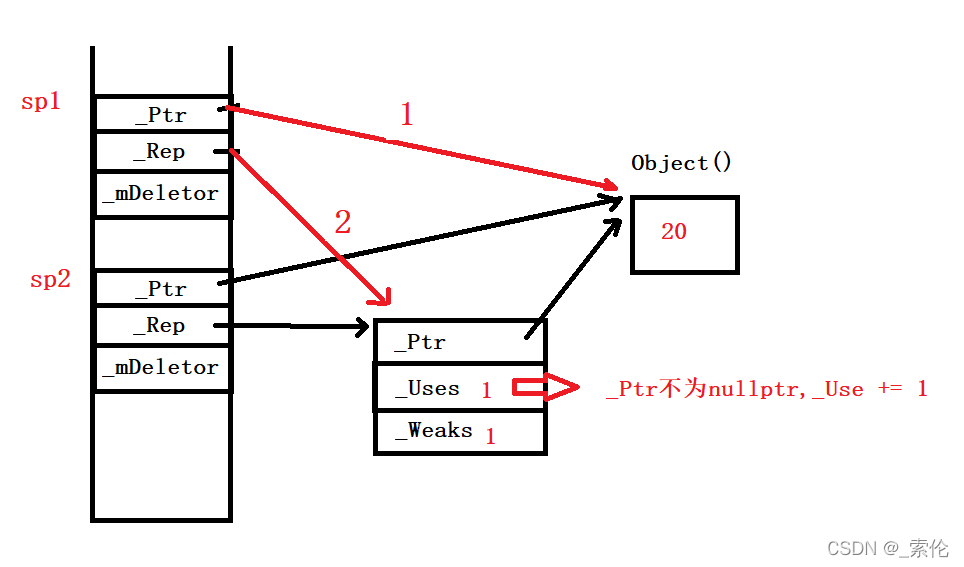
该函数算是这里面较难写的函数,和赋值函数一样,需要考虑多种情况。
- 防止自赋值。
- 若两个_Ptr不为nullptr且指向同一个对象,则将shared_ptr的引用计数减一,将参数的两个指针置为nullptr后返回。
- 如果1,2不满足,则判断当前指针是否为空,并对shared_ptr引用计数减一,如果减完为0,说明没有指针指向对象,则删除_Ptr;再对weak_ptr的引用计数减一,若为0,则删除引用计数结点。
- 处理完上面三步,此时让当前对象的_Ptr和_Ref指向参数的_Ptr和_Ref,完成资源的转移,再将参数的这些指针置为nullptr,返回*this。
7.获得指向对象的指针(_Ptr)
_Ty* get() const { return _Ptr; }
8.解引用和指向符重载
_Ty& operator*() const { return *get(); }
_Ty* operator->() const { return get(); }
9.返回当前持有该资源的shared_ptr个数
size_t use_count() const
{
if (_Rep == nullptr) return 0;
return _Rep->_Uses;
}
10.交换资源函数
void swap(my_shared_ptr& r)
{
std::swap(_Ptr, r._Ptr);
std::swap(_Rep, r._Rep);
}
11.bool()运算符重载
operator bool() const { return _Ptr != nullptr; }
12.友元类(my_weak_ptr)
template<class _Ty>
friend class my_weak_ptr;
二、weak_ptr的仿写
内存简图:
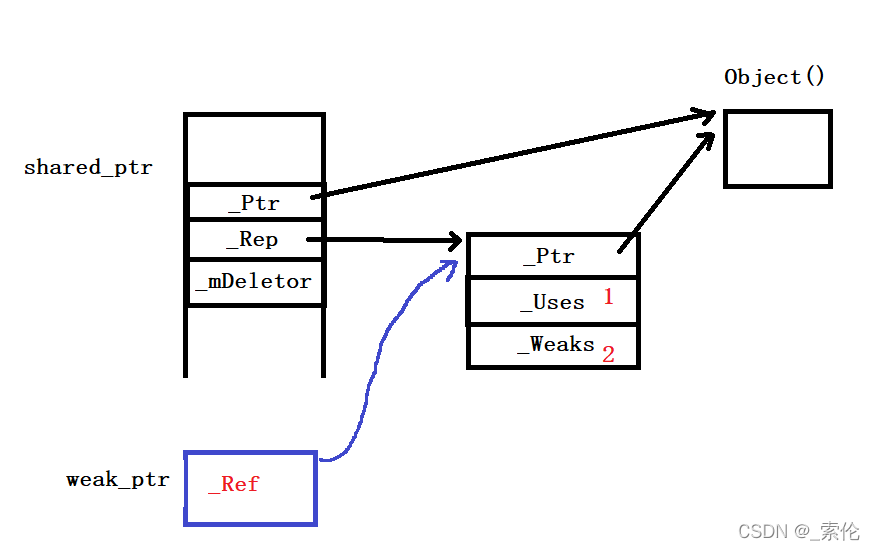
类的设计
只需要一个_Rep指针,指向引用计数结构
template<class _Ty>
class my_weak_ptr
{
private:
RefCnt<_Ty>* _Rep;
public:
my_weak_ptr() :_Rep(nullptr) {}
};
1. 构造函数:利用shared_ptr来构造
让指针指向共享型指针的引用计数结构。
my_weak_ptr(const my_shared_ptr<_Ty>& other)
:_Rep(other._Rep)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref(); // Weaks;
}
}
2. 拷贝构造
让两个指针指向统一个引用计数结构,再对引用计数的 _Weaks加一,意思是现在多了一个weak_ptr来指向该结构。
my_weak_ptr(const my_weak_ptr& other)
:_Rep(other._Rep)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref();
}
}
3.移动构造
只需要完成资源转移,再将参数的指向置为nullptr.
my_weak_ptr(my_weak_ptr&& other)
: _Rep(other._Rep)
{
other._Rep = nullptr;
}
4. 赋值构造函数
my_weak_ptr& operator=(const my_weak_ptr& other)
{
if (this == &other || this->_Rep == other._Rep) return *this;
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = other._Rep;
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref();
}
return *this;
}
- 如果自赋值或指向相同,则直接返回。
- 若当前指针不为nullptr且对弱引用计数减一后为0,则删除当前指向的引用计数结构。若减一后不为0,则执行第3步。
- 让当前_Rep指针指向参数的_Rep所指向的空间。
- 在赋值后,如果指向不为nullptr,则让弱引用计数加一。
- 返回当前对象(*this)。
5. 移动构造函数
my_weak_ptr& operator=(my_weak_ptr&& other)
{
if (this == &other) return *this;
if (this->_Rep != nullptr && other._Rep != nullptr && _Rep == other._Rep)
