目录
1、需求:
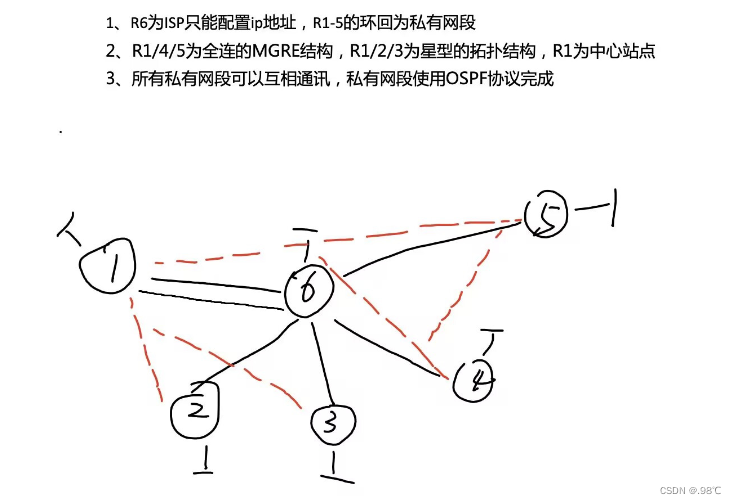
2、分析:
1、网络在基础的配置上添加了星型(点到多点)MGRE和网状的MGER。
2、因为ospf的邻接建立的原因,需要将默认的接口点到点网络类型改为以太网的类型broadcast。
3、因为R1、2、3为点到多点,需要统一DR,且r1为最佳,需要干涉选举,2、3弃选。
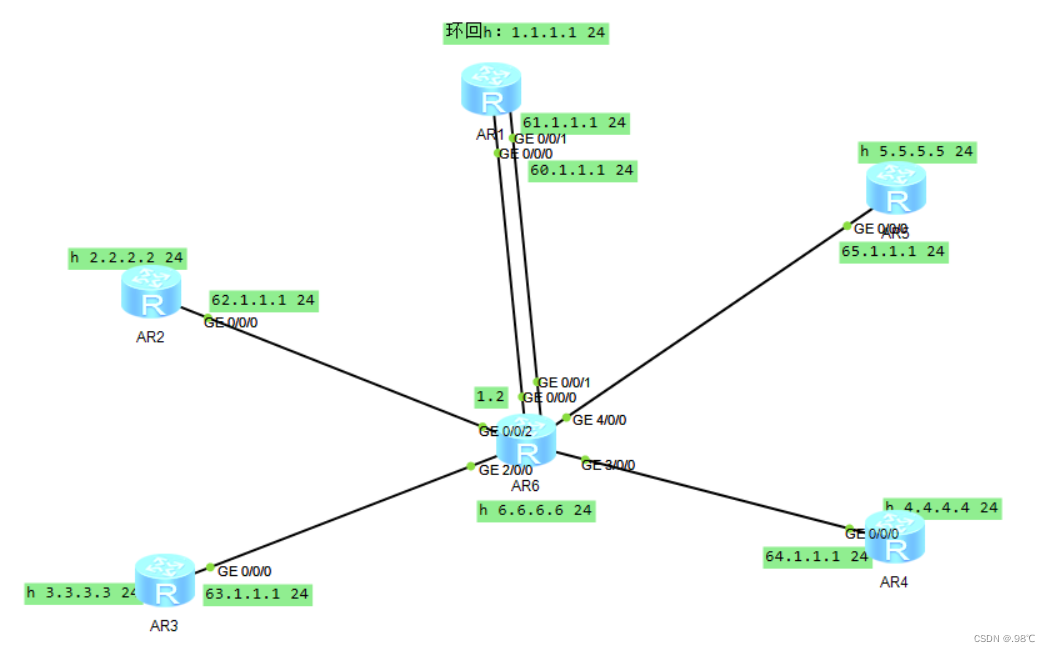
3、IP地址配置:
[r1]int l0
[r1-LoopBack0]ip add 1.1.1.1 24
[r1]int g0/0/0
[r1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 60.1.1.1 24
[r1]int g0/0/1
[r1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 61.1.1.1 24
[r2]int l0
[r2-LoopBack0]ip add 2.2.2.2 24
[r2]int g0/0/0
[r2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 62.1.1.1 24
[r3]int l0
[r3-LoopBack0]ip add 3.3.3.3 24
[r3]int g0/0/0
[r3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 63.1.1.1 24
[r4]int l0
[r4-LoopBack0]ip add 4.4.4.4 24
[r4]int g0/0/0
[r4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 64.1.1.1 24
[r5]int l0
[r5-LoopBack0]ip add 5.5.5.5 24
[r5]int g0/0/0
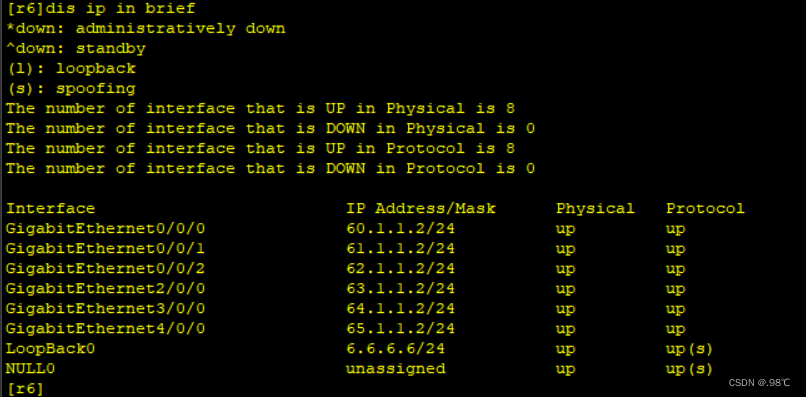
[r5-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 65.1.1.1 24部分 ip地址查看:
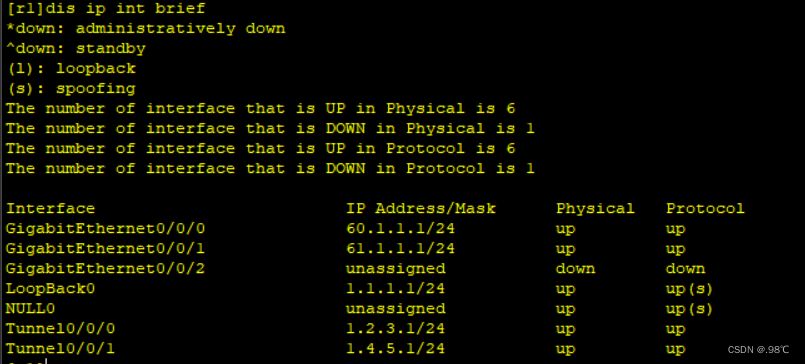
4、 缺省路由:
[r1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 60.1.1.2
[r1]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 61.1.1.2
[r2]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 62.1.1.2
