目录
2. 二叉树的结构体设计 【leftchild data rightchild】
1. 二叉树的遍历规则
先序遍历:根 -> 左 -> 右;中序遍历: 左 -> 根 -> 右;后序遍历:左 -> 右 ->根 。
2. 二叉树的结构体设计 【leftchild data rightchild】
typedef char ELEMTYPE;//typedef给char类型起别名ELEMTYPE
//二叉树结构体设计
typedef struct BtNode
{
struct BtNode* leftchild;
ELEMTYPE data;
struct BtNode* rightchild;
}BtNode,* PBtNode;3. 二叉树的递归先序、中序、后序遍历
void PreOrder(struct BtNode* ptr) //先序遍历(根左右)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) return;
printf("%3c", ptr->data);
PreOrder(ptr->leftchild);
PreOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
void InOrder(struct BtNode* ptr) //中序遍历(左根右)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) return;
InOrder(ptr->leftchild);
printf("%3c", ptr->data);
InOrder(ptr->rightchild);
}
void LastOrder(struct BtNode* ptr) //后序遍历(左右根)
{
if (nullptr == ptr) return;
LastOrder(ptr->leftchild);
LastOrder(ptr->rightchild);
printf("%3c", ptr->data);
}4. 利用已知字符串(二叉树的先序序列)递归创建一棵二叉树

(1)购买节点函数
struct BtNode* Buynode()
{
BtNode* s = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
if (s == nullptr) exit(1);
memset(s, 0, sizeof(BtNode));//此处不要写sizeof(s),由于指针永远为4bit(32bit系统下)
return s;
}(2)创建二叉树
注意:函数参数为引用!!确保每次递归时传参是对同一字符串前置++。
BtNode* CreateBT(const char*& str)//参数为引用!!是由于递归时传参为++str~为了保证每次++同步执行(即在同一个字符串序列)
{
//根据先序序列创建树~根左右
if (str == nullptr || strlen(str) <= 0) return nullptr;//空树
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (*str != '#')
{
s = Buynode();
s->data = *str;//根
s->leftchild = CreateBT(++str);//左
s->rightchild = CreateBT(++str);//右
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
const char* str = "ABC##DE##F##G#H##";
BtNode* s=CreateBT(str);
PreOrder(s);
printf("\n");
InOrder(s);
printf("\n");
LastOrder(s);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}运行结果如图: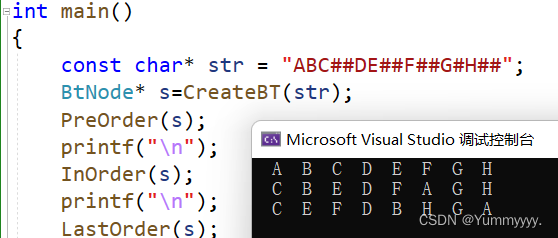
5. 使用先序遍历序列和中序遍历序列创建一棵二叉树
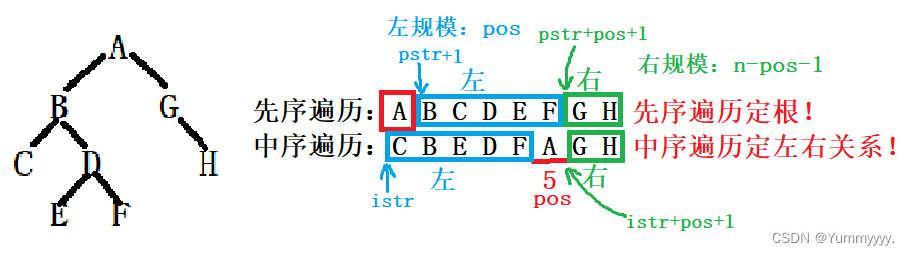
//根据先序遍历+中序遍历创建一棵二叉树
int Find(const char* istr, int n, char str) //中序序列中找根对应的下标
{
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (istr[i] == str)
{
pos = i;
break;
}
}
return pos;
}
BtNode* CreatePITree(const char* pstr, const char* istr, int n)//此处n代表规模
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (n > 0)
{
s = Buynode();
s->data = pstr[0];//先序首位为根
int pos = Find(istr, n, pstr[0]);//中序序列中找根对应的下标
if (pos == -1) exit(1);
s->leftchild = CreatePITree(pstr+1,istr,pos);
s->rightchild = CreatePITree(pstr+pos+1,istr+pos+1,n-pos-1);
}
return s;
}
BtNode* CreatePIT(const char* pstr, const char* istr)
{
int n = strlen(pstr);
int m = strlen(istr);
if (pstr == nullptr || istr == nullptr || n < 1 || m < 1 || n != m) return nullptr;
else return CreatePITree(pstr, istr, n);