{
this->_Rep->_Weaks -= 1;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = other._Rep;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
- 防止自赋值
- 若两个指针都不为nullptr且指向同一个引用计数结构,那么只需要对弱引用计数减一(_Weaks–),再将参数的指针置为nullptr,返回当前对象即可。
- 在经过1、2步后,若当前指针不为nullptr,再对弱引用计数减一,等于0时,则删除引用计数结构,因为此时没有一个指针指向它。
- 这几步都过了之后,这时再将资源转移,返回当前对象*this。
6.赋值函数:用shared_ptr来赋值
my_weak_ptr& operator=(const my_shared_ptr<_Ty>& other)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = other->_Rep;
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref();
}
return *this;
}
- 还是对弱引用计数减一判断,如果减完为0,则删除引用计数结构。
- 将_Rep指向将参数的_Rep所指向的结构。
- 如果此时_Rep不为nullptr,则将弱引用计数加一。
- 返回当前对象*this。
7. 析构函数
- 对_Rep判空,再对弱引用计数减一,等于0说明没有指针指向该引用计数结构,那么就删除该结构。
- 将_Rep置为nullptr。
~my_weak_ptr()
{
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = nullptr;
}
8.检查被引用的对象是否已经删除
意思就是查看shared_ptr引用计数是否为0,如果为0说明该对象没有指针指向,已经被删除了。
bool expired() const
{
return this->_Rep->_Uses == 0;
}
9.锁
my_shared_ptr<_Ty> lock() const
{
my_shared_ptr<_Ty> _Ret;
_Ret._Ptr = _Rep->_Ptr;
_Ret._Rep = _Rep;
_Ret._Rep->_Incref();
return _Ret;
}
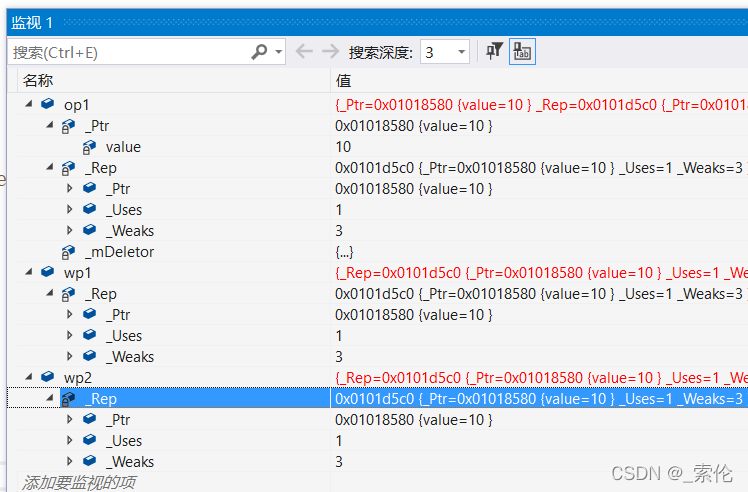
运行示例
void fun()
{
my_shared_ptr<Object> op1(new Object(10));
my_weak_ptr<Object> wp1(op1);
my_weak_ptr<Object> wp2(op1);
}
int main()
{
fun();
return 0;
}
完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<atomic>
using namespace std;
template<class _Ty>
class MyDeletor
{
public:
MyDeletor() = default;
void operator()(_Ty* ptr) const
{
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
delete ptr;// one
}
}
};
template<class _Ty>
class MyDeletor<_Ty[]>
{
public:
MyDeletor() = default;
void operator()(_Ty* ptr) const
{
if (ptr != nullptr)
{
delete[]ptr; // array
}
}
};
template<class _Ty>
class RefCnt
{
public:
_Ty* _Ptr; // Obj;
std::atomic_int _Uses; // shared_ptr;
std::atomic_int _Weaks; // weak_ptr;
public:
RefCnt(_Ty* p) :_Ptr(p), _Uses(1), _Weaks(1) {}
~RefCnt() {}
void _Incref() { _Uses += 1; }
void _Incwref() { _Weaks += 1; }
};
template<class _Ty> class my_weak_ptr;