[r3]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 63.1.1.2
[r4]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 64.1.1.2
[r5]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 65.1.1.25、星型MGRE的搭建:
中心站点r1:
[r1]interface Tunnel 0/0/0
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 1.2.3.1 24
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]source 62.1.1.1
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 520
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry multicast dynamic 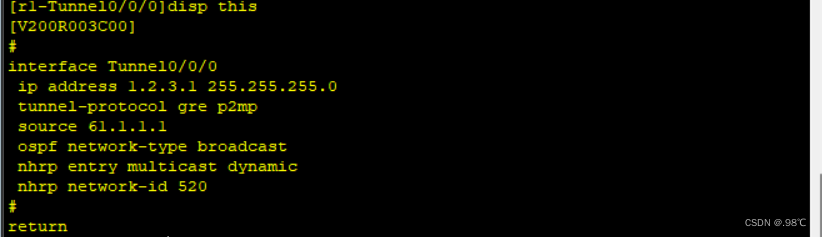
分枝站点r2、r3:
[r2]interface Tunnel 0/0/0
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]ip address 1.2.3.2 24
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]source 62.1.1.1
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 520
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 1.2.3.1 61.1.1.1 register
[r3]interface Tunnel 0/0/0
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]ip address 1.2.3.3 24
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]source 63.1.1.1
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 520
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 1.2.3.1 61.1.1.1 register 分支站点注册结果:
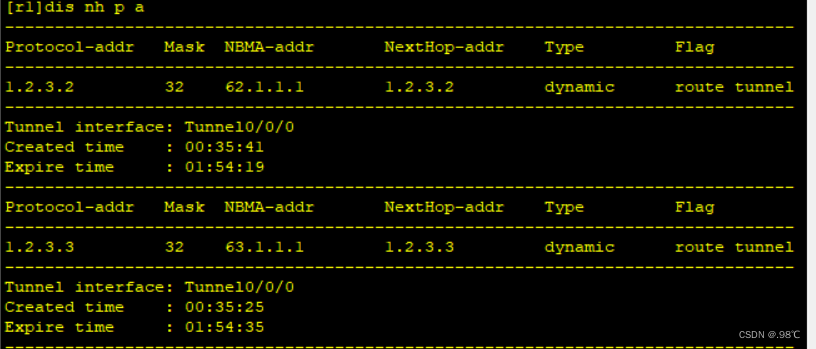
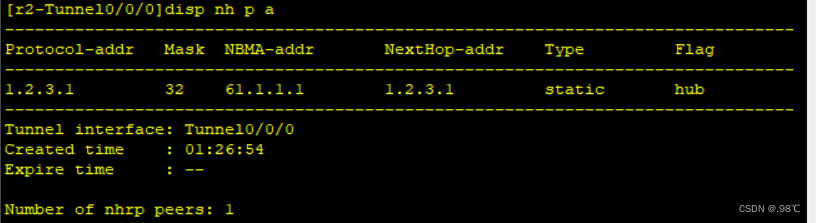
6、全连MGRE搭建:
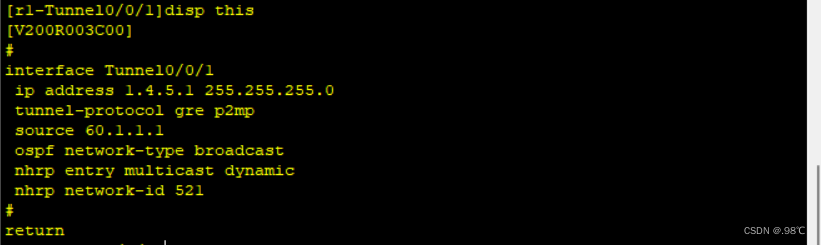
[r1]interface Tunnel 0/0/1
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]ip add 1.4.5.1 24
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]source 62.1.1.1
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]nhrp network-id 521
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]nhrp entry multicast dynamic
[r4]interface Tunnel 0/0/0
[r4-Tunnel0/0/0]ip address 1.4.5.4 24
[r4-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[r4-Tunnel0/0/0]source 64.1.1.1
[r4-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 521
[r4-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 1.4.5.1 61.1.1.1 register
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]nhrp entry multicast dynamic
[r5]interface Tunnel 0/0/0
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]ip address 1.4.5.5 24
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]source 65.1.1.1
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 521
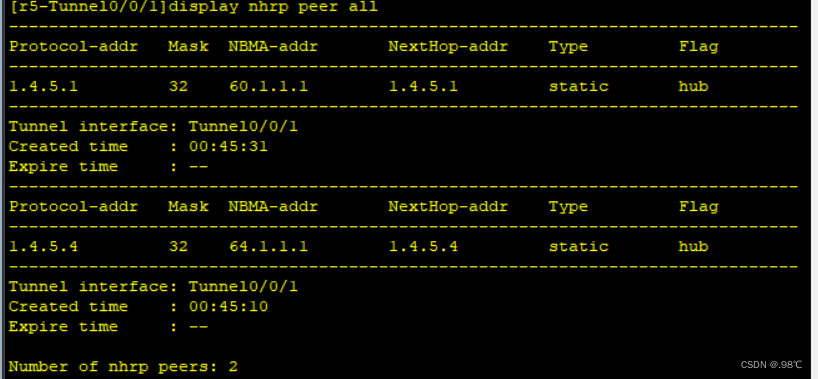
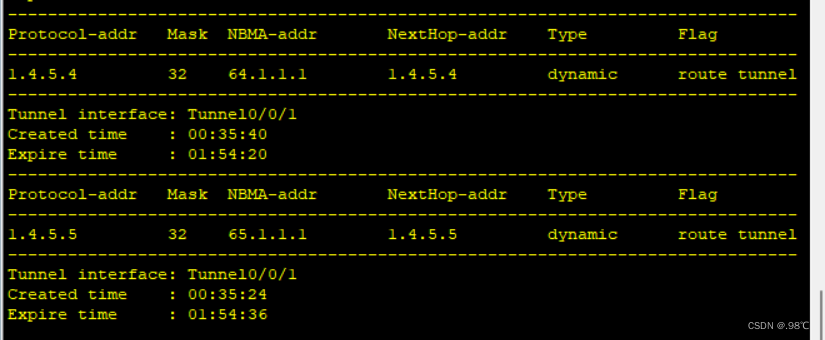
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 1.4.5.1 61.1.1.1 register