}
int main()
{
//const char* str = "ABC##DE##F##G#H##";
//BtNode* s=CreateBT(str);
const char* pstr = "ABCDEFGH";
const char* istr = "CBEDFAGH";
BtNode* s = CreatePIT(pstr, istr);
PreOrder(s);
printf("\n");
InOrder(s);
printf("\n");
LastOrder(s);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}6. 使用中序遍历序列和后序遍历序列创建一棵二叉树
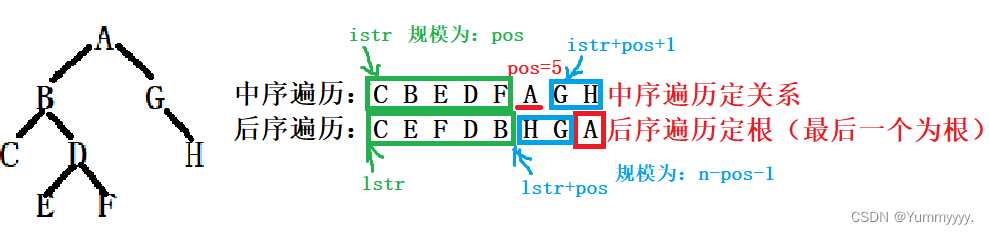
//根据中序遍历+后序遍历创建一棵二叉树
BtNode* CreateILTree(const char* istr, const char* lstr, int n)//此处n代表规模
{
BtNode* s = nullptr;
if (n > 0)
{
s = Buynode();
s->data = lstr[n - 1];//后序遍历的最后一个为根
int pos = Find(istr, n, lstr[n - 1]);
s->leftchild = CreateILTree(istr,lstr,pos);
s->rightchild = CreateILTree(istr+pos+1,lstr+pos,n-pos-1);
}
return s;
}
BtNode* CreateILT(const char* istr, const char* lstr)
{
int n = strlen(istr);
int m = strlen(lstr);
if (nullptr == istr || nullptr == lstr || n < 1 || m < 1 || n != m) return nullptr;
else return CreateILTree(istr, lstr, n);
}
int main()
{
//const char* str = "ABC##DE##F##G#H##";
//BtNode* s=CreateBT(str);
const char* pstr = "ABCDEFGH";
const char* istr = "CBEDFAGH";
const char* lstr = "CEFDBHGA";
//BtNode* s = CreatePIT(pstr, istr);
BtNode* s = CreateILT(istr, lstr);
PreOrder(s);
printf("\n");
InOrder(s);
printf("\n");
LastOrder(s);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}7. 对二叉树的物理存储(数组)进行递归先序、中序、后序遍历
主要依据:二叉树的物理存储对应逻辑存储的关系。
二叉树物理下标为i:其左孩子对应下标为i*2+1;其右孩子对应下标为i*2+2。
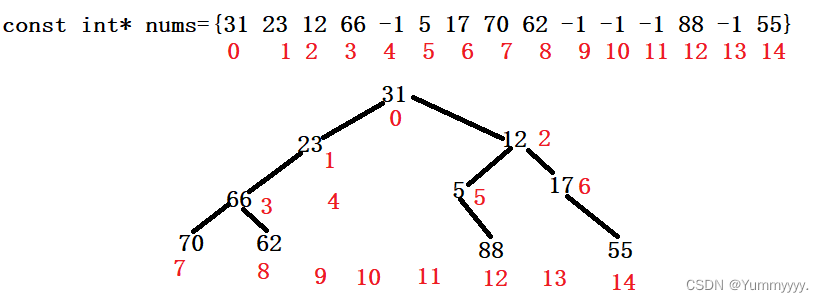
//对二叉树的物理存储数组进行递归先序、中序、后序遍历
void PreOrder(const int* nums, int i, int n)//遍历规模:i~n
{
if (i < n && nums[i] != -1) //i==n时规模为1
{
printf("%3d", nums[i]);//根
PreOrder(nums, i * 2 + 1, n);//左 左子树下标:i*2+1
PreOrder(nums, i * 2 + 2, n);//右
}
}
void InOrder(const int* nums, int i, int n)
{
if (i < n && nums[i] != -1)
{
InOrder(nums, i * 2 + 1, n);//左
printf("%3d", nums[i]);//根
InOrder(nums, i * 2 + 2, n);//右
}
}
void LastOrder(const int* nums, int i, int n)
{
if (i < n && nums[i] != -1)
{
LastOrder(nums, i * 2 + 1, n);//左
LastOrder(nums, i * 2 + 2, n);//右
printf("%3d", nums[i]);//根
}
}
int main()
{
const int nums[] = {31,23,12,66,-1,5,17,70,62,-1,-1,-1,88,-1,55};
int n = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]);
PreOrder(nums, 0, n);
printf("\n");
InOrder(nums, 0, n);
printf("\n");
LastOrder(nums, 0, n);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}




 本文详细介绍了二叉树的遍历规则,包括先序、中序和后序遍历,并通过递归方式实现。同时,讲解了如何根据先序序列、中序序列和后序序列创建二叉树的算法。此外,还展示了如何对二叉树的物理存储数组进行遍历。这些内容对于理解和操作二叉树至关重要。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的遍历规则,包括先序、中序和后序遍历,并通过递归方式实现。同时,讲解了如何根据先序序列、中序序列和后序序列创建二叉树的算法。此外,还展示了如何对二叉树的物理存储数组进行遍历。这些内容对于理解和操作二叉树至关重要。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