template<class _Ty, class _Dx = MyDeletor<_Ty> >
class my_shared_ptr // thread;
{
private:
_Ty* _Ptr; // Object;
RefCnt<_Ty> * _Rep;
_Dx _mDeletor;
public:
my_shared_ptr(_Ty* p = nullptr) :_Ptr(nullptr), _Rep(nullptr)
{
if (p != nullptr)
{
_Ptr = p;
_Rep = new RefCnt<_Ty>(p);
}
}
my_shared_ptr(const my_shared_ptr& _Y):_Ptr(_Y._Ptr),_Rep(_Y._Rep)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incref(); // _Uses
}
}
my_shared_ptr(my_shared_ptr&& other):_Ptr(other._Ptr),_Rep(other._Rep)
{
other._Ptr = nullptr;
other._Rep = nullptr;
}
my_shared_ptr& operator=(const my_shared_ptr& r)
{
if (this == &r || this->_Ptr == r._Ptr) return *this;
if (_Ptr != nullptr && --_Rep->_Uses == 0)
{
_mDeletor(_Ptr);
if (--_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
}
_Ptr = r._Ptr;
_Rep = r._Rep;
if (_Ptr != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incref(); // _Uses;
}
return *this;
}
my_shared_ptr& operator=(my_shared_ptr&& other)
{
if (this == &other) return *this;
if (_Ptr != nullptr && other._Ptr != nullptr && _Ptr == other._Ptr)
{
this->_Rep->_Uses -= 1;
other._Ptr = nullptr;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
if (_Ptr != nullptr && --_Rep->_Uses == 0)
{
_mDeletor(_Ptr);
if (--_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
}
_Ptr = other._Ptr;
_Rep = other._Rep;
other._Ptr = nullptr;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
~my_shared_ptr()
{
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Uses == 0)
{
_mDeletor(_Ptr);
if (--_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
}
_Ptr = nullptr;
_Rep = nullptr;
}
_Ty* get() const { return _Ptr; }
_Ty& operator*() const { return *get(); }
_Ty* operator->() const { return get(); }
size_t use_count() const
{
if (_Rep == nullptr) return 0;
return _Rep->_Uses;
}
void swap(my_shared_ptr& r)
{
std::swap(_Ptr, r._Ptr);
std::swap(_Rep, r._Rep);
}
operator bool() const { return _Ptr != nullptr; }
template<class _Ty>
friend class my_weak_ptr;
};
template<class _Ty>
class my_weak_ptr
{
private:
RefCnt<_Ty>* _Rep;
public:
my_weak_ptr() :_Rep(nullptr) {}
my_weak_ptr(const my_shared_ptr<_Ty>& other):_Rep(other._Rep)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref(); // Weaks;
}
}
my_weak_ptr(const my_weak_ptr& other):_Rep(other._Rep)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref();
}
}
my_weak_ptr(my_weak_ptr&& other):_Rep(other._Rep)
{
other._Rep = nullptr;
}
my_weak_ptr& operator=(const my_weak_ptr& other)
{
if (this == &other || this->_Rep == other._Rep) return *this;
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = other->_Rep;
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref();
}
return *this;
}
my_weak_ptr& operator=(my_weak_ptr&& other)
{
if (this == &other) return *this;
if (this->_Rep != nullptr && other._Rep != nullptr && _Rep == other._Rep)
{
this->_Rep->_Weaks -= 1;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = other._Rep;
other._Rep = nullptr;
return *this;
}
my_weak_ptr& operator=(const my_shared_ptr<_Ty>& other)
{
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = other._Rep;
if (_Rep != nullptr)
{
_Rep->_Incwref();
}
return *this;
}
my_weak_ptr& operator=(my_shared_ptr<_Ty>&& other) = delete;
~my_weak_ptr()
{
if (_Rep != nullptr && --_Rep->_Weaks == 0)
{
delete _Rep;
}
_Rep = nullptr;
}
bool expired() const
{
return this->_Rep->_Uses == 0;
}
my_shared_ptr<_Ty> lock() const
{
my_shared_ptr<_Ty> _Ret;
_Ret._Ptr = _Rep->_Ptr;
_Ret._Rep = _Rep;
_Ret._Rep->_Incref();
return _Ret;
}
};
class Object
{
private:
int value;
public:
Object(int x = 0) :value(x) { cout << "Obejct" << endl; }
~Object() { cout << "~Object:" << endl; }
void Print() const { cout << "value: " << value << endl; }
};
void fun()
{
my_shared_ptr<Object> op1(new Object(10));
my_weak_ptr<Object> wp1(op1);
my_weak_ptr<Object> wp2(op1);
}
int main()
{
fun();
return 0;
}





 本文详细介绍了C++智能指针shared_ptr和weak_ptr的内部结构及实现,包括构造函数、析构函数、拷贝与移动操作、引用计数管理等关键功能,并提供了完整的仿写代码示例。
本文详细介绍了C++智能指针shared_ptr和weak_ptr的内部结构及实现,包括构造函数、析构函数、拷贝与移动操作、引用计数管理等关键功能,并提供了完整的仿写代码示例。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