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 1.4.5.4 64.1.1.1 register 配置查看、以及分支站点注册结果:
7、修改接口的网络类型,干涉选举:
[r1]int t0/0/0
[r1-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[r1]int t0/0/1
[r1-Tunnel0/0/1]ospf network-type broadcast
[r2]int t0/0/0
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[r2-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf dr-priority 0
[r3]int t0/0/0
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[r3-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf dr-priority 0
[r4]int t0/0/1
[r4-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[r5]int t0/0/1
[r5-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast 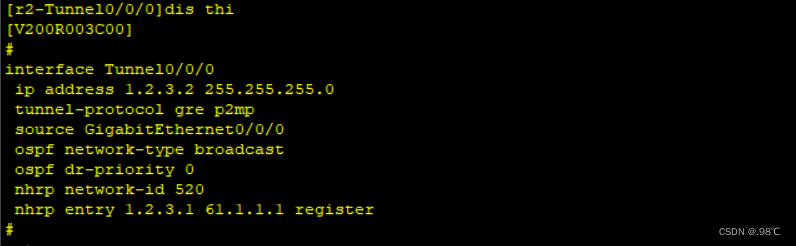
8、ospf宣告:
[r1]OSPF 1 router-id 1.1.1.1
[r1-ospf-1]area 0
[r1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[r1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.2.3.1 0.0.0.0
[r1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.4.5.1 0.0.0.0
[r2]OSPF 1 router-id 2.2.2.2
[r2-ospf-1]area 0
[r2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
[r2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.2.3.2 0.0.0.0
[r3]OSPF 1 router-id 3.3.3.3
[r3-ospf-1]area 0
