目录
-
前言:idea连接Mysql
1、创建工程,导入驱动jar包

2、注册驱动
//1、注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");3、获取连接
//2、获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
String username="root";
String password="12345678";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
4、定义SQL语句
//3.定义sql语句
String sql="UPDATE account set money=2000 WHERE id=1";5、获取执行SQL对象 Statement
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
6、执行SQL
//5.执行sql
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//受影响的行数7、处理返回结果
System.out.println(count);8、释放资源
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();-
JDBC-API:DriverManager
DriverManager(驱动管理类)功能:
1、注册驱动
2、获取数据库连接
查看Driver类源码:
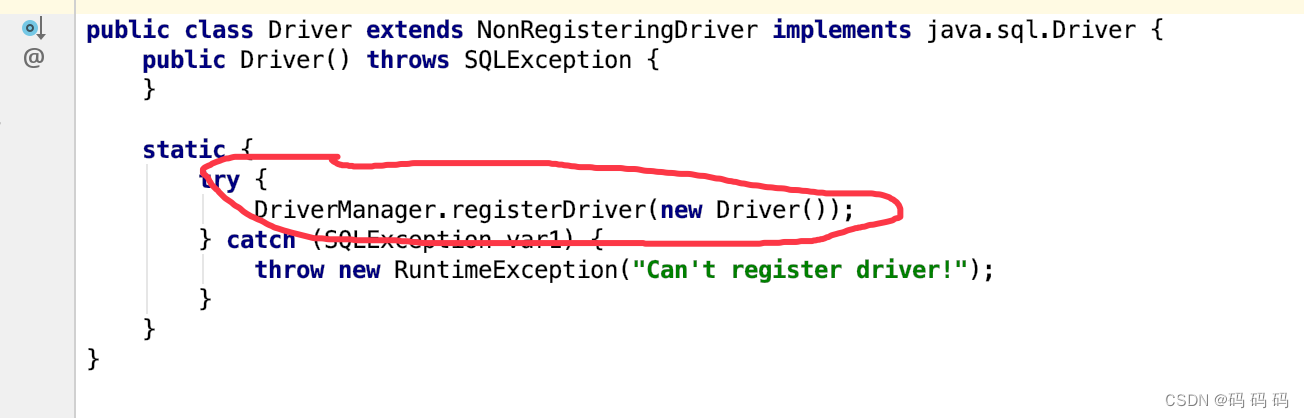
获取连接:
通过 getConnection(String url,String username,String password)
参数:
1、url :连接路径
语法:jdbc:mysql://ip地址(域名):端口号/数据库名称?参数键值对1&参数键值对2.......
实例:String url="jdbc:mysql://db1";(简化写法)
2、username:用户名
3、password:密码
-
JDBC-API:Connection
Connection的作用
1.获取执行SQL的对象
2.管理事务
1.创建执行SQL的对象

执行SQL语句对象:
- Statement :执行SQL
- CallableStatement :执行数据库中存储过程
- PreparedStatement :执行SQL.对SQL进行预处理。解决SQL注入漏洞。
2.管理事务

package com.itheima.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* jdbc API 详解:DriverManager
*/
public class JDBCDemo3_Connection {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、注册驱动
//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//通过反射将Driver类加载进内存
//2、获取连接 :如果连接的是本机mysql并且端口号是默认的3306可以简化书写
//String url="jdbc:mysql://db1?useSSL=false";
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8" +
"&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true" ;
String username="root";
String password="12345678";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql1="UPDATE account set money=3000 WHERE id=1";
String sql2="UPDATE account set money=3000 WHERE id=2";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//开启事务
//快捷键 control+Alt+T 使用try/catch抛出
try {
//开启事务
//conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//5.执行sql
int count1=stmt.executeUpdate(sql1);//受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(count1);
//造一个异常
int i=3/0;
//5.执行sql
int count2=stmt.executeUpdate(sql2);//受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
System.out.println(count2);
//提交事务
//conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚事务
//conn.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
//提交事务
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
-
JDBC-API:Statement
作用:执行SQL语句
1、int executeUpdate(sql):执行DML(对数据增删改)、DDL(对表和库的增删改查)语句
2、ResultSet executrQuery(sql): 执行DQL语句(查询语句)(比较常用)
返回值:ResultSet 结果集对象(封装了DQL查询语句的结果)
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* jdbc API 详解:Statement
*/
public class JDBCDemo4_Statement {
/**
* 执行DML语句
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDML() throws Exception {
//1、注册驱动
//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//通过反射将Driver类加载进内存
//2、获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
String username="root";
String password="12345678";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql="UPDATE account set money=3000 WHERE id=5";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//执行完DML语句,受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
//System.out.println(count);
if (count>0){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else{
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
/**
* 执行DDL语句 对数据库和表的操作
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDDL() throws Exception {
//1、注册驱动
//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//通过反射将Driver类加载进内存
//2、获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
String username="root";
String password="12345678";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql语句
String sql="drop database db2";
//4.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//执行完DML语句,受影响的行数
//6.处理结果
//System.out.println(count);
// if (count>0){
// System.out.println("修改成功");
// }else{
// System.out.println("修改失败");
// }
System.out.println(count);
//7.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}
-
JDBC-API:ResultSet
在查询数据库后会返回一个ResultSet,它就像是查询结果集的一张数据表。ResultSet对象维护了一个游标,指向当前的数据 行。开始的时候这个游标指向的是第一行。如果调用了ResultSet的next()方法游标会下移一行,如果没有更多的数据了, next()方法会返回false。可以在for循环中用它来遍历数据集。
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import com.itheima.pojo.Account;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* jdbc API 详解:ResultSet
*/
public class JDBCDemo5_ResultSet {
/**
* 执行DQL查询语句
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testDML() throws Exception {
//1、注册驱动
//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//通过反射将Driver类加载进内存
//2、获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
String username="root";
String password="12345678";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql
String sql="select * from account";
//4.获取sql对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
ResultSet res = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果,遍历res中所有数据
//6.1 光标向下移动一行,并且判断当前行是否存在数据
/*while (res.next()){
//6.2 获取数据
int id = res.getInt(1);
String name = res.getString(2);
double money = res.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(money);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
}*/
while (res.next()){
//6.2 获取数据
int id = res.getInt("id");
String name = res.getString("name");
double money = res.getDouble("money");
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(money);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
}
//7.释放资源
res.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
/**
* 查询account用户表数据,封装为account对象,并且存储为ArrayList集合中
* 1.定义实体类Account
* 2.查询数据,并且封装到account对象中
* 3.将Account对象存入ArrayList集合中
*
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testResultSet2() throws Exception {
//1、注册驱动
//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//通过反射将Driver类加载进内存
//2、获取连接
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
String username="root";
String password="12345678";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
//3.定义sql
String sql="select * from account";
//4.获取sql对象 Statement
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
ResultSet res = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//创建集合
List<Account> list=new ArrayList<>();
//6.处理结果,遍历res中所有数据
//6.1 光标向下移动一行,并且判断当前行是否存在数据
while (res.next()){
Account account=new Account();
//6.2 获取数据
int id = res.getInt("id");
String name = res.getString("name");
double money = res.getDouble("money");
//赋值
account.setId(id);
account.setName(username);
account.setMoney(money);
//存入集合
list.add(account);
}
System.out.println(list);
//7.释放资源
res.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
}





















 384
384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