[r3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0
[r3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.2.3.3 0.0.0.0
[r4]OSPF 1 router-id 4.4.4.4
[r4-ospf-1]area 0
[r4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0
[r4-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.4.5.4 0.0.0.0
[r5]OSPF 1 router-id 5.5.5.5
[r5-ospf-1]area 0
[r5-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
[r5-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]network 1.4.5.5 0.0.0.0
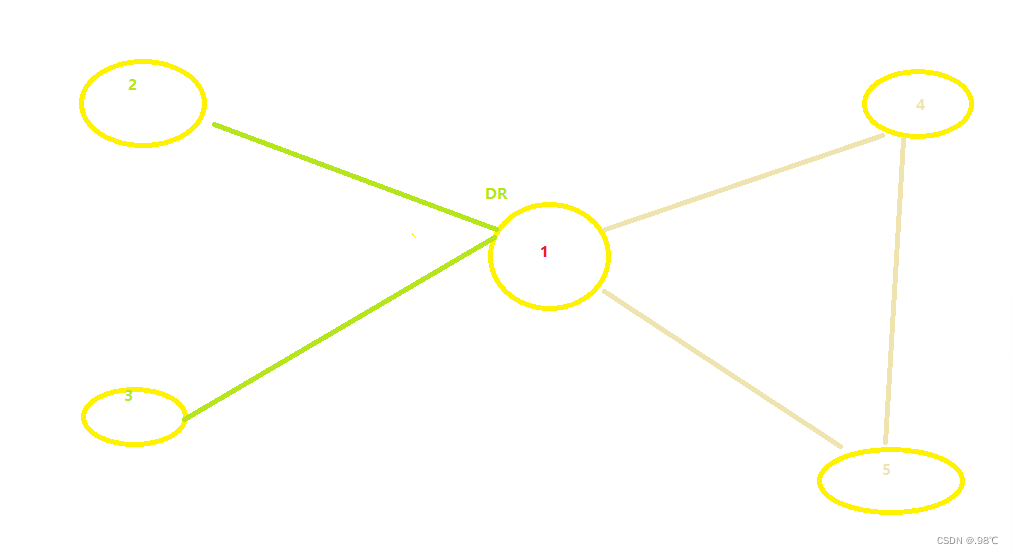
9、查看关系:
在星型1、2、3中只有dr:r1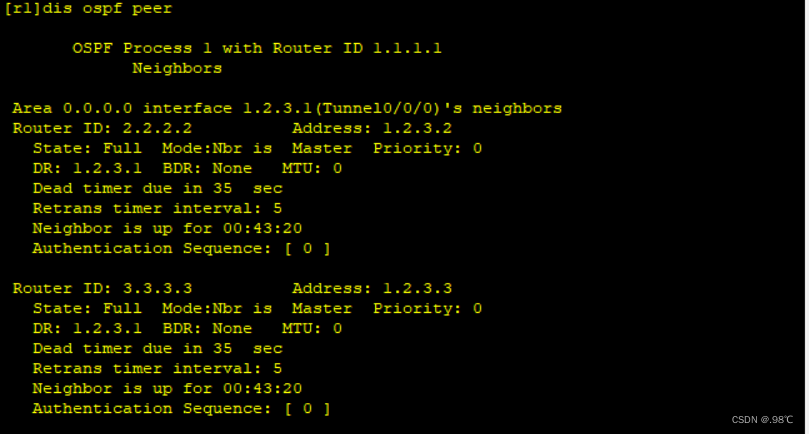
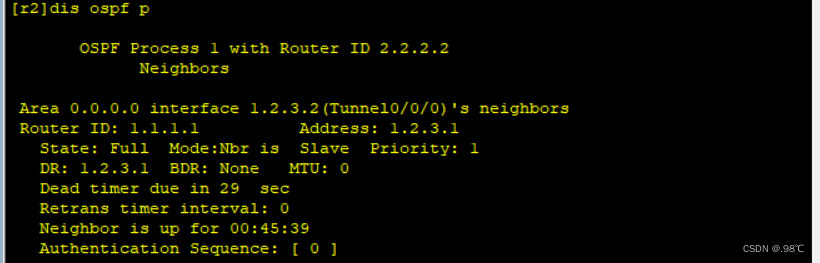
网络测试:
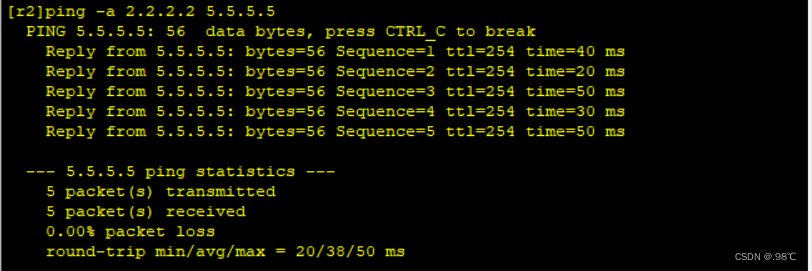
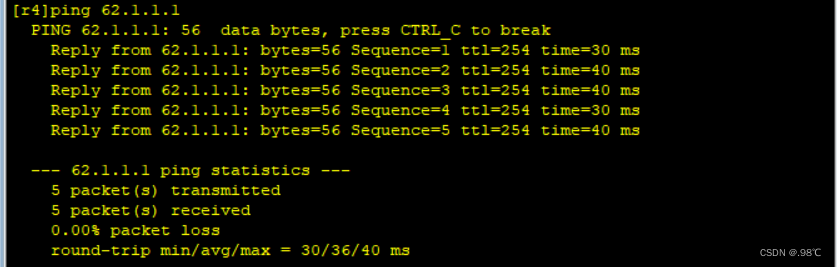
2 - - - > 5
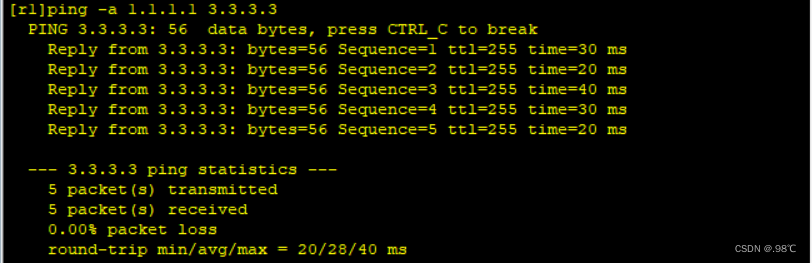
1 - - - > 3





 该文详细描述了一个MGRE(MulticastGRE)网络的搭建过程,包括星型和全连接拓扑结构的实现。在配置中,中心站点R1与分支站点R2、R3进行了点到多点的MGRE连接,并通过NHRP进行动态注册。同时,为了优化OSPF邻接关系,修改了接口网络类型并干涉了DR选举,确保R1成为DR。此外,配置了IP地址和缺省路由,以及OSPF宣告,以实现网络间的通信。
该文详细描述了一个MGRE(MulticastGRE)网络的搭建过程,包括星型和全连接拓扑结构的实现。在配置中,中心站点R1与分支站点R2、R3进行了点到多点的MGRE连接,并通过NHRP进行动态注册。同时,为了优化OSPF邻接关系,修改了接口网络类型并干涉了DR选举,确保R1成为DR。此外,配置了IP地址和缺省路由,以及OSPF宣告,以实现网络间的通信。

















 495
495

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










